Deniz Başkent
Use of a humanoid robot for auditory psychophysical testing
Jun 16, 2023
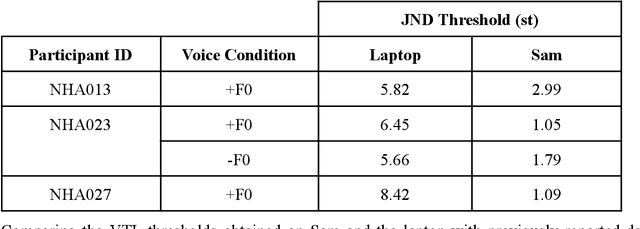
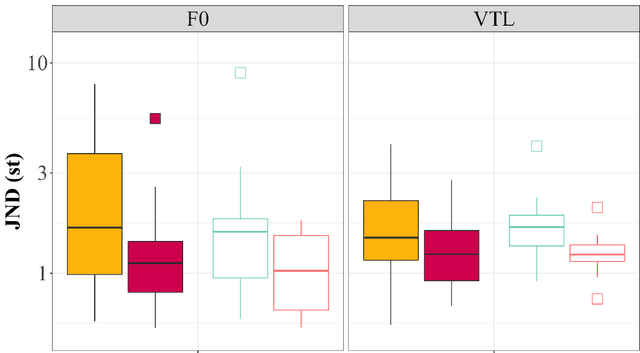
Abstract:Tasks in psychophysical tests can at times be repetitive and cause individuals to lose engagement during the test. To facilitate engagement, we propose the use of a humanoid NAO robot as an alternative interface for conducting psychophysical tests. Specifically, we aim to evaluate the performance of the NAO as an auditory testing interface, given its potential limitations and technical differences, in comparison to the current laptop interface. We examine the results and durations of two voice perception tests, voice cue sensitivity and voice gender categorisation, obtained from both the conventionally used laptop interface and the new NAO interface. Both tests investigate the perception and use of two speaker-specific voice cues, fundamental frequency (F0) and vocal tract length (VTL), important for characterising voice gender. Responses are logged on the laptop using a connected mouse, and on the NAO using the tactile sensors. Comparison of test results from both interfaces shows functional similarity between the interfaces and replicates findings from previous studies with similar tests. Comparison of test durations shows longer testing times with NAO, primarily due to longer processing times in comparison to the laptop, as well as other design limitations due to the implementation of the test on the robot. Despite the inherent constraints of the NAO robot, such as in sound quality, relatively long processing and testing times, and different methods of response logging, the NAO interface appears to facilitate collecting similar data to the current laptop interface, confirming its potential as an alternative psychophysical test interface for auditory perception tests.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge