Ekant Sharma
Load Balanced ISAC Systems for URLLC Users
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:This paper presents an energy-efficient downlink cell-free massive multiple-input multiple-output (CF-mMIMO) integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) network that serves ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC) users while simultaneously detecting a target. We propose a load-balancing algorithm that minimizes the total network power consumption; including transmit power, fixed static power, and traffic-dependent fronthaul power at the access points (APs) without degrading system performance. To this end, we formulate a mixed-integer non-convex optimization problem and introduce an iterative joint power allocation and AP load balancing (JPALB) algorithm. The algorithm aims to reduce total power usage while meeting both the communication quality-of-service (QoS) requirements of URLLC users and the sensing QoS needed for target detection. Proposed JPALB algorithm for ISAC systems was simulated with maximum-ratio transmission (MRT) and regularized zero-forcing (RZF) precoders. Simulation results show approximately 33% reduction in power consumption, using JPALB algorithm compared to a baseline with no load balancing, without compromising communication and sensing QoS requirements.
Target Detection for OTFS-Aided Cell-Free MIMO ISAC System
Aug 23, 2024Abstract:This letter focuses on enhancing target detection performance for a multi-user integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) system using orthogonal time frequency space (OTFS)-aided cell-free multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) technology in high-speed vehicular environments. We propose a sensing-centric (SC) approach for target detection using communication signals with or without sensing signals. Power allocation is optimized to maximize the sensing signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the proposed SC scheme while ensuring a required quality-of-service (QoS) for the communication user equipment (UEs), and adhering to each access points (APs) power budget. Numerical results show that the proposed SC scheme vastly outperforms a communication-centric method that minimizes the total power consumed at the APs subject to the same constraints.
Analysis and Optimization of RIS-Assisted Cell-Free Massive MIMO NOMA Systems
Jul 04, 2024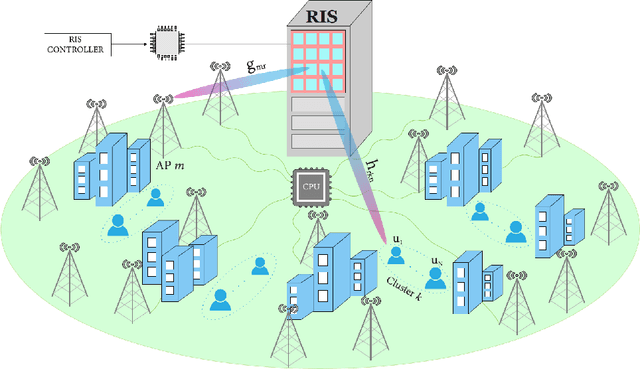
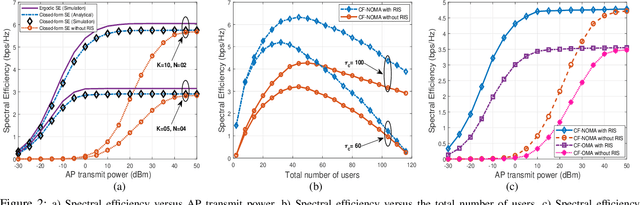
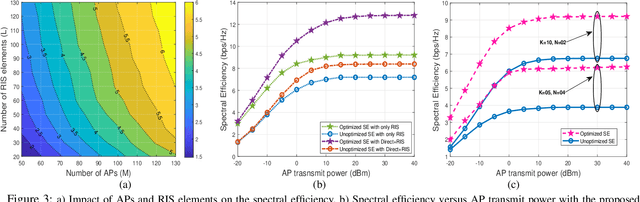
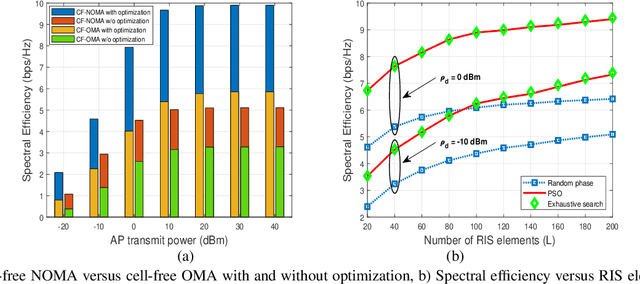
Abstract:We consider a reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) assisted cell-free massive multiple-input multiple-output non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) system, where each access point (AP) serves all the users with the aid of the RIS. We practically model the system by considering imperfect instantaneous channel state information (CSI) and employing imperfect successive interference cancellation at the users end. We first obtain the channel estimates using linear minimum mean square error approach considering the spatial correlation at the RIS and then derive a closed-form downlink spectral efficiency (SE) expression using the statistical CSI. We next formulate a joint optimization problem to maximize the sum SE of the system. We first introduce a novel successive Quadratic Transform (successive-QT) algorithm to optimize the transmit power coefficients using the concept of block optimization along with quadratic transform and then use the particle swarm optimization technique to design the RIS phase shifts. Note that most of the existing works on RIS-aided cell-free systems are specific instances of the general scenario studied in this work. We numerically show that i) the RIS-assisted link is more advantageous at lower transmit power regions where the direct link between AP and user is weak, ii) NOMA outperforms orthogonal multiple access schemes in terms of SE, and iii) the proposed joint optimization framework significantly improves the sum SE of the system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge