Get our free extension to see links to code for papers anywhere online!Free add-on: code for papers everywhere!Free add-on: See code for papers anywhere!
Eun-Kyoung Rosa Lee
A Psycholinguistic Evaluation of Language Models' Sensitivity to Argument Roles
Oct 21, 2024Figures and Tables:
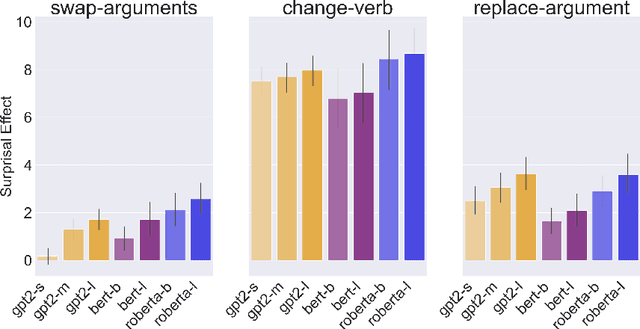
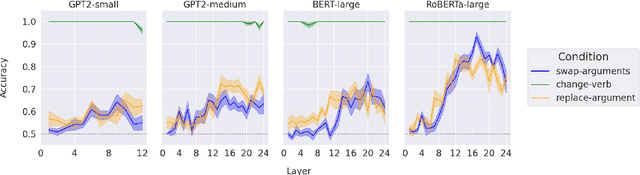
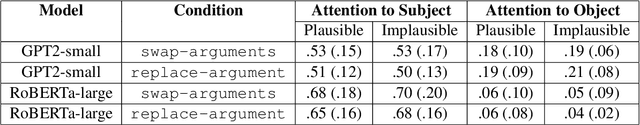




Abstract:We present a systematic evaluation of large language models' sensitivity to argument roles, i.e., who did what to whom, by replicating psycholinguistic studies on human argument role processing. In three experiments, we find that language models are able to distinguish verbs that appear in plausible and implausible contexts, where plausibility is determined through the relation between the verb and its preceding arguments. However, none of the models capture the same selective patterns that human comprehenders exhibit during real-time verb prediction. This indicates that language models' capacity to detect verb plausibility does not arise from the same mechanism that underlies human real-time sentence processing.
Via
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge