Davood G. Samani
Exploring the Impact of Virtualization on the Usability of the Deep Learning Applications
Dec 17, 2021
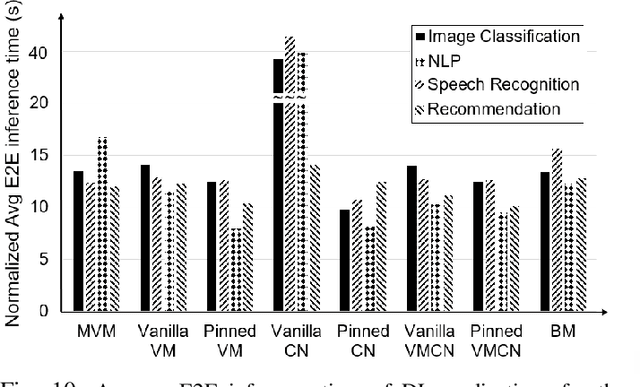
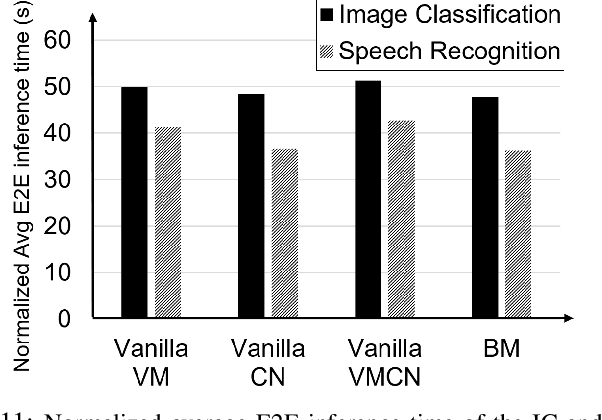
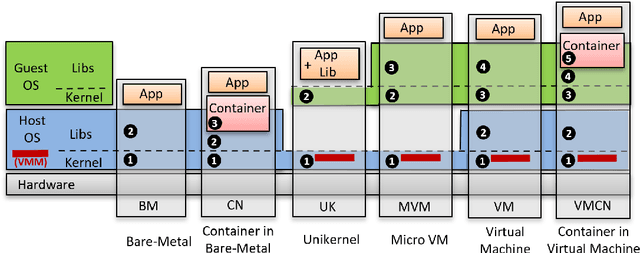
Abstract:Deep Learning-based (DL) applications are becoming increasingly popular and advancing at an unprecedented pace. While many research works are being undertaken to enhance Deep Neural Networks (DNN) -- the centerpiece of DL applications -- practical deployment challenges of these applications in the Cloud and Edge systems, and their impact on the usability of the applications have not been sufficiently investigated. In particular, the impact of deploying different virtualization platforms, offered by the Cloud and Edge, on the usability of DL applications (in terms of the End-to-End (E2E) inference time) has remained an open question. Importantly, resource elasticity (by means of scale-up), CPU pinning, and processor type (CPU vs GPU) configurations have shown to be influential on the virtualization overhead. Accordingly, the goal of this research is to study the impact of these potentially decisive deployment options on the E2E performance, thus, usability of the DL applications. To that end, we measure the impact of four popular execution platforms (namely, bare-metal, virtual machine (VM), container, and container in VM) on the E2E inference time of four types of DL applications, upon changing processor configuration (scale-up, CPU pinning) and processor types. This study reveals a set of interesting and sometimes counter-intuitive findings that can be used as best practices by Cloud solution architects to efficiently deploy DL applications in various systems. The notable finding is that the solution architects must be aware of the DL application characteristics, particularly, their pre- and post-processing requirements, to be able to optimally choose and configure an execution platform, determine the use of GPU, and decide the efficient scale-up range.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge