Edwin Arkel Rios
Fine-Grained Image Recognition from Scratch with Teacher-Guided Data Augmentation
Jul 16, 2025Abstract:Fine-grained image recognition (FGIR) aims to distinguish visually similar sub-categories within a broader class, such as identifying bird species. While most existing FGIR methods rely on backbones pretrained on large-scale datasets like ImageNet, this dependence limits adaptability to resource-constrained environments and hinders the development of task-specific architectures tailored to the unique challenges of FGIR. In this work, we challenge the conventional reliance on pretrained models by demonstrating that high-performance FGIR systems can be trained entirely from scratch. We introduce a novel training framework, TGDA, that integrates data-aware augmentation with weak supervision via a fine-grained-aware teacher model, implemented through knowledge distillation. This framework unlocks the design of task-specific and hardware-aware architectures, including LRNets for low-resolution FGIR and ViTFS, a family of Vision Transformers optimized for efficient inference. Extensive experiments across three FGIR benchmarks over diverse settings involving low-resolution and high-resolution inputs show that our method consistently matches or surpasses state-of-the-art pretrained counterparts. In particular, in the low-resolution setting, LRNets trained with TGDA improve accuracy by up to 23\% over prior methods while requiring up to 20.6x less parameters, lower FLOPs, and significantly less training data. Similarly, ViTFS-T can match the performance of a ViT B-16 pretrained on ImageNet-21k while using 15.3x fewer trainable parameters and requiring orders of magnitudes less data. These results highlight TGDA's potential as an adaptable alternative to pretraining, paving the way for more efficient fine-grained vision systems.
Cross-Layer Cache Aggregation for Token Reduction in Ultra-Fine-Grained Image Recognition
Dec 31, 2024



Abstract:Ultra-fine-grained image recognition (UFGIR) is a challenging task that involves classifying images within a macro-category. While traditional FGIR deals with classifying different species, UFGIR goes beyond by classifying sub-categories within a species such as cultivars of a plant. In recent times the usage of Vision Transformer-based backbones has allowed methods to obtain outstanding recognition performances in this task but this comes at a significant cost in terms of computation specially since this task significantly benefits from incorporating higher resolution images. Therefore, techniques such as token reduction have emerged to reduce the computational cost. However, dropping tokens leads to loss of essential information for fine-grained categories, specially as the token keep rate is reduced. Therefore, to counteract the loss of information brought by the usage of token reduction we propose a novel Cross-Layer Aggregation Classification Head and a Cross-Layer Cache mechanism to recover and access information from previous layers in later locations. Extensive experiments covering more than 2000 runs across diverse settings including 5 datasets, 9 backbones, 7 token reduction methods, 5 keep rates, and 2 image sizes demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed plug-and-play modules and allow us to push the boundaries of accuracy vs cost for UFGIR by reducing the kept tokens to extremely low ratios of up to 10\% while maintaining a competitive accuracy to state-of-the-art models. Code is available at: \url{https://github.com/arkel23/CLCA}
Down-Sampling Inter-Layer Adapter for Parameter and Computation Efficient Ultra-Fine-Grained Image Recognition
Sep 17, 2024



Abstract:Ultra-fine-grained image recognition (UFGIR) categorizes objects with extremely small differences between classes, such as distinguishing between cultivars within the same species, as opposed to species-level classification in fine-grained image recognition (FGIR). The difficulty of this task is exacerbated due to the scarcity of samples per category. To tackle these challenges we introduce a novel approach employing down-sampling inter-layer adapters in a parameter-efficient setting, where the backbone parameters are frozen and we only fine-tune a small set of additional modules. By integrating dual-branch down-sampling, we significantly reduce the number of parameters and floating-point operations (FLOPs) required, making our method highly efficient. Comprehensive experiments on ten datasets demonstrate that our approach obtains outstanding accuracy-cost performance, highlighting its potential for practical applications in resource-constrained environments. In particular, our method increases the average accuracy by at least 6.8\% compared to other methods in the parameter-efficient setting while requiring at least 123x less trainable parameters compared to current state-of-the-art UFGIR methods and reducing the FLOPs by 30\% in average compared to other methods.
Global-Local Similarity for Efficient Fine-Grained Image Recognition with Vision Transformers
Jul 17, 2024



Abstract:Fine-grained recognition involves the classification of images from subordinate macro-categories, and it is challenging due to small inter-class differences. To overcome this, most methods perform discriminative feature selection enabled by a feature extraction backbone followed by a high-level feature refinement step. Recently, many studies have shown the potential behind vision transformers as a backbone for fine-grained recognition, but their usage of its attention mechanism to select discriminative tokens can be computationally expensive. In this work, we propose a novel and computationally inexpensive metric to identify discriminative regions in an image. We compare the similarity between the global representation of an image given by the CLS token, a learnable token used by transformers for classification, and the local representation of individual patches. We select the regions with the highest similarity to obtain crops, which are forwarded through the same transformer encoder. Finally, high-level features of the original and cropped representations are further refined together in order to make more robust predictions. Through extensive experimental evaluation we demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method, obtaining favorable results in terms of accuracy across a variety of datasets. Furthermore, our method achieves these results at a much lower computational cost compared to the alternatives. Code and checkpoints are available at: \url{https://github.com/arkel23/GLSim}.
DAF:re: A Challenging, Crowd-Sourced, Large-Scale, Long-Tailed Dataset For Anime Character Recognition
Jan 21, 2021
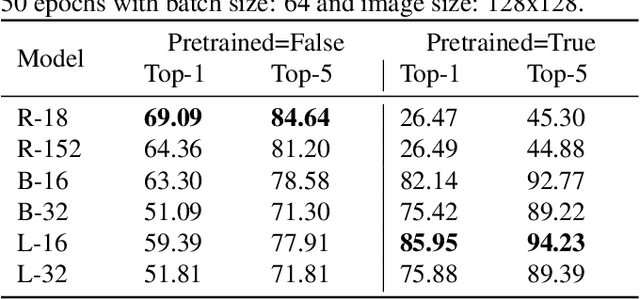
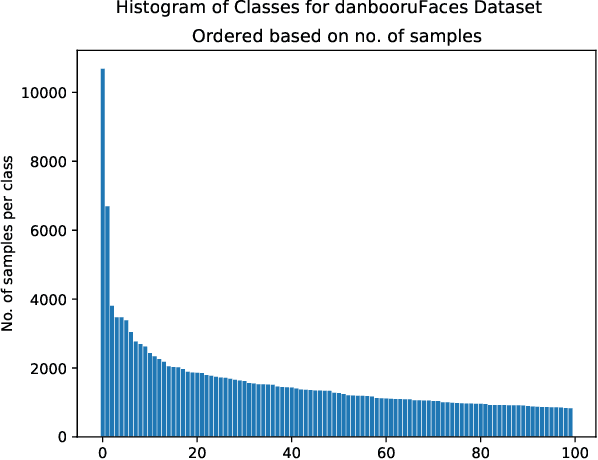
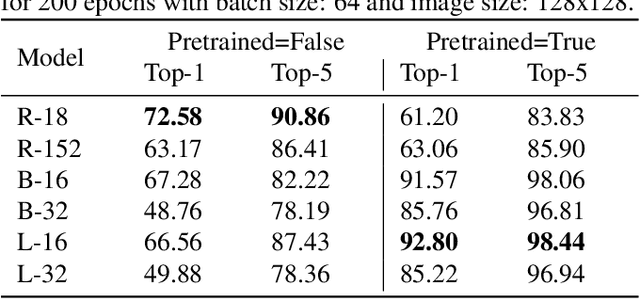
Abstract:In this work we tackle the challenging problem of anime character recognition. Anime, referring to animation produced within Japan and work derived or inspired from it. For this purpose we present DAF:re (DanbooruAnimeFaces:revamped), a large-scale, crowd-sourced, long-tailed dataset with almost 500 K images spread across more than 3000 classes. Additionally, we conduct experiments on DAF:re and similar datasets using a variety of classification models, including CNN based ResNets and self-attention based Vision Transformer (ViT). Our results give new insights into the generalization and transfer learning properties of ViT models on substantially different domain datasets from those used for the upstream pre-training, including the influence of batch and image size in their training. Additionally, we share our dataset, source-code, pre-trained checkpoints and results, as Animesion, the first end-to-end framework for large-scale anime character recognition: https://github.com/arkel23/animesion
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge