Debanjan Goswami
ACIL: Active Class Incremental Learning for Image Classification
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Continual learning (or class incremental learning) is a realistic learning scenario for computer vision systems, where deep neural networks are trained on episodic data, and the data from previous episodes are generally inaccessible to the model. Existing research in this domain has primarily focused on avoiding catastrophic forgetting, which occurs due to the continuously changing class distributions in each episode and the inaccessibility of the data from previous episodes. However, these methods assume that all the training samples in every episode are annotated; this not only incurs a huge annotation cost, but also results in a wastage of annotation effort, since most of the samples in a given episode will not be accessible to the model in subsequent episodes. Active learning algorithms identify the salient and informative samples from large amounts of unlabeled data and are instrumental in reducing the human annotation effort in inducing a deep neural network. In this paper, we propose ACIL, a novel active learning framework for class incremental learning settings. We exploit a criterion based on uncertainty and diversity to identify the exemplar samples that need to be annotated in each episode, and will be appended to the data in the next episode. Such a framework can drastically reduce annotation cost and can also avoid catastrophic forgetting. Our extensive empirical analyses on several vision datasets corroborate the promise and potential of our framework against relevant baselines.
Active Learning for Video Classification with Frame Level Queries
Jul 10, 2023
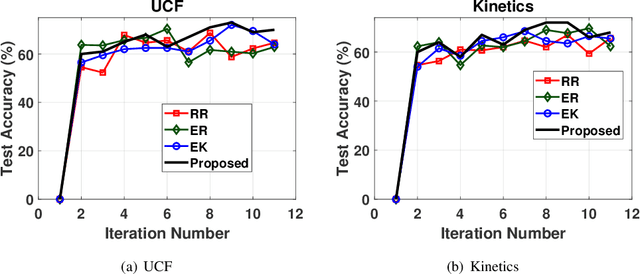
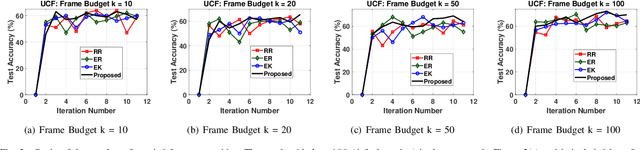
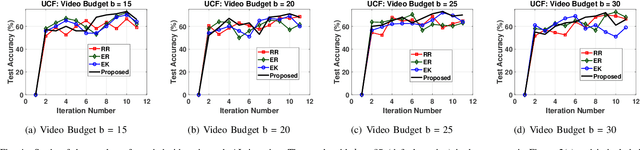
Abstract:Deep learning algorithms have pushed the boundaries of computer vision research and have depicted commendable performance in a variety of applications. However, training a robust deep neural network necessitates a large amount of labeled training data, acquiring which involves significant time and human effort. This problem is even more serious for an application like video classification, where a human annotator has to watch an entire video end-to-end to furnish a label. Active learning algorithms automatically identify the most informative samples from large amounts of unlabeled data; this tremendously reduces the human annotation effort in inducing a machine learning model, as only the few samples that are identified by the algorithm, need to be labeled manually. In this paper, we propose a novel active learning framework for video classification, with the goal of further reducing the labeling onus on the human annotators. Our framework identifies a batch of exemplar videos, together with a set of informative frames for each video; the human annotator needs to merely review the frames and provide a label for each video. This involves much less manual work than watching the complete video to come up with a label. We formulate a criterion based on uncertainty and diversity to identify the informative videos and exploit representative sampling techniques to extract a set of exemplar frames from each video. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first research effort to develop an active learning framework for video classification, where the annotators need to inspect only a few frames to produce a label, rather than watching the end-to-end video.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge