Charles-Henry Bertrand Van Ouytsel
Malware Analysis with Symbolic Execution and Graph Kernel
Apr 12, 2022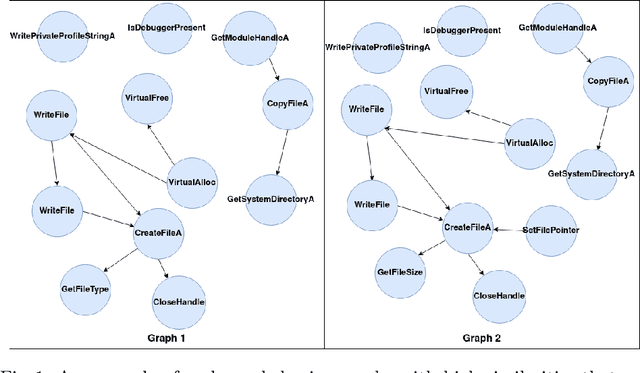

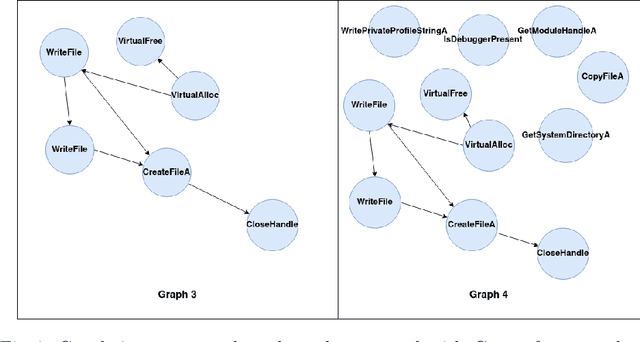
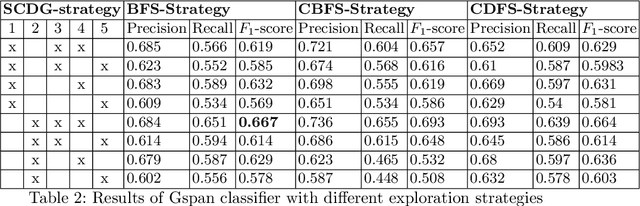
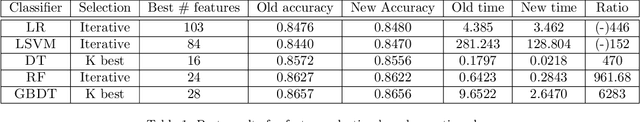
Abstract:Malware analysis techniques are divided into static and dynamic analysis. Both techniques can be bypassed by circumvention techniques such as obfuscation. In a series of works, the authors have promoted the use of symbolic executions combined with machine learning to avoid such traps. Most of those works rely on natural graph-based representations that can then be plugged into graph-based learning algorithms such as Gspan. There are two main problems with this approach. The first one is in the cost of computing the graph. Indeed, working with graphs requires one to compute and representing the entire state-space of the file under analysis. As such computation is too cumbersome, the techniques often rely on developing strategies to compute a representative subgraph of the behaviors. Unfortunately, efficient graph-building strategies remain weakly explored. The second problem is in the classification itself. Graph-based machine learning algorithms rely on comparing the biggest common structures. This sidelines small but specific parts of the malware signature. In addition, it does not allow us to work with efficient algorithms such as support vector machine. We propose a new efficient open source toolchain for machine learning-based classification. We also explore how graph-kernel techniques can be used in the process. We focus on the 1-dimensional Weisfeiler-Lehman kernel, which can capture local similarities between graphs. Our experimental results show that our approach outperforms existing ones by an impressive factor.
Analysis of Machine Learning Approaches to Packing Detection
May 02, 2021
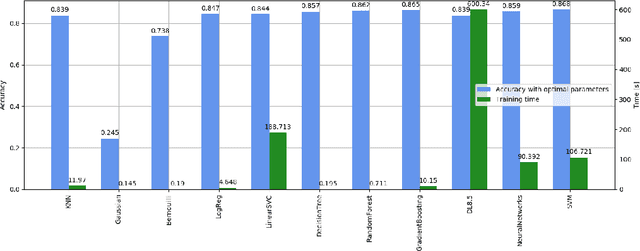

Abstract:Packing is an obfuscation technique widely used by malware to hide the content and behavior of a program. Much prior research has explored how to detect whether a program is packed. This research includes a broad variety of approaches such as entropy analysis, syntactic signatures and more recently machine learning classifiers using various features. However, no robust results have indicated which algorithms perform best, or which features are most significant. This is complicated by considering how to evaluate the results since accuracy, cost, generalization capabilities, and other measures are all reasonable. This work explores eleven different machine learning approaches using 119 features to understand: which features are most significant for packing detection; which algorithms offer the best performance; and which algorithms are most economical.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge