Daniel Davison
Usability of a Robot's Realistic Facial Expressions and Peripherals in Autistic Children's Therapy
Jul 23, 2020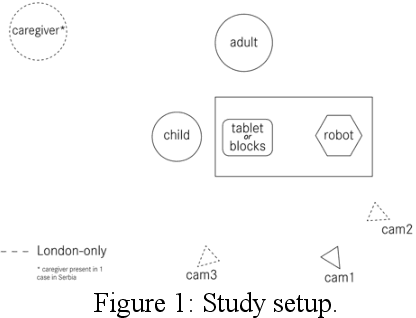



Abstract:Robot-assisted therapy is an emerging form of therapy for autistic children, although designing effective robot behaviors is a challenge for effective implementation of such therapy. A series of usability tests assessed trends in the effectiveness of modelling a robot's facial expressions on realistic facial expressions and of adding peripherals enabling child-led control of emotion learning activities with autistic children. Nineteen autistic children interacted with a small humanoid robot and an adult therapist in several emotion-learning activities that featured realistic facial expressions modelled on either a pre-existing database or live facial mirroring, and that used peripherals (tablets or tangible 'squishies') to enable child-led activities. Both types of realistic facial expressions by the robot were less effective than exaggerated expressions, with the mirroring being unintuitive for children. The tablet was usable but required more feedback and lower latency, while the tactile tangibles were engaging aids.
Physical extracurricular activities in educational child-robot interaction
Jun 08, 2016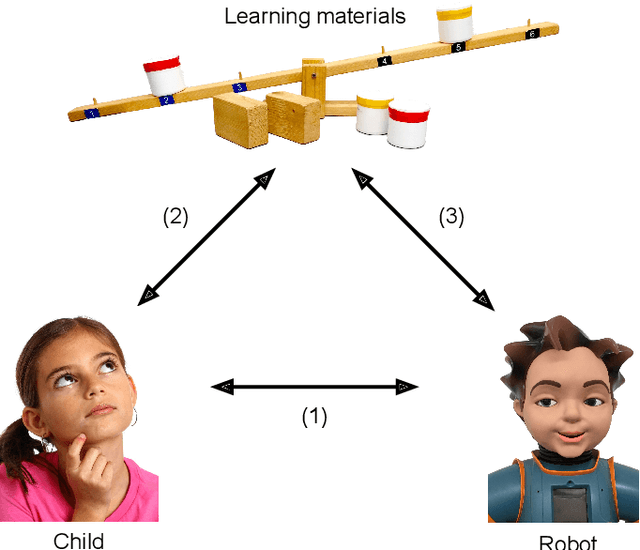
Abstract:In an exploratory study on educational child-robot interaction we investigate the effect of alternating a learning activity with an additional shared activity. Our aim is to enhance and enrich the relationship between child and robot by introducing "physical extracurricular activities". This enriched relationship might ultimately influence the way the child and robot interact with the learning material. We use qualitative measurement techniques to evaluate the effect of the additional activity on the child-robot relationship. We also explore how these metrics can be integrated in a highly exploratory cumulative score for the relationship between child and robot. This cumulative score suggests a difference in the overall child-robot relationship between children who engage in a physical extracurricular activity with the robot, and children who only engage in the learning activity with the robot.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge