Cosmin Bonchis
Mechanism Design With Predictions for Obnoxious Facility Location
Dec 19, 2022


Abstract:We study mechanism design with predictions for the obnoxious facility location problem. We present deterministic strategyproof mechanisms that display tradeoffs between robustness and consistency on segments, squares, circles and trees. All these mechanisms are actually group strategyproof, with the exception of the case of squares, where manipulations from coalitions of two agents exist. We prove that these tradeoffs are optimal in the 1-dimensional case.
Dilated filters for edge detection algorithms
Jun 14, 2021

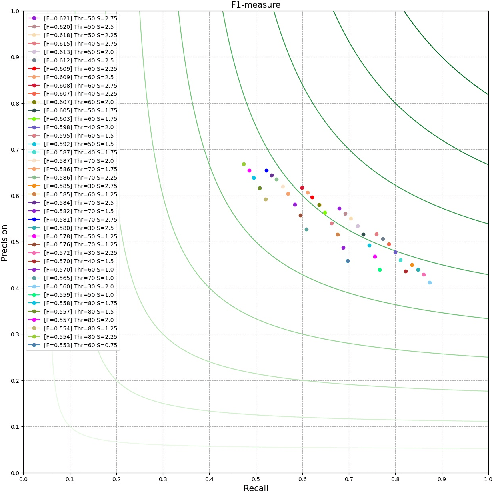
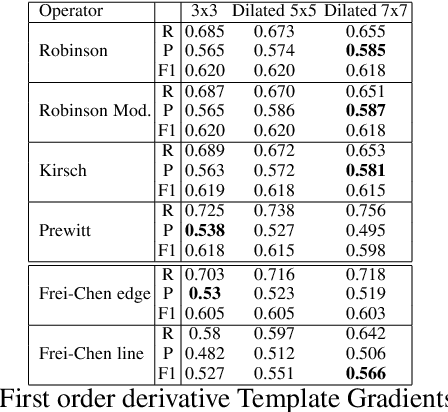
Abstract:Edges are a basic and fundamental feature in image processing, that are used directly or indirectly in huge amount of applications. Inspired by the expansion of image resolution and processing power dilated convolution techniques appeared. Dilated convolution have impressive results in machine learning, we discuss here the idea of dilating the standard filters which are used in edge detection algorithms. In this work we try to put together all our previous and current results by using instead of the classical convolution filters a dilated one. We compare the results of the edge detection algorithms using the proposed dilation filters with original filters or custom variants. Experimental results confirm our statement that dilation of filters have positive impact for edge detection algorithms form simple to rather complex algorithms.
It's Not Whom You Know, It's What You Can Do: Succint Coalitional Frameworks for Network Centralities
Sep 24, 2019
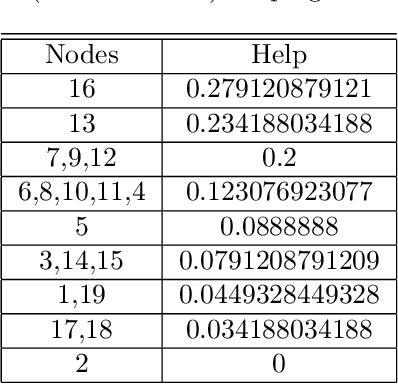
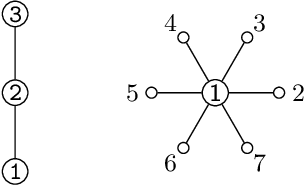
Abstract:We investigate the representation of measures of network centrality using a framework that blends a social network representation with the succint formalism of cooperative skill games. We discuss the expressiveness of the new framework and highlight some of its advantages, including a fixed-parameter tractability result for computing centrality measures under such representations. As an application we introduce new network centrality measures that capture the extent to which neighbors of a certain node can help it complete relevant tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge