Debapriyo Majumdar
One Word is Enough: Minimal Adversarial Perturbations for Neural Text Ranking
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Neural ranking models (NRMs) achieve strong retrieval effectiveness, yet prior work has shown they are vulnerable to adversarial perturbations. We revisit this robustness question with a minimal, query-aware attack that promotes a target document by inserting or substituting a single, semantically aligned word - the query center. We study heuristic and gradient-guided variants, including a white-box method that identifies influential insertion points. On TREC-DL 2019/2020 with BERT and monoT5 re-rankers, our single-word attacks achieve up to 91% success while modifying fewer than two tokens per document on average, achieving competitive rank and score boosts with far fewer edits under a comparable white-box setup to ensure fair evaluation against PRADA. We also introduce new diagnostic metrics to analyze attack sensitivity beyond aggregate success rates. Our analysis reveals a Goldilocks zone in which mid-ranked documents are most vulnerable. These findings demonstrate practical risks and motivate future defenses for robust neural ranking.
Explainability of Text Processing and Retrieval Methods: A Critical Survey
Dec 14, 2022
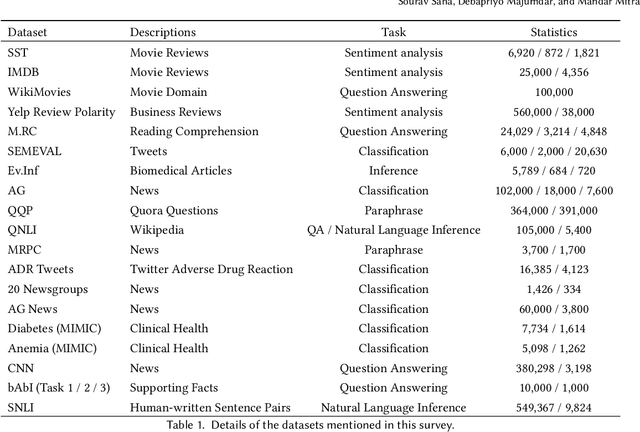
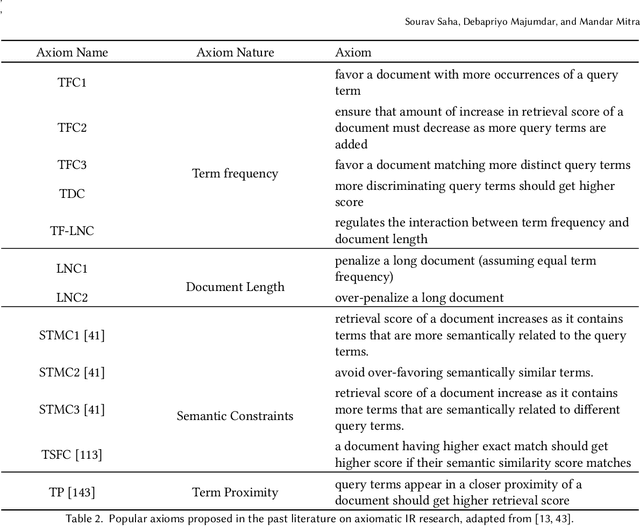
Abstract:Deep Learning and Machine Learning based models have become extremely popular in text processing and information retrieval. However, the non-linear structures present inside the networks make these models largely inscrutable. A significant body of research has focused on increasing the transparency of these models. This article provides a broad overview of research on the explainability and interpretability of natural language processing and information retrieval methods. More specifically, we survey approaches that have been applied to explain word embeddings, sequence modeling, attention modules, transformers, BERT, and document ranking. The concluding section suggests some possible directions for future research on this topic.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge