Driss Aboutajdine
GSCM-LRIT
A Dashboard to Analysis and Synthesis of Dimensionality Reduction Methods in Remote Sensing
Oct 18, 2022


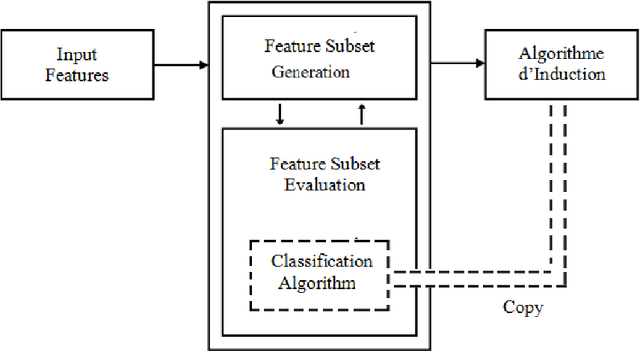
Abstract:Hyperspectral images (HSI) classification is a high technical remote sensing software. The purpose is to reproduce a thematic map . The HSI contains more than a hundred hyperspectral measures, as bands (or simply images), of the concerned region. They are taken at neighbors frequencies. Unfortunately, some bands are redundant features, others are noisily measured, and the high dimensionality of features made classification accuracy poor. The problematic is how to find the good bands to classify the regions items. Some methods use Mutual Information (MI) and thresholding, to select relevant images, without processing redundancy. Others control and avoid redundancy. But they process the dimensionality reduction, some times as selection, other times as wrapper methods without any relationship . Here , we introduce a survey on all scheme used, and after critics and improvement, we synthesize a dashboard, that helps user to analyze an hypothesize features selection and extraction softwares.
* Journal Paper On Concepts Of Selection
A blind Robust Image Watermarking Approach exploiting the DFT Magnitude
Oct 22, 2019
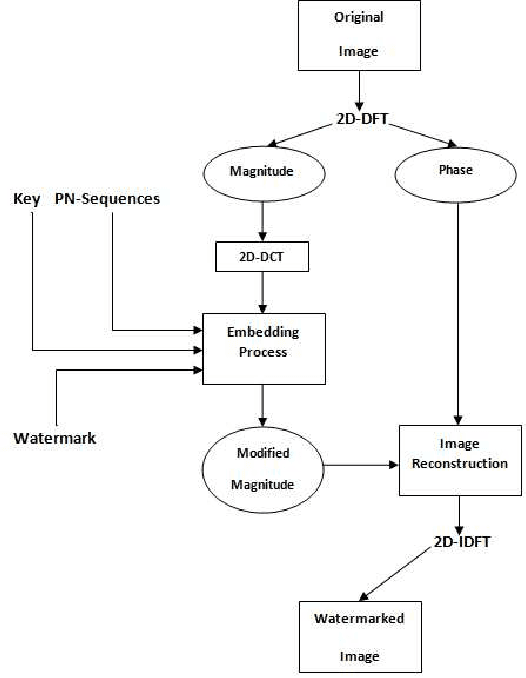
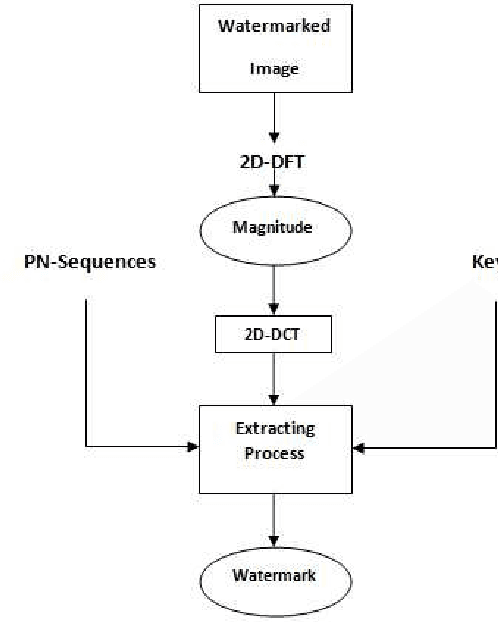

Abstract:Due to the current progress in Internet, digital contents (video, audio and images) are widely used. Distribution of multimedia contents is now faster and it allows for easy unauthorized reproduction of information. Digital watermarking came up while trying to solve this problem. Its main idea is to embed a watermark into a host digital content without affecting its quality. Moreover, watermarking can be used in several applications such as authentication, copy control, indexation, Copyright protection, etc. In this paper, we propose a blind robust image watermarking approach as a solution to the problem of copyright protection of digital images. The underlying concept of our method is to apply a discrete cosine transform (DCT) to the magnitude resulting from a discrete Fourier transform (DFT) applied to the original image. Then, the watermark is embedded by modifying the coefficients of the DCT using a secret key to increase security. Experimental results show the robustness of the proposed technique to a wide range of common attacks, e.g., Low-Pass Gaussian Filtering, JPEG compression, Gaussian noise, salt & pepper noise, Gaussian Smoothing and Histogram equalization. The proposed method achieves a Peak signal-to-noise-ration (PSNR) value greater than 66 (dB) and ensures a perfect watermark extraction.
Image quality assessment measure based on natural image statistics in the Tetrolet domain
Dec 08, 2014
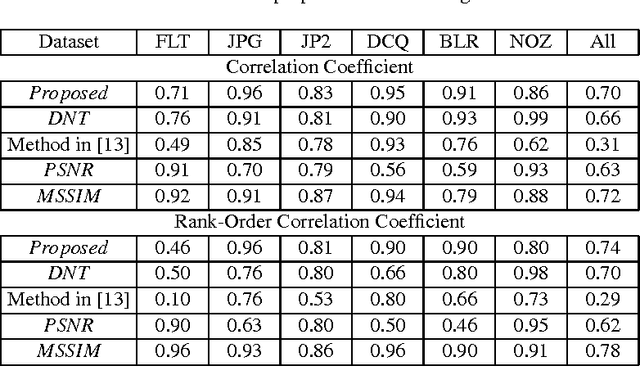
Abstract:This paper deals with a reduced reference (RR) image quality measure based on natural image statistics modeling. For this purpose, Tetrolet transform is used since it provides a convenient way to capture local geometric structures. This transform is applied to both reference and distorted images. Then, Gaussian Scale Mixture (GSM) is proposed to model subbands in order to take account statistical dependencies between tetrolet coefficients. In order to quantify the visual degradation, a measure based on Kullback Leibler Divergence (KLD) is provided. The proposed measure was tested on the Cornell VCL A-57 dataset and compared with other measures according to FR-TV1 VQEG framework.
Application of Symmetric Uncertainty and Mutual Information to Dimensionality Reduction and Classification of Hyperspectral Images
Dec 17, 2012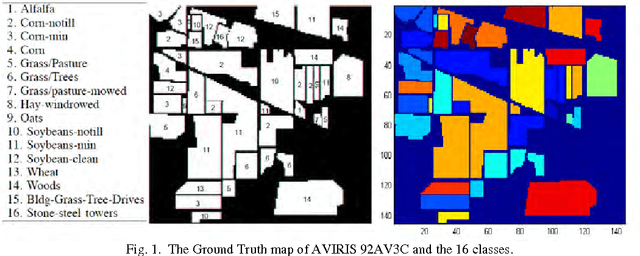
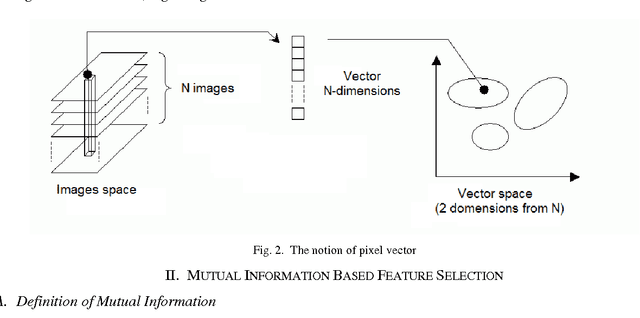
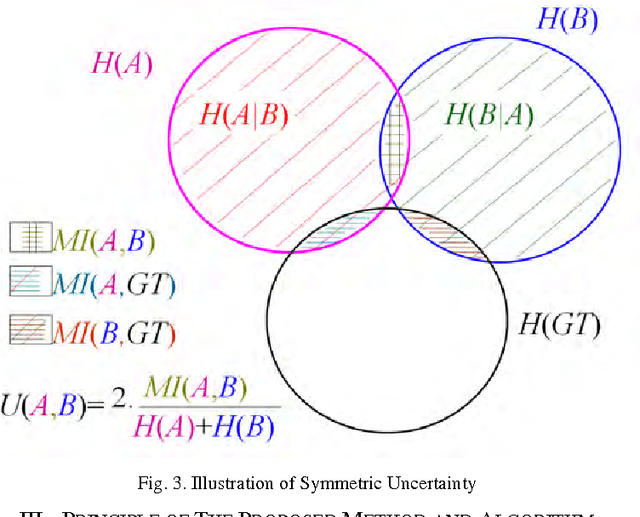
Abstract:Remote sensing is a technology to acquire data for disatant substances, necessary to construct a model knowledge for applications as classification. Recently Hyperspectral Images (HSI) becomes a high technical tool that the main goal is to classify the point of a region. The HIS is more than a hundred bidirectional measures, called bands (or simply images), of the same region called Ground Truth Map (GT). But some bands are not relevant because they are affected by different atmospheric effects; others contain redundant information; and high dimensionality of HSI features make the accuracy of classification lower. All these bands can be important for some applications; but for the classification a small subset of these is relevant. The problematic related to HSI is the dimensionality reduction. Many studies use mutual information (MI) to select the relevant bands. Others studies use the MI normalized forms, like Symmetric Uncertainty, in medical imagery applications. In this paper we introduce an algorithm based also on MI to select relevant bands and it apply the Symmetric Uncertainty coefficient to control redundancy and increase the accuracy of classification. This algorithm is feature selection tool and a Filter strategy. We establish this study on HSI AVIRIS 92AV3C. This is an effectiveness, and fast scheme to control redundancy.
* 14 pages, 7 Figure, 2 Tables, Paper keywords: Hyperspectral images, Classification, Feature Selection, Mutual information, Redundancy. arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:1210.0052, arXiv:1211.0055
Dimensionality Reduction and Classification Feature Using Mutual Information Applied to Hyperspectral Images: A Wrapper Strategy Algorithm Based on Minimizing the Error Probability Using the Inequality of Fano
Oct 31, 2012

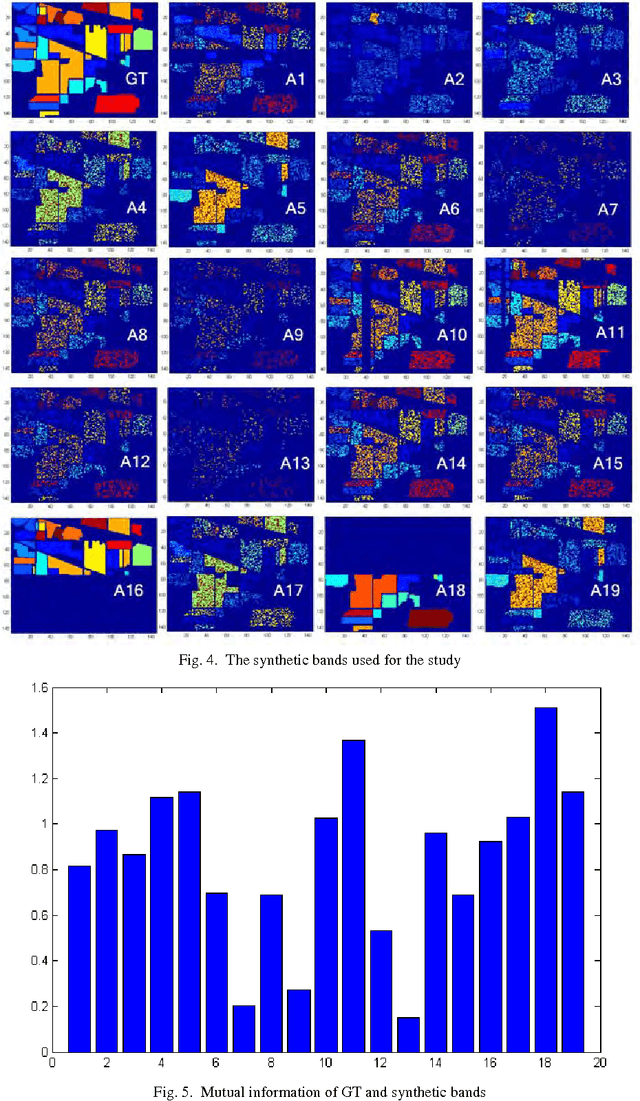
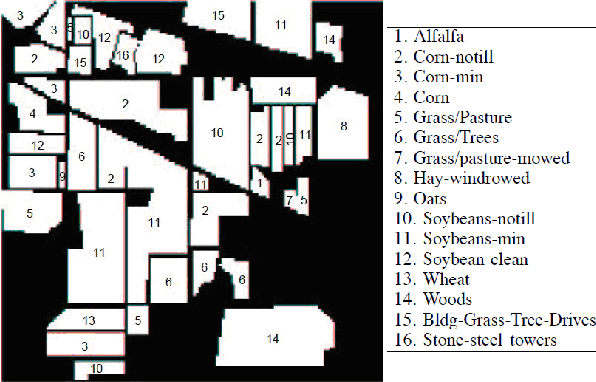
Abstract:In the feature classification domain, the choice of data affects widely the results. For the Hyperspectral image, the bands dont all contain the information; some bands are irrelevant like those affected by various atmospheric effects, see Figure.4, and decrease the classification accuracy. And there exist redundant bands to complicate the learning system and product incorrect prediction [14]. Even the bands contain enough information about the scene they may can't predict the classes correctly if the dimension of space images, see Figure.3, is so large that needs many cases to detect the relationship between the bands and the scene (Hughes phenomenon) [10]. We can reduce the dimensionality of hyperspectral images by selecting only the relevant bands (feature selection or subset selection methodology), or extracting, from the original bands, new bands containing the maximal information about the classes, using any functions, logical or numerical (feature extraction methodology) [11][9]. Here we focus on the feature selection using mutual information. Hyperspectral images have three advantages regarding the multispectral images [6],
* 12 page, 5 figures. arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:1210.0528, arXiv:1210.0052
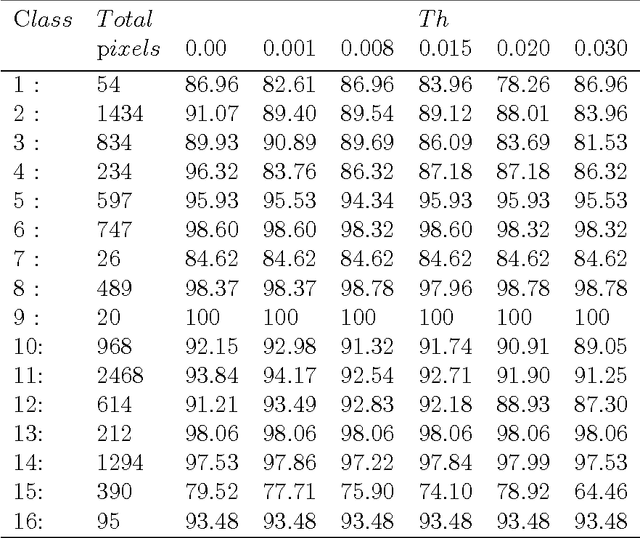
Band Selection and Classification of Hyperspectral Images using Mutual Information: An algorithm based on minimizing the error probability using the inequality of Fano
Sep 28, 2012

Abstract:Hyperspectral image is a substitution of more than a hundred images, called bands, of the same region. They are taken at juxtaposed frequencies. The reference image of the region is called Ground Truth map (GT). the problematic is how to find the good bands to classify the pixels of regions; because the bands can be not only redundant, but a source of confusion, and decreasing so the accuracy of classification. Some methods use Mutual Information (MI) and threshold, to select relevant bands. Recently there's an algorithm selection based on mutual information, using bandwidth rejection and a threshold to control and eliminate redundancy. The band top ranking the MI is selected, and if its neighbors have sensibly the same MI with the GT, they will be considered redundant and so discarded. This is the most inconvenient of this method, because this avoids the advantage of hyperspectral images: some precious information can be discarded. In this paper we'll make difference between useful and useless redundancy. A band contains useful redundancy if it contributes to decreasing error probability. According to this scheme, we introduce new algorithm using also mutual information, but it retains only the bands minimizing the error probability of classification. To control redundancy, we introduce a complementary threshold. So the good band candidate must contribute to decrease the last error probability augmented by the threshold. This process is a wrapper strategy; it gets high performance of classification accuracy but it is expensive than filter strategy.
Dimensionality Reduction and Classification feature using Mutual Information applied to Hyperspectral Images : A Filter strategy based algorithm
Sep 28, 2012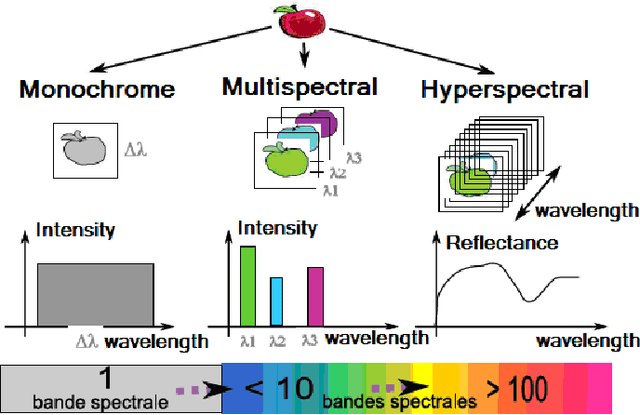
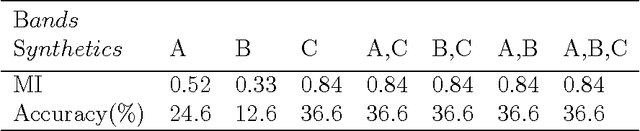
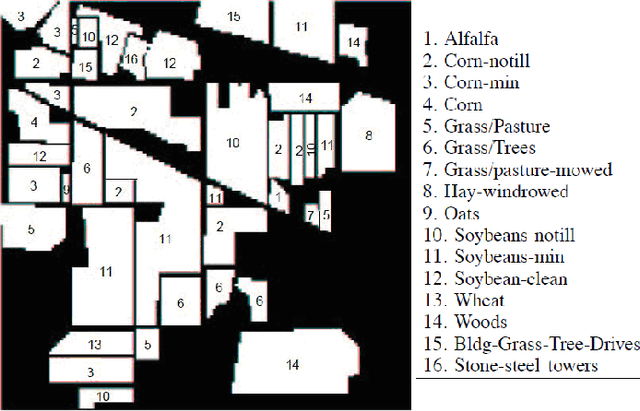
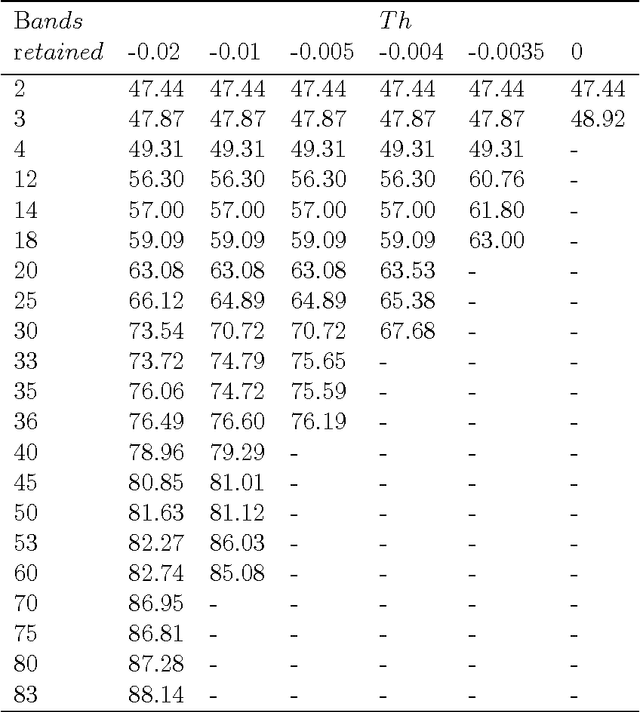
Abstract:Hyperspectral images (HIS) classification is a high technical remote sensing tool. The goal is to reproduce a thematic map that will be compared with a reference ground truth map (GT), constructed by expecting the region. The HIS contains more than a hundred bidirectional measures, called bands (or simply images), of the same region. They are taken at juxtaposed frequencies. Unfortunately, some bands contain redundant information, others are affected by the noise, and the high dimensionality of features made the accuracy of classification lower. The problematic is how to find the good bands to classify the pixels of regions. Some methods use Mutual Information (MI) and threshold, to select relevant bands, without treatment of redundancy. Others control and eliminate redundancy by selecting the band top ranking the MI, and if its neighbors have sensibly the same MI with the GT, they will be considered redundant and so discarded. This is the most inconvenient of this method, because this avoids the advantage of hyperspectral images: some precious information can be discarded. In this paper we'll accept the useful redundancy. A band contains useful redundancy if it contributes to produce an estimated reference map that has higher MI with the GT.nTo control redundancy, we introduce a complementary threshold added to last value of MI. This process is a Filter strategy; it gets a better performance of classification accuracy and not expensive, but less preferment than Wrapper strategy.
* 11 pages, 5 figures, journal paper
A Reduced Reference Image Quality Measure Using Bessel K Forms Model for Tetrolet Coefficients
Dec 18, 2011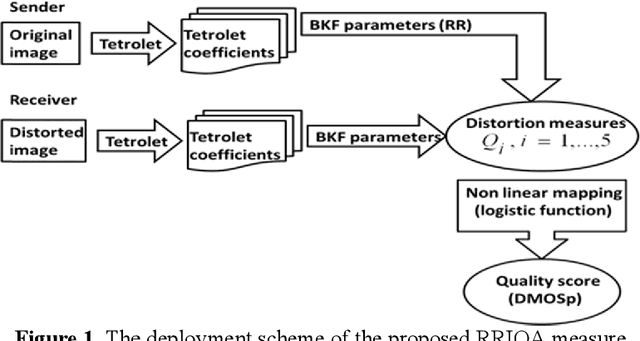
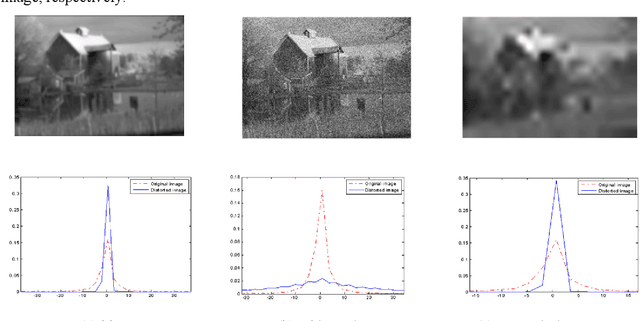
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a Reduced Reference Image Quality Assessment (RRIQA) measure based on the natural image statistic approach. A new adaptive transform called "Tetrolet" is applied to both reference and distorted images. To model the marginal distribution of tetrolet coefficients Bessel K Forms (BKF) density is proposed. Estimating the parameters of this distribution allows to summarize the reference image with a small amount of side information. Five distortion measures based on the BKF parameters of the original and processed image are used to predict quality scores. A comparison between these measures is presented showing a good consistency with human judgment.
3D-Mesh denoising using an improved vertex based anisotropic diffusion
Sep 23, 2010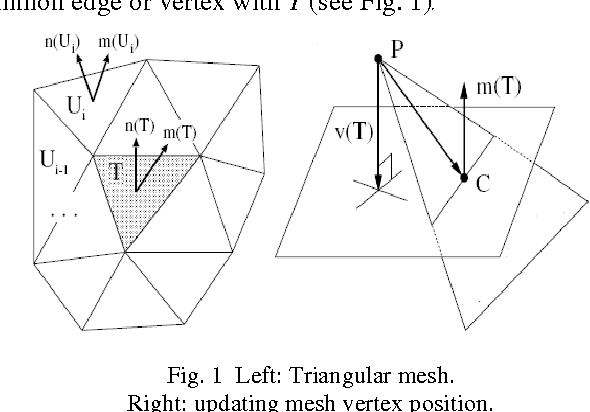
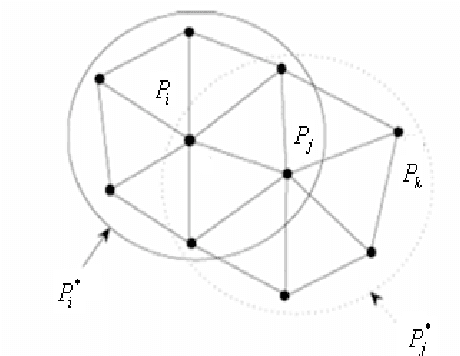
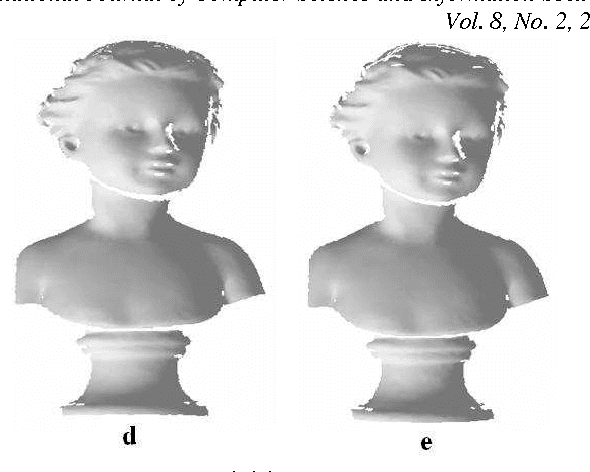
Abstract:This paper deals with an improvement of vertex based nonlinear diffusion for mesh denoising. This method directly filters the position of the vertices using Laplace, reduced centered Gaussian and Rayleigh probability density functions as diffusivities. The use of these PDFs improves the performance of a vertex-based diffusion method which are adapted to the underlying mesh structure. We also compare the proposed method to other mesh denoising methods such as Laplacian flow, mean, median, min and the adaptive MMSE filtering. To evaluate these methods of filtering, we use two error metrics. The first is based on the vertices and the second is based on the normals. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method in comparison with the existing methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge