Elizaveta Petrova
Training Strategies for Isolated Sign Language Recognition
Dec 16, 2024
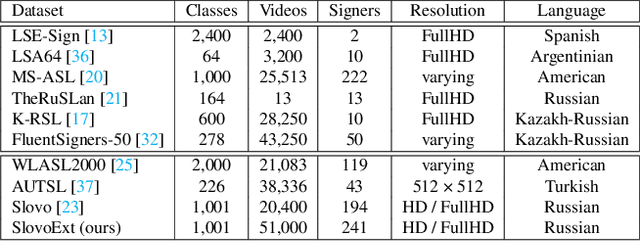
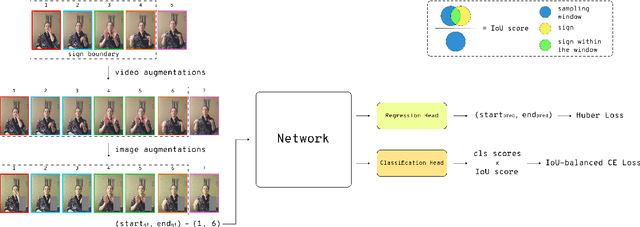
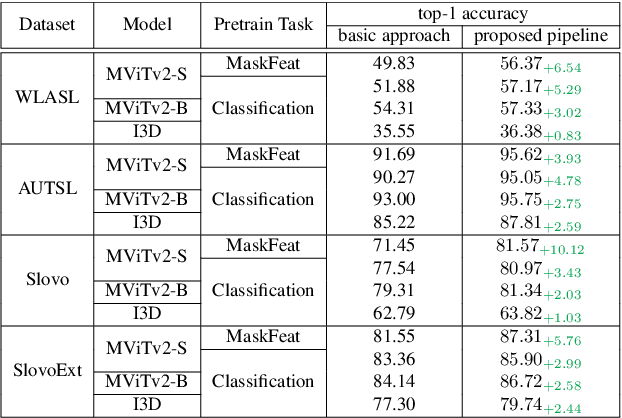
Abstract:This paper introduces a comprehensive model training pipeline for Isolated Sign Language Recognition (ISLR) designed to accommodate the distinctive characteristics and constraints of the Sign Language (SL) domain. The constructed pipeline incorporates carefully selected image and video augmentations to tackle the challenges of low data quality and varying sign speeds. Including an additional regression head combined with IoU-balanced classification loss enhances the model's awareness of the gesture and simplifies capturing temporal information. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the developed training pipeline easily adapts to different datasets and architectures. Additionally, the ablation study shows that each proposed component expands the potential to consider ISLR task specifics. The presented strategies improve recognition performance on a broad set of ISLR benchmarks. Moreover, we achieved a state-of-the-art result on the WLASL and Slovo benchmarks with 1.63% and 14.12% improvements compared to the previous best solution, respectively.
Bukva: Russian Sign Language Alphabet
Oct 11, 2024



Abstract:This paper investigates the recognition of the Russian fingerspelling alphabet, also known as the Russian Sign Language (RSL) dactyl. Dactyl is a component of sign languages where distinct hand movements represent individual letters of a written language. This method is used to spell words without specific signs, such as proper nouns or technical terms. The alphabet learning simulator is an essential isolated dactyl recognition application. There is a notable issue of data shortage in isolated dactyl recognition: existing Russian dactyl datasets lack subject heterogeneity, contain insufficient samples, or cover only static signs. We provide Bukva, the first full-fledged open-source video dataset for RSL dactyl recognition. It contains 3,757 videos with more than 101 samples for each RSL alphabet sign, including dynamic ones. We utilized crowdsourcing platforms to increase the subject's heterogeneity, resulting in the participation of 155 deaf and hard-of-hearing experts in the dataset creation. We use a TSM (Temporal Shift Module) block to handle static and dynamic signs effectively, achieving 83.6% top-1 accuracy with a real-time inference with CPU only. The dataset, demo code, and pre-trained models are publicly available.
PHNet: Patch-based Normalization for Portrait Harmonization
Mar 08, 2024



Abstract:A common problem for composite images is the incompatibility of their foreground and background components. Image harmonization aims to solve this problem, making the whole image look more authentic and coherent. Most existing solutions predict lookup tables (LUTs) or reconstruct images, utilizing various attributes of composite images. Recent approaches have primarily focused on employing global transformations like normalization and color curve rendering to achieve visual consistency, and they often overlook the importance of local visual coherence. We present a patch-based harmonization network consisting of novel Patch-based normalization (PN) blocks and a feature extractor based on statistical color transfer. Extensive experiments demonstrate the network's high generalization capability for different domains. Our network achieves state-of-the-art results on the iHarmony4 dataset. Also, we created a new human portrait harmonization dataset based on FFHQ and checked the proposed method to show the generalization ability by achieving the best metrics on it. The benchmark experiments confirm that the suggested patch-based normalization block and feature extractor effectively improve the network's capability to harmonize portraits. Our code and model baselines are publicly available.
Slovo: Russian Sign Language Dataset
May 23, 2023Abstract:One of the main challenges of the sign language recognition task is the difficulty of collecting a suitable dataset due to the gap between deaf and hearing society. In addition, the sign language in each country differs significantly, which obliges the creation of new data for each of them. This paper presents the Russian Sign Language (RSL) video dataset Slovo, produced using crowdsourcing platforms. The dataset contains 20,000 FullHD recordings, divided into 1,000 classes of RSL gestures received by 194 signers. We also provide the entire dataset creation pipeline, from data collection to video annotation, with the following demo application. Several neural networks are trained and evaluated on the Slovo to demonstrate its teaching ability. Proposed data and pre-trained models are publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge