Diego Volpatto
Accelerated reactive transport simulations in heterogeneous porous medium using Reaktoro and Firedrake
Aug 17, 2020


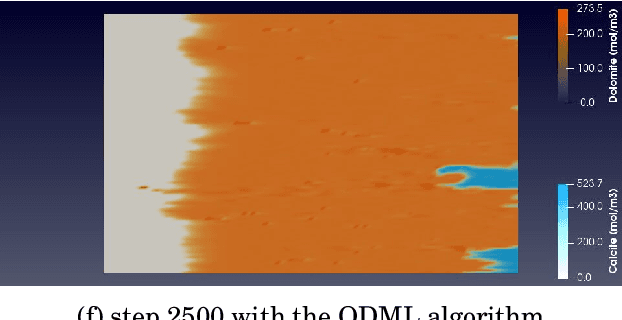
Abstract:Geochemical reaction calculations in reactive transport modeling are costly in general. They become more expensive the more complex is the chemical system and the activity models used to describe the non-ideal thermodynamic behavior of its phases. Accounting for many aqueous species, gases, and minerals also contributes to more expensive computations. This work investigates the performance of the on-demand machine learning (ODML) algorithm presented in Allan etal. (2020) when applied to different reactive transport problems in heterogeneous porous media. We demonstrate that the ODML algorithm enables faster chemical equilibrium calculations by one to three orders of magnitude. This, in turn, significantly accelerates the entire reactive transport simulations. The numerical experiments are carried out using the coupling of two open-source software packages: Firedrake (Rathgeber, 2016) and Reaktoro (Leal, 2015).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge