Davide Bertozzi
An Efficient Multicast Addressing Encoding Scheme for Multi-Core Neuromorphic Processors
Nov 18, 2024Abstract:Multi-core neuromorphic processors are becoming increasingly significant due to their energy-efficient local computing and scalable modular architecture, particularly for event-based processing applications. However, minimizing the cost of inter-core communication, which accounts for the majority of energy usage, remains a challenging issue. Beyond optimizing circuit design at lower abstraction levels, an efficient multicast addressing scheme is crucial. We propose a hierarchical bit string encoding scheme that largely expands the addressing capability of state-of-the-art symbol-based schemes for the same number of routing bits. When put at work with a real neuromorphic task, this hierarchical bit string encoding achieves a reduction in area cost by approximately 29% and decreases energy consumption by about 50%.
Logic Programming approaches for routing fault-free and maximally-parallel Wavelength Routed Optical Networks on Chip (Application paper)
Jul 18, 2017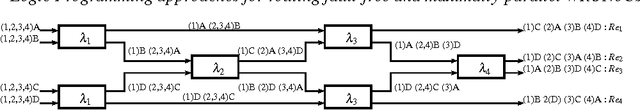
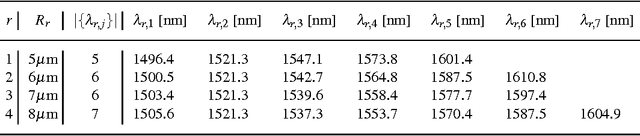
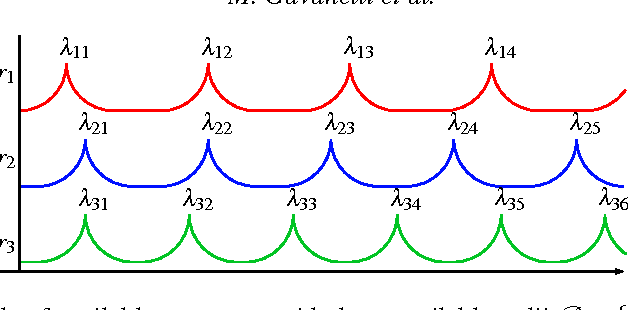
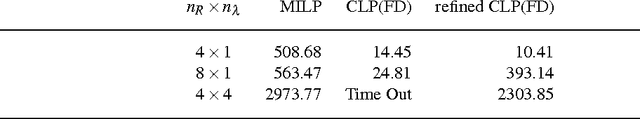
Abstract:One promising trend in digital system integration consists of boosting on-chip communication performance by means of silicon photonics, thus materializing the so-called Optical Networks-on-Chip (ONoCs). Among them, wavelength routing can be used to route a signal to destination by univocally associating a routing path to the wavelength of the optical carrier. Such wavelengths should be chosen so to minimize interferences among optical channels and to avoid routing faults. As a result, physical parameter selection of such networks requires the solution of complex constrained optimization problems. In previous work, published in the proceedings of the International Conference on Computer-Aided Design, we proposed and solved the problem of computing the maximum parallelism obtainable in the communication between any two endpoints while avoiding misrouting of optical signals. The underlying technology, only quickly mentioned in that paper, is Answer Set Programming (ASP). In this work, we detail the ASP approach we used to solve such problem. Another important design issue is to select the wavelengths of optical carriers such that they are spread across the available spectrum, in order to reduce the likelihood that, due to imperfections in the manufacturing process, unintended routing faults arise. We show how to address such problem in Constraint Logic Programming on Finite Domains (CLP(FD)). This paper is under consideration for possible publication on Theory and Practice of Logic Programming.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge