Deressa Wodajo
Deepfake Video Detection Using Generative Convolutional Vision Transformer
Jul 13, 2023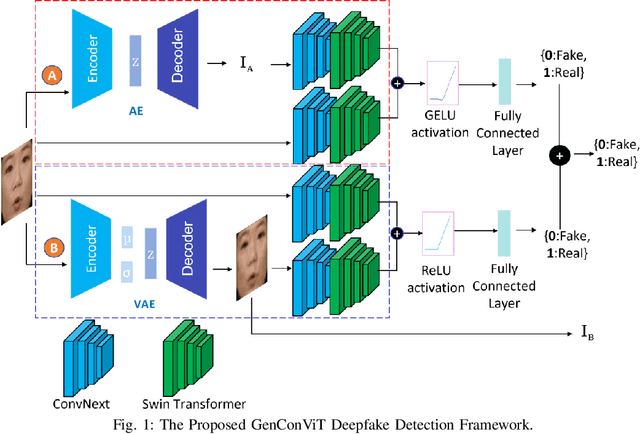

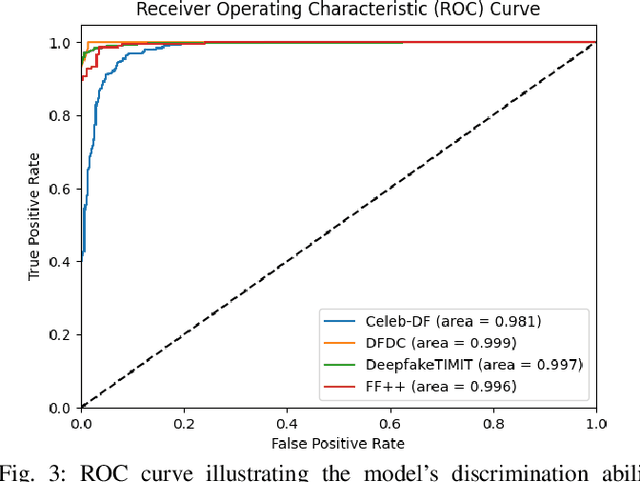
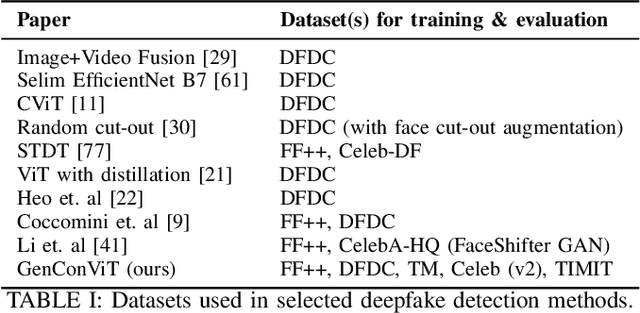
Abstract:Deepfakes have raised significant concerns due to their potential to spread false information and compromise digital media integrity. In this work, we propose a Generative Convolutional Vision Transformer (GenConViT) for deepfake video detection. Our model combines ConvNeXt and Swin Transformer models for feature extraction, and it utilizes Autoencoder and Variational Autoencoder to learn from the latent data distribution. By learning from the visual artifacts and latent data distribution, GenConViT achieves improved performance in detecting a wide range of deepfake videos. The model is trained and evaluated on DFDC, FF++, DeepfakeTIMIT, and Celeb-DF v2 datasets, achieving high classification accuracy, F1 scores, and AUC values. The proposed GenConViT model demonstrates robust performance in deepfake video detection, with an average accuracy of 95.8% and an AUC value of 99.3% across the tested datasets. Our proposed model addresses the challenge of generalizability in deepfake detection by leveraging visual and latent features and providing an effective solution for identifying a wide range of fake videos while preserving media integrity. The code for GenConViT is available at https://github.com/erprogs/GenConViT.
Deepfake Video Detection Using Convolutional Vision Transformer
Mar 11, 2021



Abstract:The rapid advancement of deep learning models that can generate and synthesis hyper-realistic videos known as Deepfakes and their ease of access to the general public have raised concern from all concerned bodies to their possible malicious intent use. Deep learning techniques can now generate faces, swap faces between two subjects in a video, alter facial expressions, change gender, and alter facial features, to list a few. These powerful video manipulation methods have potential use in many fields. However, they also pose a looming threat to everyone if used for harmful purposes such as identity theft, phishing, and scam. In this work, we propose a Convolutional Vision Transformer for the detection of Deepfakes. The Convolutional Vision Transformer has two components: Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and Vision Transformer (ViT). The CNN extracts learnable features while the ViT takes in the learned features as input and categorizes them using an attention mechanism. We trained our model on the DeepFake Detection Challenge Dataset (DFDC) and have achieved 91.5 percent accuracy, an AUC value of 0.91, and a loss value of 0.32. Our contribution is that we have added a CNN module to the ViT architecture and have achieved a competitive result on the DFDC dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge