Debarshi Sen
RL-Controller: a reinforcement learning framework for active structural control
Mar 13, 2021



Abstract:To maintain structural integrity and functionality during the designed life cycle of a structure, engineers are expected to accommodate for natural hazards as well as operational load levels. Active control systems are an efficient solution for structural response control when a structure is subjected to unexpected extreme loads. However, development of these systems through traditional means is limited by their model dependent nature. Recent advancements in adaptive learning methods, in particular, reinforcement learning (RL), for real-time decision making problems, along with rapid growth in high-performance computational resources, help structural engineers to transform the classic model-based active control problem to a purely data-driven one. In this paper, we present a novel RL-based approach for designing active controllers by introducing RL-Controller, a flexible and scalable simulation environment. The RL-Controller includes attributes and functionalities that are defined to model active structural control mechanisms in detail. We show that the proposed framework is easily trainable for a five story benchmark building with 65% reductions on average in inter story drifts (ISD) when subjected to strong ground motions. In a comparative study with LQG active control method, we demonstrate that the proposed model-free algorithm learns more optimal actuator forcing strategies that yield higher performance, e.g., 25% more ISD reductions on average with respect to LQG, without using prior information about the mechanical properties of the system.
Transfer Learning for Input Estimation of Vehicle Systems
Oct 26, 2020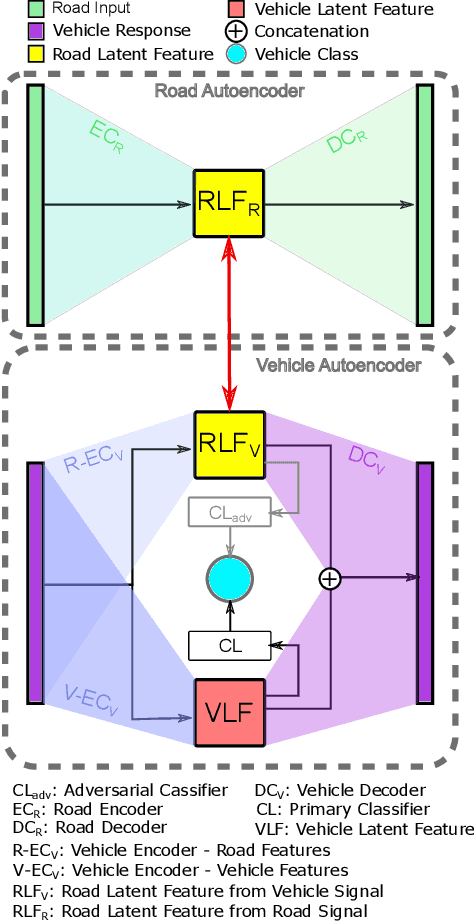

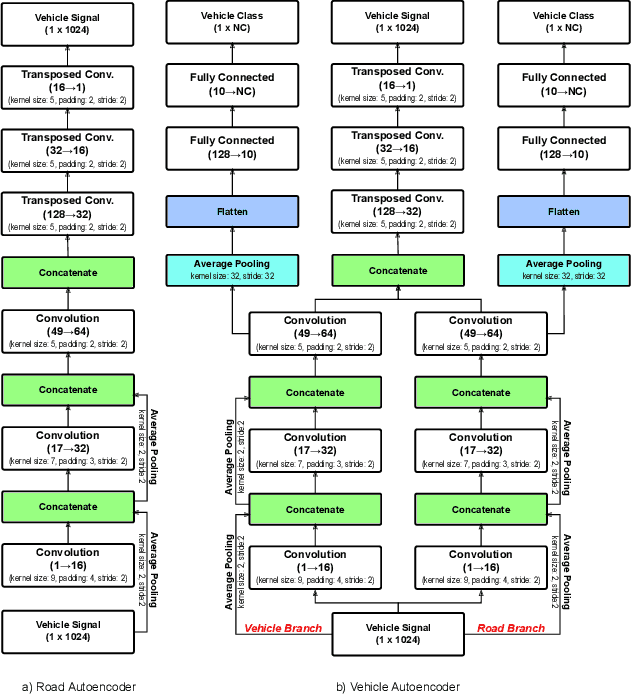
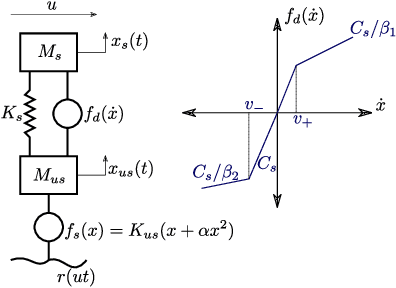
Abstract:This study proposes a learning-based method with domain adaptability for input estimation of vehicle suspension systems. In a crowdsensing setting for bridge health monitoring, vehicles carry sensors to collect samples of the bridge's dynamic response. The primary challenge is in preprocessing; signals are highly contaminated from road profile roughness and vehicle suspension dynamics. Additionally, signals are collected from a diverse set of vehicles vitiating model-based approaches. In our data-driven approach, two autoencoders for the cabin signal and the tire-level signal are constrained to force the separation of the tire-level input from the suspension system in the latent state representation. From the extracted features, we estimate the tire-level signal and determine the vehicle class with high accuracy (98% classification accuracy). Compared to existing solutions for the vehicle suspension deconvolution problem, we show that the proposed methodology is robust to vehicle dynamic variations and suspension system nonlinearity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge