Diego Martín
Human interaction classifier for LLM based chatbot
Jul 31, 2024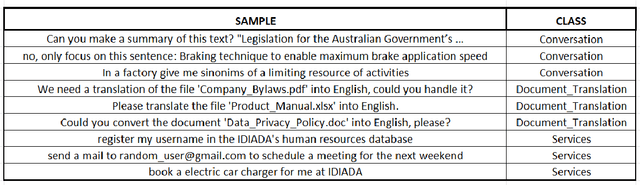
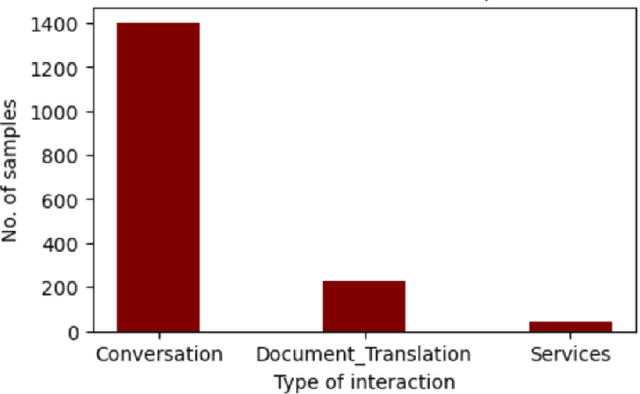

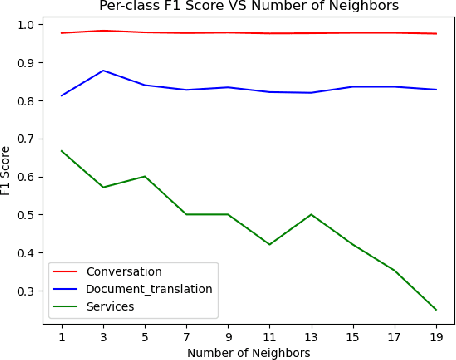
Abstract:This study investigates different approaches to classify human interactions in an artificial intelligence-based environment, specifically for Applus+ IDIADA's intelligent agent AIDA. The main objective is to develop a classifier that accurately identifies the type of interaction received (Conversation, Services, or Document Translation) to direct requests to the appropriate channel and provide a more specialized and efficient service. Various models are compared, including LLM-based classifiers, KNN using Titan and Cohere embeddings, SVM, and artificial neural networks. Results show that SVM and ANN models with Cohere embeddings achieve the best overall performance, with superior F1 scores and faster execution times compared to LLM-based approaches. The study concludes that the SVM model with Cohere embeddings is the most suitable option for classifying human interactions in the AIDA environment, offering an optimal balance between accuracy and computational efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge