Doğan Küçük
OntoWind: An Improved and Extended Wind Energy Ontology
Mar 07, 2018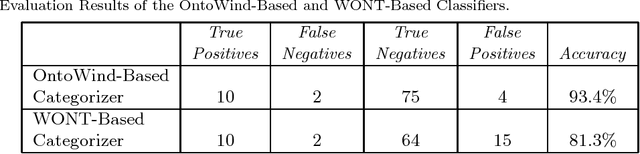
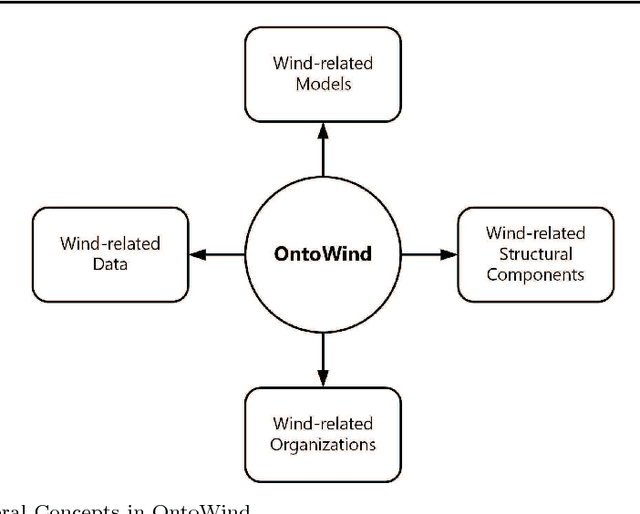
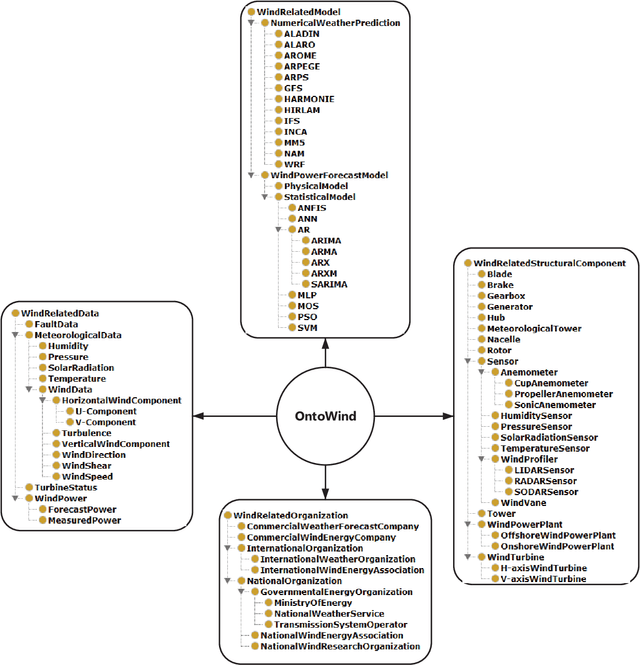
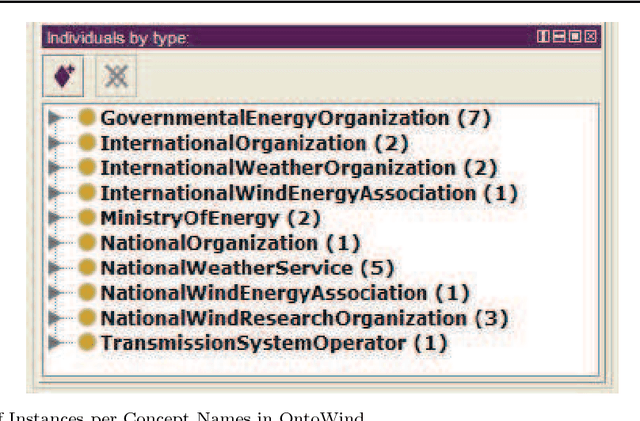
Abstract:Ontologies are critical sources of semantic information for many application domains. Hence, there are ontologies proposed and utilized for domains such as medicine, chemical engineering, and electrical energy. In this paper, we present an improved and extended version of a wind energy ontology previously proposed. First, the ontology is restructured to increase its understandability and coverage. Secondly, it is enriched with new concepts, crisp/fuzzy attributes, and instances to increase its usability in semantic applications regarding wind energy. The ultimate ontology is utilized within a Web-based semantic portal application for wind energy, in order to showcase its contribution in a genuine application. Hence, the current study is a significant to wind and thereby renewable energy informatics, with the presented publicly-available wind energy ontology and the implemented proof-of-concept system.
On TimeML-Compliant Temporal Expression Extraction in Turkish
Sep 03, 2015



Abstract:It is commonly acknowledged that temporal expression extractors are important components of larger natural language processing systems like information retrieval and question answering systems. Extraction and normalization of temporal expressions in Turkish has not been given attention so far except the extraction of some date and time expressions within the course of named entity recognition. As TimeML is the current standard of temporal expression and event annotation in natural language texts, in this paper, we present an analysis of temporal expressions in Turkish based on the related TimeML classification (i.e., date, time, duration, and set expressions). We have created a lexicon for Turkish temporal expressions and devised considerably wide-coverage patterns using the lexical classes as the building blocks. We believe that the proposed patterns, together with convenient normalization rules, can be readily used by prospective temporal expression extraction tools for Turkish.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge