Chase Zimmerman
Near-Term Advances in Quantum Natural Language Processing
Jun 05, 2022
Abstract:This paper describes experiments showing that some problems in natural language processing can already be addressed using quantum computers. The examples presented here include topic classification using both a quantum support vector machine and a bag-of-words approach, bigram modeling that can be applied to sequences of words and formal concepts, and ambiguity resolution in verb-noun composition. While the datasets used are still small, the systems described have been run on physical quantum computers. These implementations and their results are described along with the algorithms and mathematical approaches used.
Packet2Vec: Utilizing Word2Vec for Feature Extraction in Packet Data
Apr 29, 2020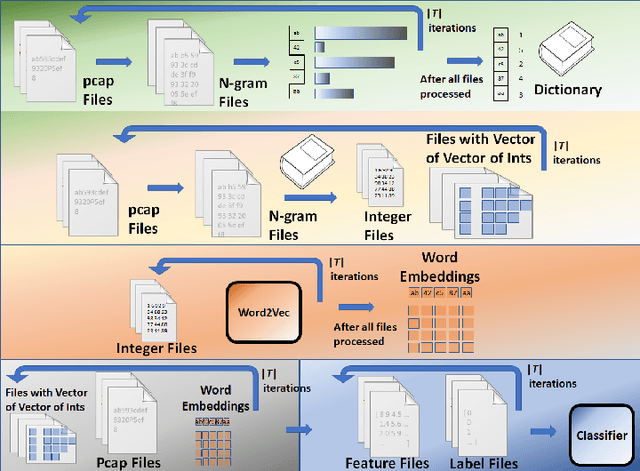

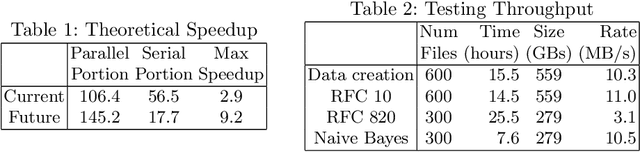

Abstract:One of deep learning's attractive benefits is the ability to automatically extract relevant features for a target problem from largely raw data, instead of utilizing human engineered and error prone handcrafted features. While deep learning has shown success in fields such as image classification and natural language processing, its application for feature extraction on raw network packet data for intrusion detection is largely unexplored. In this paper we modify a Word2Vec approach, used for text processing, and apply it to packet data for automatic feature extraction. We call this approach Packet2Vec. For the classification task of benign versus malicious traffic on a 2009 DARPA network data set, we obtain an area under the curve (AUC) of the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) between 0.988-0.996 and an AUC of the Precision/Recall curve between 0.604-0.667.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge