Ervin Sejdic
ECG-SMART-NET: A Deep Learning Architecture for Precise ECG Diagnosis of Occlusion Myocardial Infarction
May 08, 2024



Abstract:In this paper we describe ECG-SMART-NET for identification of occlusion myocardial infarction (OMI). OMI is a severe form of heart attack characterized by complete blockage of one or more coronary arteries requiring immediate referral for cardiac catheterization to restore blood flow to the heart. Two thirds of OMI cases are difficult to visually identify from a 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) and can be potentially fatal if not identified in a timely fashion. Previous works on this topic are scarce, and current state-of-the-art evidence suggests that both random forests with engineered features and convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are promising approaches to improve the ECG detection of OMI. While the ResNet architecture has been successfully adapted for use with ECG recordings, it is not ideally suited to capture informative temporal features within each lead and the spatial concordance or discordance across leads. We propose a clinically informed modification of the ResNet-18 architecture. The model first learns temporal features through temporal convolutional layers with 1xk kernels followed by a spatial convolutional layer, after the residual blocks, with 12x1 kernels to learn spatial features. The new ECG-SMART-NET was benchmarked against the original ResNet-18 and other state-of-the-art models on a multisite real-word clinical dataset that consists of 10,893 ECGs from 7,297 unique patients (rate of OMI = 6.5%). ECG-SMART-NET outperformed other models in the classification of OMI with a test AUC score of 0.889 +/- 0.027 and a test average precision score of 0.587 +/- 0.087.
Single neuron-based neural networks are as efficient as dense deep neural networks in binary and multi-class recognition problems
May 28, 2019



Abstract:Recent advances in neuroscience have revealed many principles about neural processing. In particular, many biological systems were found to reconfigure/recruit single neurons to generate multiple kinds of decisions. Such findings have the potential to advance our understanding of the design and optimization process of artificial neural networks. Previous work demonstrated that dense neural networks are needed to shape complex decision surfaces required for AI-level recognition tasks. We investigate the ability to model high dimensional recognition problems using single or several neurons networks that are relatively easier to train. By employing three datasets, we test the use of a population of single neuron networks in performing multi-class recognition tasks. Surprisingly, we find that sparse networks can be as efficient as dense networks in both binary and multi-class tasks. Moreover, single neuron networks demonstrate superior performance in binary classification scheme and competing results when combined for multi-class recognition.
Radiological images and machine learning: trends, perspectives, and prospects
Mar 27, 2019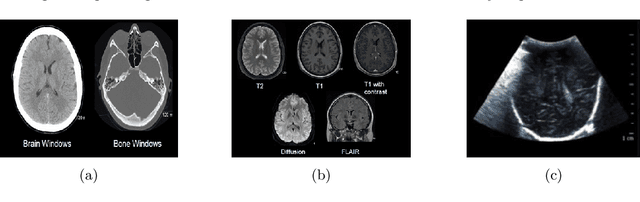
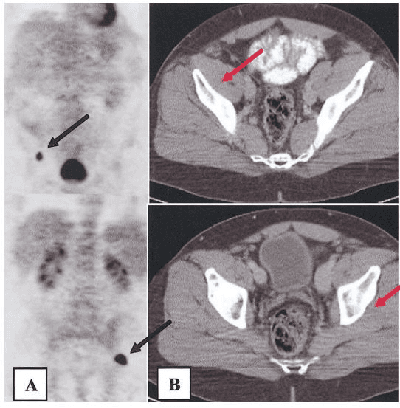
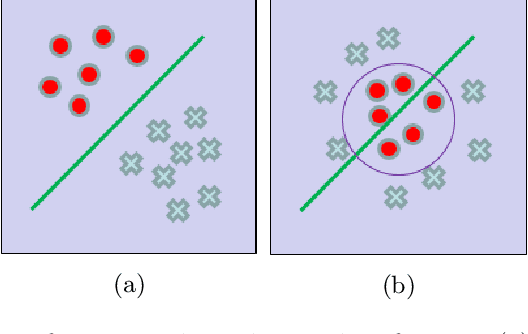
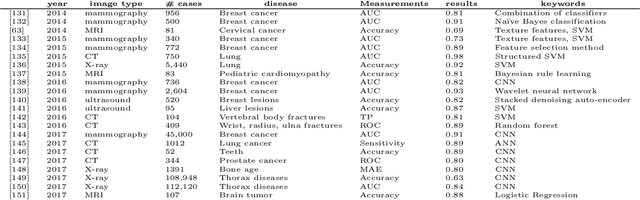
Abstract:The application of machine learning to radiological images is an increasingly active research area that is expected to grow in the next five to ten years. Recent advances in machine learning have the potential to recognize and classify complex patterns from different radiological imaging modalities such as x-rays, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging and positron emission tomography imaging. In many applications, machine learning based systems have shown comparable performance to human decision-making. The applications of machine learning are the key ingredients of future clinical decision making and monitoring systems. This review covers the fundamental concepts behind various machine learning techniques and their applications in several radiological imaging areas, such as medical image segmentation, brain function studies and neurological disease diagnosis, as well as computer-aided systems, image registration, and content-based image retrieval systems. Synchronistically, we will briefly discuss current challenges and future directions regarding the application of machine learning in radiological imaging. By giving insight on how take advantage of machine learning powered applications, we expect that clinicians can prevent and diagnose diseases more accurately and efficiently.
* 13 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge