David Ada Adama
Mitigating Adversarial Attacks in Deepfake Detection: An Exploration of Perturbation and AI Techniques
Feb 22, 2023



Abstract:Deep learning is a crucial aspect of machine learning, but it also makes these techniques vulnerable to adversarial examples, which can be seen in a variety of applications. These examples can even be targeted at humans, leading to the creation of false media, such as deepfakes, which are often used to shape public opinion and damage the reputation of public figures. This article will explore the concept of adversarial examples, which are comprised of perturbations added to clean images or videos, and their ability to deceive DL algorithms. The proposed approach achieved a precision value of accuracy of 76.2% on the DFDC dataset.
Estimating the Power Consumption of Heterogeneous Devices when performing AI Inference
Jul 13, 2022



Abstract:Modern-day life is driven by electronic devices connected to the internet. The emerging research field of the Internet-of-Things (IoT) has become popular, just as there has been a steady increase in the number of connected devices - now over 50 billion. Since many of these devices are utilised to perform \gls*{cv} tasks, it is essential to understand their power consumption against performance. We report the power consumption profile and analysis of the NVIDIA Jetson Nano board while performing object classification. The authors present an extensive analysis regarding power consumption per frame and the output in frames per second (FPS) using YOLOv5 models. The results show that the YOLOv5n outperforms other YOLOV5 variants in terms of throughput (i.e. 12.34 fps) and low power consumption (i.e. 0.154 mWh/frame).
Real-Time Gesture Recognition with Virtual Glove Markers
Jul 06, 2022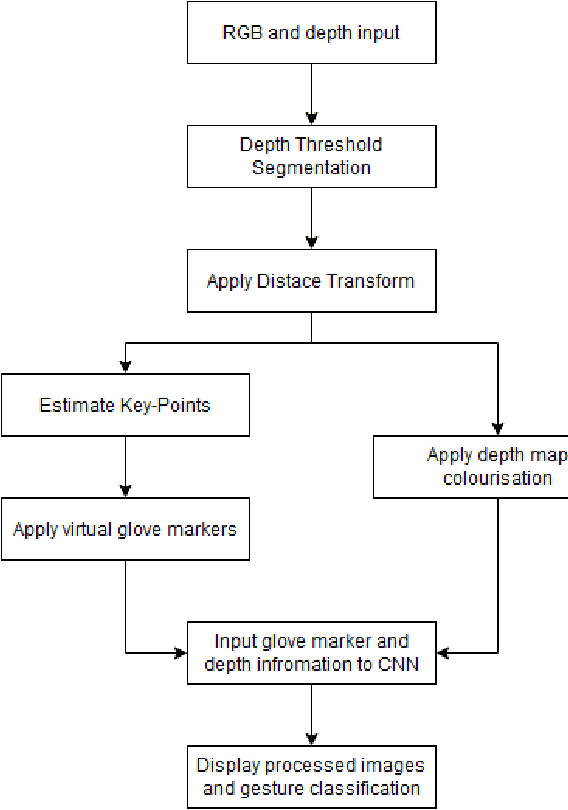
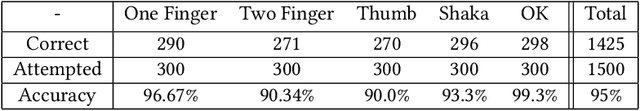
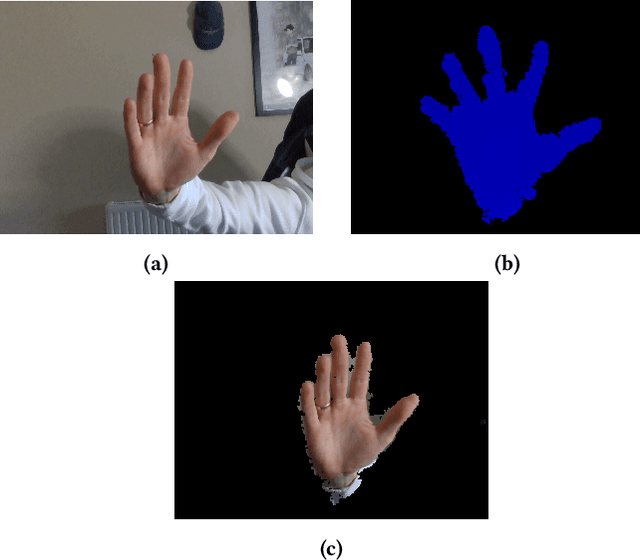

Abstract:Due to the universal non-verbal natural communication approach that allows for effective communication between humans, gesture recognition technology has been steadily developing over the previous few decades. Many different strategies have been presented in research articles based on gesture recognition to try to create an effective system to send non-verbal natural communication information to computers, using both physical sensors and computer vision. Hyper accurate real-time systems, on the other hand, have only recently began to occupy the study field, with each adopting a range of methodologies due to past limits such as usability, cost, speed, and accuracy. A real-time computer vision-based human-computer interaction tool for gesture recognition applications that acts as a natural user interface is proposed. Virtual glove markers on users hands will be created and used as input to a deep learning model for the real-time recognition of gestures. The results obtained show that the proposed system would be effective in real-time applications including social interaction through telepresence and rehabilitation.
Deep Learning approach for Classifying Trusses and Runners of Strawberries
Jul 06, 2022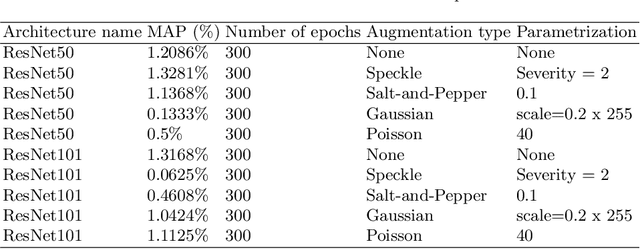
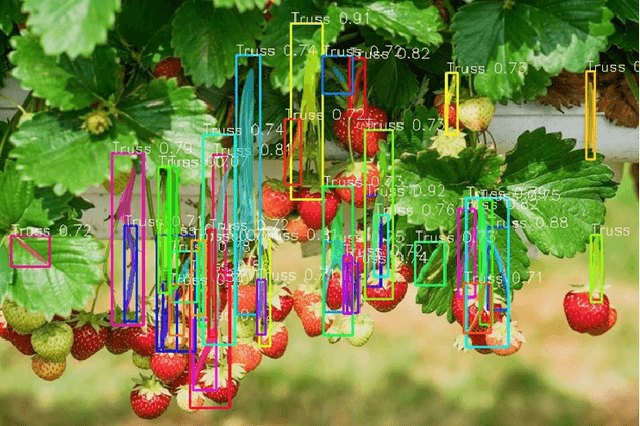
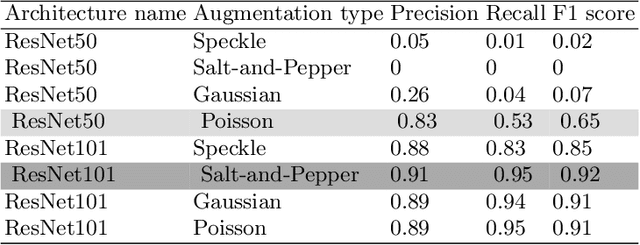
Abstract:The use of artificial intelligence in the agricultural sector has been growing at a rapid rate to automate farming activities. Emergent farming technologies focus on mapping and classification of plants, fruits, diseases, and soil types. Although, assisted harvesting and pruning applications using deep learning algorithms are in the early development stages, there is a demand for solutions to automate such processes. This paper proposes the use of Deep Learning for the classification of trusses and runners of strawberry plants using semantic segmentation and dataset augmentation. The proposed approach is based on the use of noises (i.e. Gaussian, Speckle, Poisson and Salt-and-Pepper) to artificially augment the dataset and compensate the low number of data samples and increase the overall classification performance. The results are evaluated using mean average of precision, recall and F1 score. The proposed approach achieved 91\%, 95\% and 92\% on precision, recall and F1 score, respectively, for truss detection using the ResNet101 with dataset augmentation utilising Salt-and-Pepper noise; and 83\%, 53\% and 65\% on precision, recall and F1 score, respectively, for truss detection using the ResNet50 with dataset augmentation utilising Poisson noise.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge