Eisaku Maeda
Meta-control of Dialogue Systems Using Large Language Models
Dec 21, 2023Abstract:Utilizing Large Language Models (LLMs) facilitates the creation of flexible and natural dialogues, a task that has been challenging with traditional rule-based dialogue systems. However, LLMs also have the potential to produce unexpected responses, which may not align with the intentions of dialogue system designers. To address this issue, this paper introduces a meta-control method that employs LLMs to develop more stable and adaptable dialogue systems. The method includes dialogue flow control to ensure that utterances conform to predefined scenarios and turn-taking control to foster natural dialogues. Furthermore, we have implemented a dialogue system that utilizes this meta-control strategy and verified that the dialogue system utilizing meta-control operates as intended.
Spoken Dialogue Strategy Focusing on Asymmetric Communication with Android Robots
Oct 18, 2022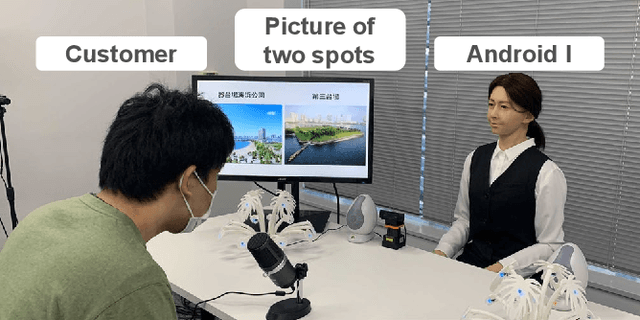

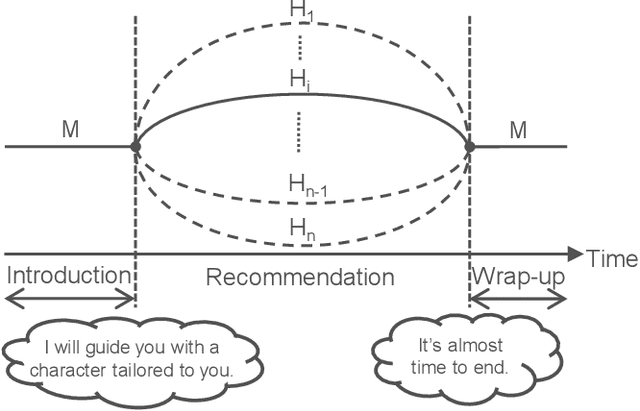
Abstract:Humans are easily conscious of small differences in an android robot's (AR's) behaviors and utterances, resulting in treating the AR as not-human, while ARs treat us as humans. Thus, there exists asymmetric communication between ARs and humans. In our system at Dialogue Robot Competition 2022, this asymmetry was a considerable research target in our dialogue strategy. For example, tricky phrases such as questions related to personal matters and forceful requests for agreement were experimentally used in AR's utterances. We assumed that these AR phrases would have a reasonable chance of success, although humans would likely hesitate to use the phrases. Additionally, during a five-minute dialogue, our AR's character, such as its voice tones and sentence expressions, changed from mechanical to human-like type in order to pretend to tailor to customers. The characteristics of the AR developed by our team, DSML-TDU, are introduced in this paper.
Improving User's Sense of Participation in Robot-Driven Dialogue
Oct 18, 2022



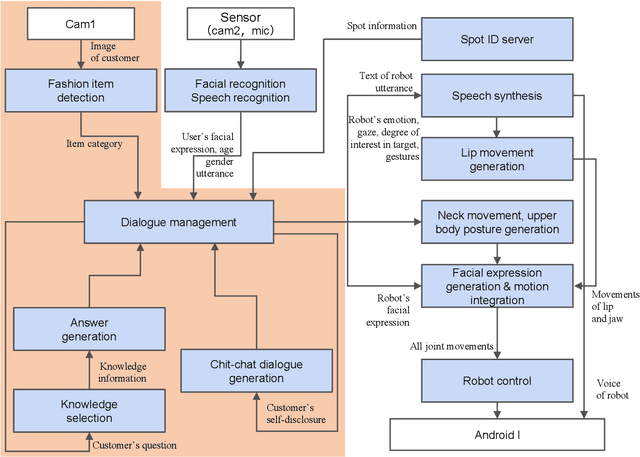
Abstract:In task-oriented dialogues with symbiotic robots, the robot usually takes the initiative in dialogue progression and topic selection. In such robot-driven dialogue, the user's sense of participation in the dialogue is reduced because the degree of freedom in timing and content of speech is limited, and as a result, the user's familiarity with and trust in the robot as a dialogue partner and the level of dialogue satisfaction decrease. In this study, we constructed a travel agent dialogue system focusing on improving the sense of dialogue participation. At the beginning of the dialogue, the robot tells the user the purpose of the upcoming dialogue and indicates that it is responsible for assisting the user in making decisions. In addition, in situations where users were asked to state their preferences, the robot encourages them to express their intentions with actions, as well as spoken language responses. In addition, we attempted to reduce the sense of discomfort felt toward the android robot by devising a timing control for the robot's detailed movements and facial expressions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge