David Dunwoody
Flight Testing an Optionally Piloted Aircraft: a Case Study on Trust Dynamics in Human-Autonomy Teaming
Mar 20, 2025
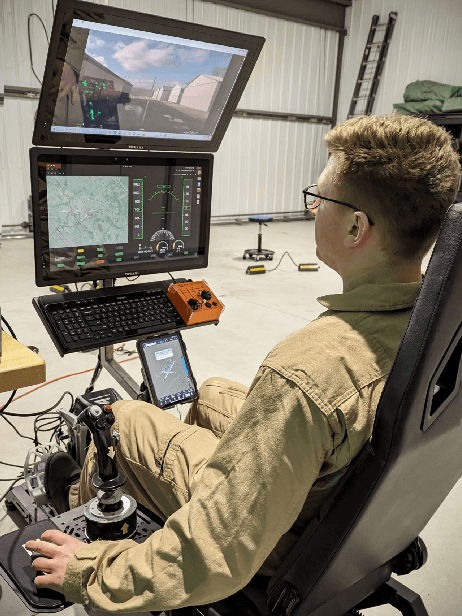

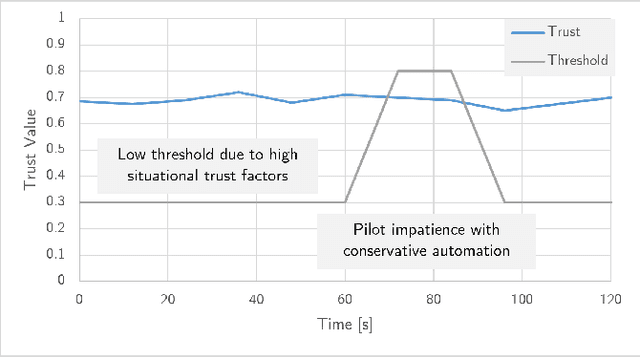
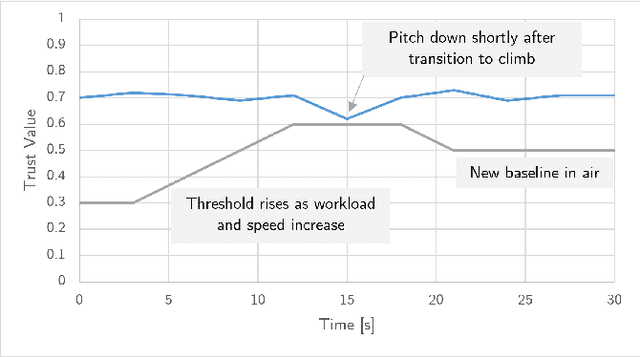
Abstract:This paper examines how trust is formed, maintained, or diminished over time in the context of human-autonomy teaming with an optionally piloted aircraft. Whereas traditional factor-based trust models offer a static representation of human confidence in technology, here we discuss how variations in the underlying factors lead to variations in trust, trust thresholds, and human behaviours. Over 200 hours of flight test data collected over a multi-year test campaign from 2021 to 2023 were reviewed. The dispositional-situational-learned, process-performance-purpose, and IMPACTS homeostasis trust models are applied to illuminate trust trends during nominal autonomous flight operations. The results offer promising directions for future studies on trust dynamics and design-for-trust in human-autonomy teaming.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge