Get our free extension to see links to code for papers anywhere online!Free add-on: code for papers everywhere!Free add-on: See code for papers anywhere!
Chris Schneider
Autonomous Fault Detection in Self-Healing Systems using Restricted Boltzmann Machines
Jan 07, 2015Figures and Tables: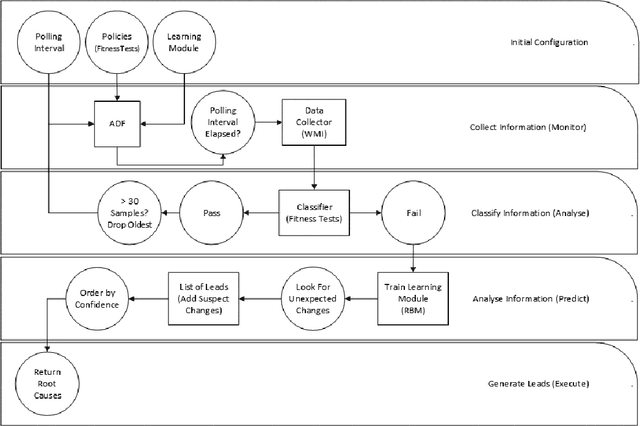
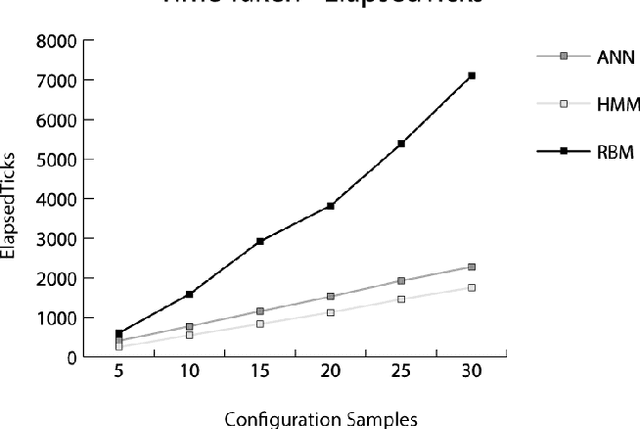
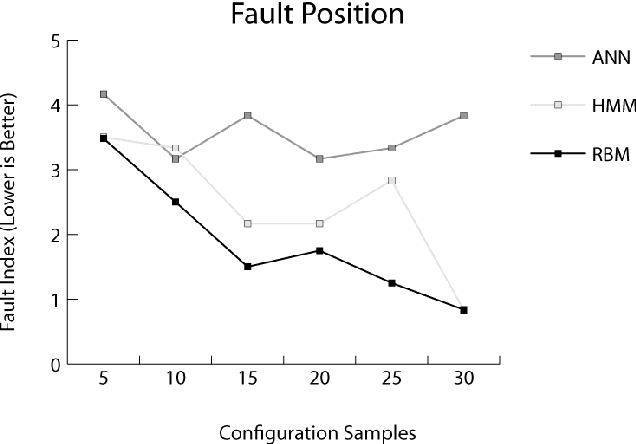
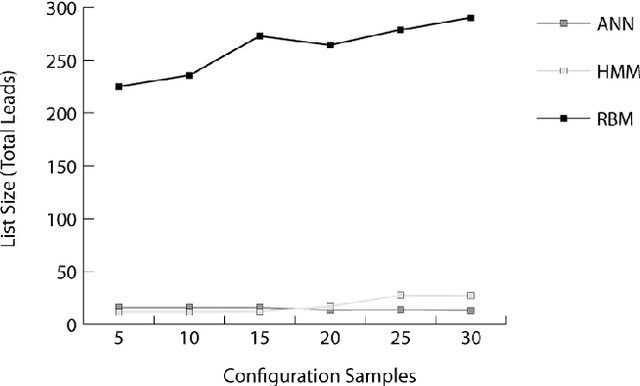




Abstract:Autonomously detecting and recovering from faults is one approach for reducing the operational complexity and costs associated with managing computing environments. We present a novel methodology for autonomously generating investigation leads that help identify systems faults, and extends our previous work in this area by leveraging Restricted Boltzmann Machines (RBMs) and contrastive divergence learning to analyse changes in historical feature data. This allows us to heuristically identify the root cause of a fault, and demonstrate an improvement to the state of the art by showing feature data can be predicted heuristically beyond a single instance to include entire sequences of information.
* Published and presented in the 11th IEEE International Conference and
Workshops on Engineering of Autonomic and Autonomous Systems (EASe 2014)
Via
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge