David Alonso del Barrio
Examining European Press Coverage of the Covid-19 No-Vax Movement: An NLP Framework
Apr 29, 2023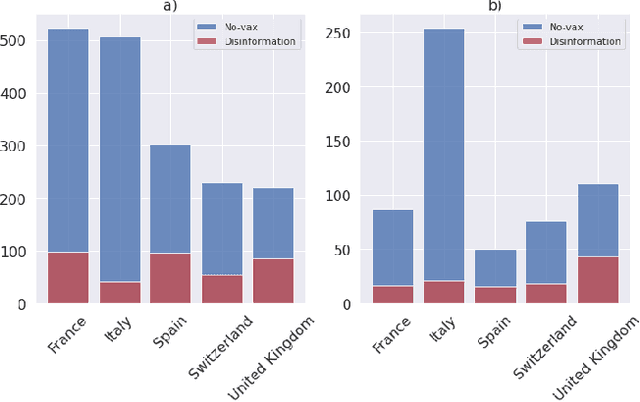
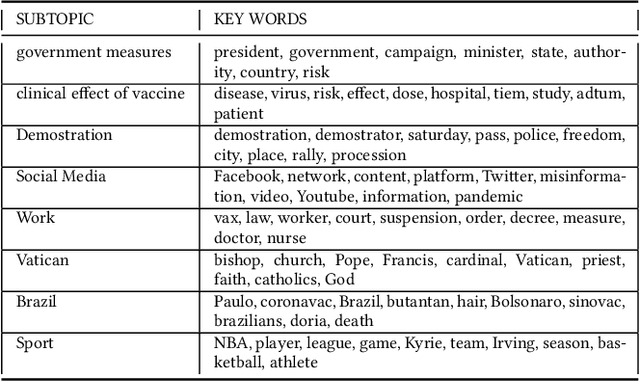
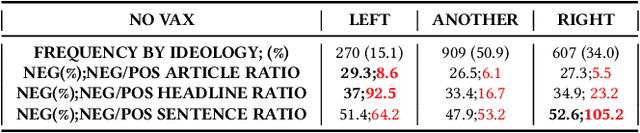
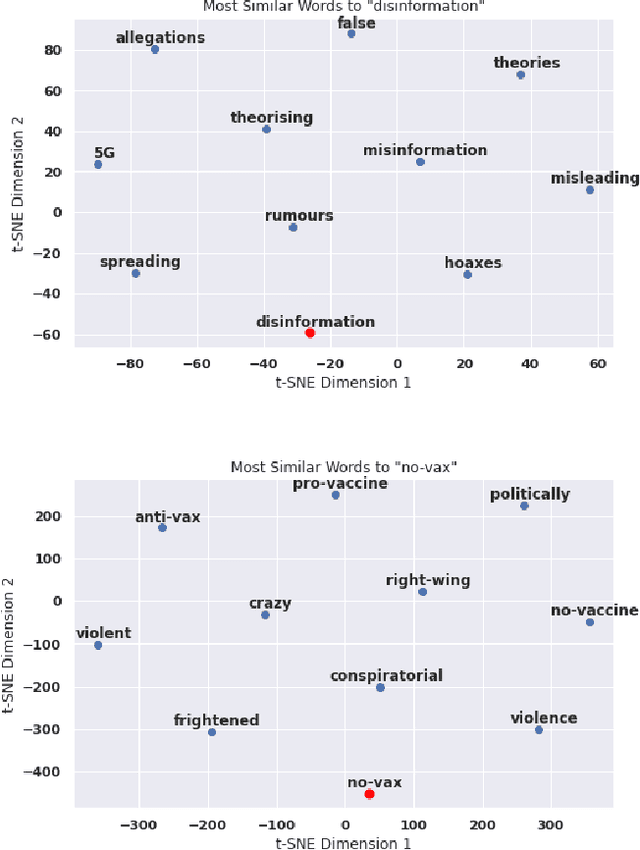
Abstract:This paper examines how the European press dealt with the no-vax reactions against the Covid-19 vaccine and the dis- and misinformation associated with this movement. Using a curated dataset of 1786 articles from 19 European newspapers on the anti-vaccine movement over a period of 22 months in 2020-2021, we used Natural Language Processing techniques including topic modeling, sentiment analysis, semantic relationship with word embeddings, political analysis, named entity recognition, and semantic networks, to understand the specific role of the European traditional press in the disinformation ecosystem. The results of this multi-angle analysis demonstrate that the European well-established press actively opposed a variety of hoaxes mainly spread on social media, and was critical of the anti-vax trend, regardless of the political orientation of the newspaper. This confirms the relevance of studying the role of high-quality press in the disinformation ecosystem.
Framing the News:From Human Perception to Large Language Model Inferences
Apr 27, 2023



Abstract:Identifying the frames of news is important to understand the articles' vision, intention, message to be conveyed, and which aspects of the news are emphasized. Framing is a widely studied concept in journalism, and has emerged as a new topic in computing, with the potential to automate processes and facilitate the work of journalism professionals. In this paper, we study this issue with articles related to the Covid-19 anti-vaccine movement. First, to understand the perspectives used to treat this theme, we developed a protocol for human labeling of frames for 1786 headlines of No-Vax movement articles of European newspapers from 5 countries. Headlines are key units in the written press, and worth of analysis as many people only read headlines (or use them to guide their decision for further reading.) Second, considering advances in Natural Language Processing (NLP) with large language models, we investigated two approaches for frame inference of news headlines: first with a GPT-3.5 fine-tuning approach, and second with GPT-3.5 prompt-engineering. Our work contributes to the study and analysis of the performance that these models have to facilitate journalistic tasks like classification of frames, while understanding whether the models are able to replicate human perception in the identification of these frames.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge