Christopher Angelini
Dynamic Continual Learning: Harnessing Parameter Uncertainty for Improved Network Adaptation
Jan 18, 2025Abstract:When fine-tuning Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) to new data, DNNs are prone to overwriting network parameters required for task-specific functionality on previously learned tasks, resulting in a loss of performance on those tasks. We propose using parameter-based uncertainty to determine which parameters are relevant to a network's learned function and regularize training to prevent change in these important parameters. We approach this regularization in two ways: (1), we constrain critical parameters from significant changes by associating more critical parameters with lower learning rates, thereby limiting alterations in those parameters; (2), important parameters are restricted from change by imposing a higher regularization weighting, causing parameters to revert to their states prior to the learning of subsequent tasks. We leverage a Bayesian Moment Propagation framework which learns network parameters concurrently with their associated uncertainties while allowing each parameter to contribute uncertainty to the network's predictive distribution, avoiding the pitfalls of existing sampling-based methods. The proposed approach is evaluated for common sequential benchmark datasets and compared to existing published approaches from the Continual Learning community. Ultimately, we show improved Continual Learning performance for Average Test Accuracy and Backward Transfer metrics compared to sampling-based methods and other non-uncertainty-based approaches.
* 8 pages, 2 figures
Variational Density Propagation Continual Learning
Aug 22, 2023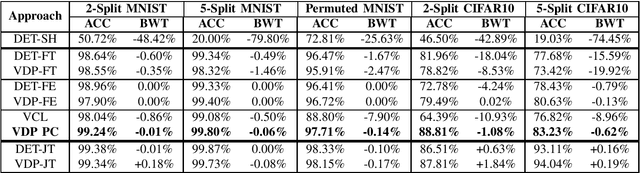
Abstract:Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) deployed to the real world are regularly subject to out-of-distribution (OoD) data, various types of noise, and shifting conceptual objectives. This paper proposes a framework for adapting to data distribution drift modeled by benchmark Continual Learning datasets. We develop and evaluate a method of Continual Learning that leverages uncertainty quantification from Bayesian Inference to mitigate catastrophic forgetting. We expand on previous approaches by removing the need for Monte Carlo sampling of the model weights to sample the predictive distribution. We optimize a closed-form Evidence Lower Bound (ELBO) objective approximating the predictive distribution by propagating the first two moments of a distribution, i.e. mean and covariance, through all network layers. Catastrophic forgetting is mitigated by using the closed-form ELBO to approximate the Minimum Description Length (MDL) Principle, inherently penalizing changes in the model likelihood by minimizing the KL Divergence between the variational posterior for the current task and the previous task's variational posterior acting as the prior. Leveraging the approximation of the MDL principle, we aim to initially learn a sparse variational posterior and then minimize additional model complexity learned for subsequent tasks. Our approach is evaluated for the task incremental learning scenario using density propagated versions of fully-connected and convolutional neural networks across multiple sequential benchmark datasets with varying task sequence lengths. Ultimately, this procedure produces a minimally complex network over a series of tasks mitigating catastrophic forgetting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge