David Limbaugh
Towards a Cyber Information Ontology
Jul 26, 2024Abstract:This paper introduces a set of terms that are intended to act as an interface between cyber ontologies (like a file system ontology or a data fusion ontology) and top- and mid-level ontologies, specifically Basic Formal Ontology and the Common Core Ontologies. These terms center on what makes cyberinformation management unique: numerous acts of copying items of information, the aggregates of copies that result from those acts, and the faithful members of those aggregates that represent all other members.
Capabilities
Apr 30, 2024
Abstract:In our daily lives, as in science and in all other domains, we encounter huge numbers of dispositions (tendencies, potentials, powers) which are realized in processes such as sneezing, sweating, shedding dandruff, and on and on. Among this plethora of what we can think of as mere dispositions is a subset of dispositions in whose realizations we have an interest a car responding well when driven on ice, a rabbits lungs responding well when it is chased by a wolf, and so on. We call the latter capabilities and we attempt to provide a robust ontological account of what capabilities are that is of sufficient generality to serve a variety of purposes, for example by providing a useful extension to ontology-based research in areas where capabilities data are currently being collected in siloed fashion.
Ontology and Cognitive Outcomes
May 16, 2020
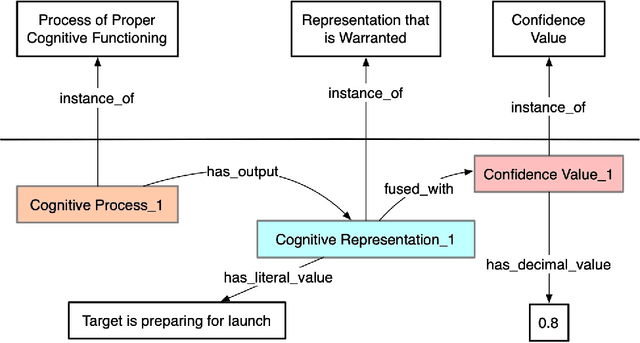
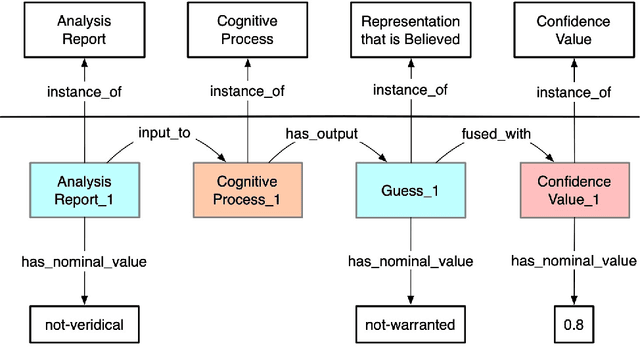
Abstract:The intelligence community relies on human-machine-based analytic strategies that 1) access and integrate vast amounts of information from disparate sources, 2) continuously process this information, so that, 3) a maximally comprehensive understanding of world actors and their behaviors can be developed and updated. Herein we describe an approach to utilizing outcomes-based learning (OBL) to support these efforts that is based on an ontology of the cognitive processes performed by intelligence analysts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge