Edgard Chammas
Fine-tuning Handwriting Recognition systems with Temporal Dropout
Jan 31, 2021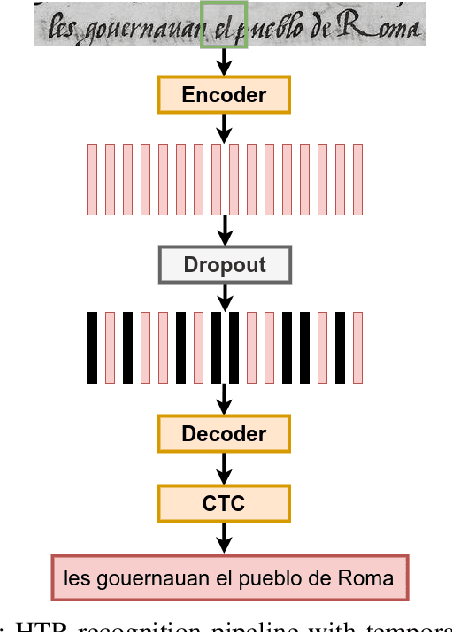
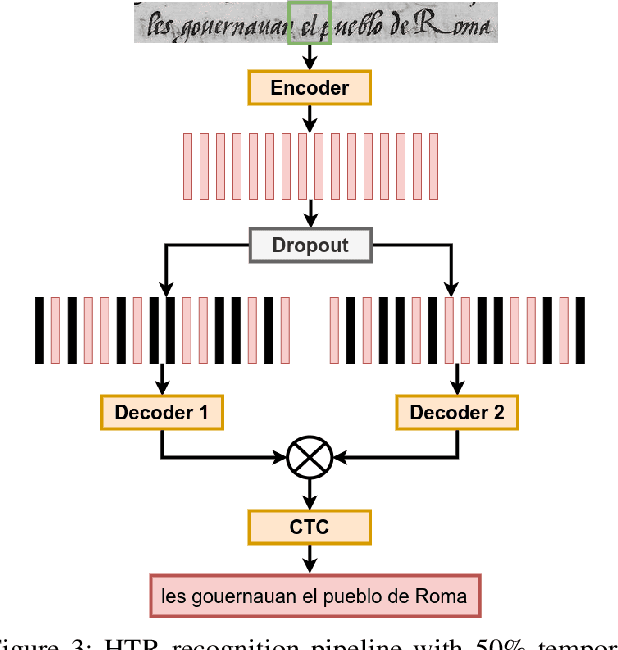
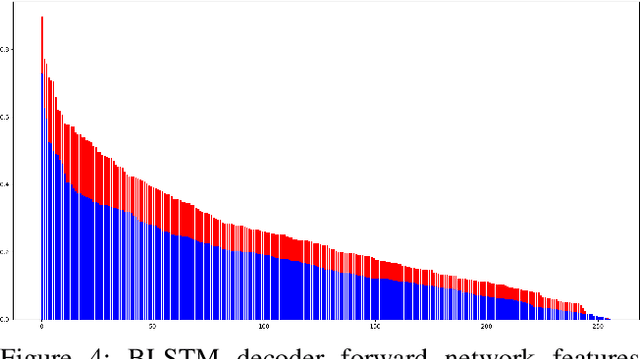
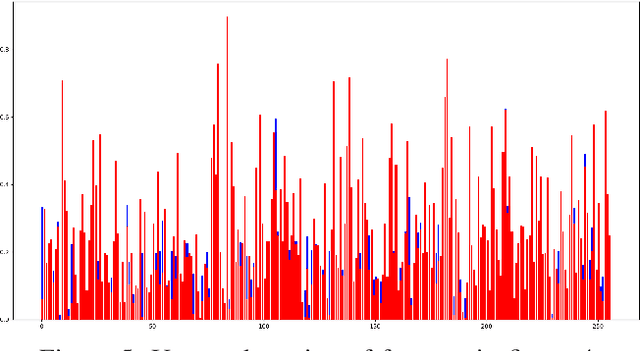
Abstract:This paper introduces a novel method to fine-tune handwriting recognition systems based on Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN). Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks are good at modeling long sequences but they tend to overfit over time. To improve the system's ability to model sequences, we propose to drop information at random positions in the sequence. We call our approach Temporal Dropout (TD). We apply TD at the image level as well to internal network representation. We show that TD improves the results on two different datasets. Our method outperforms previous state-of-the-art on Rodrigo dataset.
Handwriting Recognition of Historical Documents with few labeled data
Nov 10, 2018
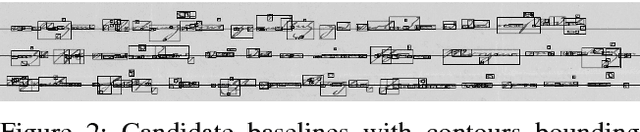

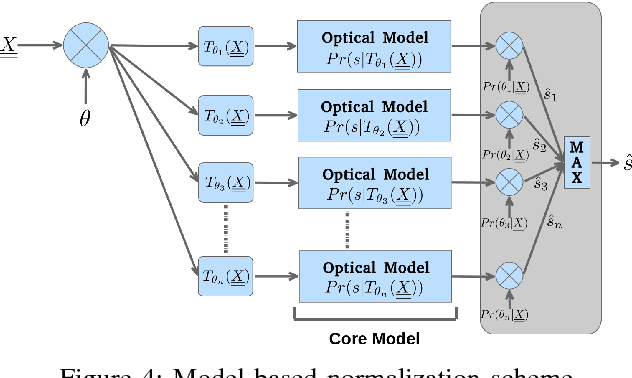
Abstract:Historical documents present many challenges for offline handwriting recognition systems, among them, the segmentation and labeling steps. Carefully annotated textlines are needed to train an HTR system. In some scenarios, transcripts are only available at the paragraph level with no text-line information. In this work, we demonstrate how to train an HTR system with few labeled data. Specifically, we train a deep convolutional recurrent neural network (CRNN) system on only 10% of manually labeled text-line data from a dataset and propose an incremental training procedure that covers the rest of the data. Performance is further increased by augmenting the training set with specially crafted multiscale data. We also propose a model-based normalization scheme which considers the variability in the writing scale at the recognition phase. We apply this approach to the publicly available READ dataset. Our system achieved the second best result during the ICDAR2017 competition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge