Elise Beck
PACTE
Agent-based simulation of pedestrians' earthquake evacuation; application to Beirut, Lebanon
Sep 06, 2023Abstract:Most seismic risk assessment methods focus on estimating the damages to the built environment and the consequent socioeconomic losses without fully taking into account the social aspect of risk. Yet, human behaviour is a key element in predicting the human impact of an earthquake, therefore, it is important to include it in quantitative risk assessment studies. In this study, an interdisciplinary approach simulating pedestrians' evacuation during earthquakes at the city scale is developed using an agent-based model. The model integrates the seismic hazard, the physical vulnerability as well as individuals' behaviours and mobility. The simulator is applied to the case of Beirut, Lebanon. Lebanon is at the heart of the Levant fault system that has generated several Mw>7 earthquakes, the latest being in 1759. It is one of the countries with the highest seismic risk in the Mediterranean region. This is due to the high seismic vulnerability of the buildings due to the absence of mandatory seismic regulation until 2012, the high level of urbanization, and the lack of adequate spatial planning and risk prevention policies. Beirut as the main residential, economic and institutional hub of Lebanon is densely populated. To accommodate the growing need for urban development, constructions have almost taken over all of the green areas of the city; squares and gardens are disappearing to give place to skyscrapers. However, open spaces are safe places to shelter, away from debris, and therefore play an essential role in earthquake evacuation. Despite the massive urbanization, there are a few open spaces but locked gates and other types of anthropogenic barriers often limit their access. To simulate this complex context, pedestrians' evacuation simulations are run in a highly realistic spatial environment implemented in GAMA [1]. Previous data concerning soil and buildings in Beirut [2, 3] are complemented by new geographic data extracted from high-resolution Pleiades satellite images. The seismic loading is defined as a peak ground acceleration of 0.3g, as stated in Lebanese seismic regulations. Building damages are estimated using an artificial neural network trained to predict the mean damage [4] based on the seismic loading as well as the soil and building vibrational properties [5]. Moreover, the quantity and the footprint of the generated debris around each building are also estimated and included in the model. We simulate how topography, buildings, debris, and access to open spaces, affect individuals' mobility. Two city configurations are implemented: 1. Open spaces are accessible without any barriers; 2. Access to some open spaces is blocked. The first simulation results show that while 52% of the population is able to arrive to an open space within 5 minutes after an earthquake, this number is reduced to 39% when one of the open spaces is locked. These results show that the presence of accessible open spaces in a city and their proximity to the residential buildings is a crucial factor for ensuring people's safety when an earthquake occurs.
Mapping and Describing Geospatial Data to Generalize Complex Mapping and Describing Geospatial Data to Generalize Complex Models: The Case of LittoSIM-GEN Models
Jan 19, 2021



Abstract:For some scientific questions, empirical data are essential to develop reliable simulation models. These data usually come from different sources with diverse and heterogeneous formats. The design of complex data-driven models is often shaped by the structure of the data available in research projects. Hence, applying such models to other case studies requires either to get similar data or to transform new data to fit the model inputs. It is the case of agent-based models (ABMs) that use advanced data structures such as Geographic Information Systems data. We faced this problem in the LittoSIM-GEN project when generalizing our participatory flooding model (LittoSIM) to new territories. From this experience, we provide a mapping approach to structure, describe, and automatize the integration of geospatial data into ABMs.
A methodology for co-constructing an interdisciplinary model: from model to survey, from survey to model
Nov 27, 2020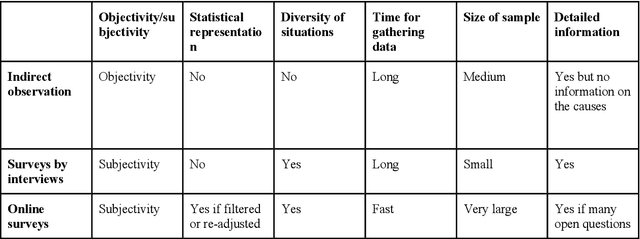
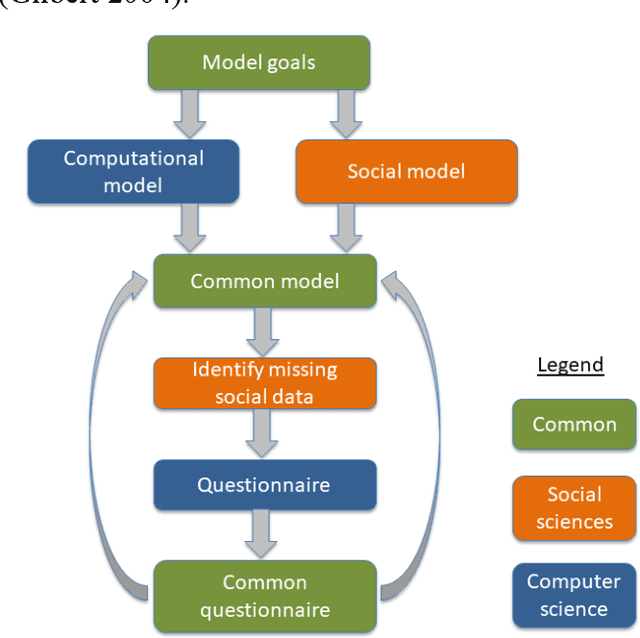

Abstract:How should computer science and social science collaborate to build a common model? How should they proceed to gather data that is really useful to the modelling? How can they design a survey that is tailored to the target model? This paper aims to answer those crucial questions in the framework of a multidisciplinary research project. This research addresses the issue of co-constructing a model when several disciplines are involved, and is applied to modelling human behaviour immediately after an earthquake. The main contribution of the work is to propose a tool dedicated to multidisciplinary dialogue. It also proposes a reflexive analysis of the enriching intellectual process carried out by the different disciplines involved. Finally, from working with an anthropologist, a complementary view of the multidisciplinary process is given.
A multi-agent system approach in evaluating human spatio-temporal vulnerability to seismic risk using social attachment
May 02, 2019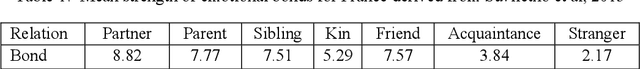
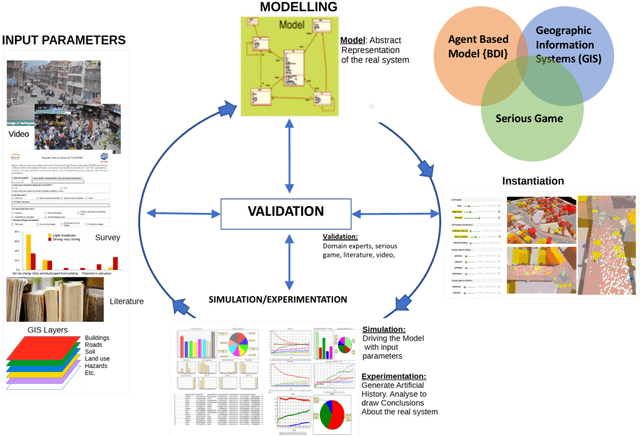
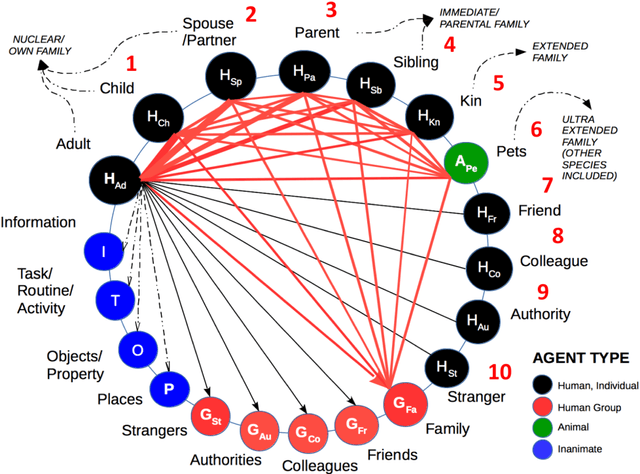
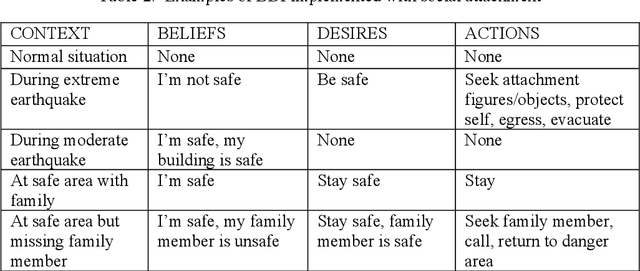
Abstract:Social attachment theory states that individuals seek the proximity of attachment figures (e.g. family members, friends, colleagues, familiar places or objects) when faced with threat. During disasters, this means that family members may seek each other before evacuating, gather personal property before heading to familiar exits and places, or follow groups/crowds, etc. This hard-wired human tendency should be considered in the assessment of risk and the creation of disaster management plans. Doing so may result in more realistic evacuation procedures and may minimise the number of casualties and injuries. In this context, a dynamic spatio-temporal analysis of seismic risk is presented using SOLACE, a multi-agent model of pedestrian behaviour based on social attachment theory implemented using the Belief-Desire-Intention approach. The model focuses on the influence of human, social, physical and temporal factors on successful evacuation. Human factors considered include perception and mobility defined by age. Social factors are defined by attachment bonds, social groups, population distribution, and cultural norms. Physical factors refer to the location of the epicentre of the earthquake, spatial distribution/layout and attributes of environmental objects such as buildings, roads, barriers (cars), placement of safe areas, evacuation routes, and the resulting debris/damage from the earthquake. Experiments tested the influence of time of the day, presence of disabled persons and earthquake intensity. Initial results show that factors that influence arrivals in safe areas include (a) human factors (age, disability, speed), (b) pre-evacuation behaviours, (c) perception distance (social attachment, time of day), (d) social interaction during evacuation, and (e) physical and spatial aspects, such as limitations imposed by debris (damage), and the distance to safe areas. To validate the results, scenarios will be designed with stakeholders, who will also take part in the definition of a serious game. The recommendation of this research is that both social and physical aspects should be considered when defining vulnerability in the analysis of risk.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge