Changshan Li
MDSF: Context-Aware Multi-Dimensional Data Storytelling Framework based on Large language Model
Jan 02, 2025



Abstract:The exponential growth of data and advancements in big data technologies have created a demand for more efficient and automated approaches to data analysis and storytelling. However, automated data analysis systems still face challenges in leveraging large language models (LLMs) for data insight discovery, augmented analysis, and data storytelling. This paper introduces the Multidimensional Data Storytelling Framework (MDSF) based on large language models for automated insight generation and context-aware storytelling. The framework incorporates advanced preprocessing techniques, augmented analysis algorithms, and a unique scoring mechanism to identify and prioritize actionable insights. The use of fine-tuned LLMs enhances contextual understanding and generates narratives with minimal manual intervention. The architecture also includes an agent-based mechanism for real-time storytelling continuation control. Key findings reveal that MDSF outperforms existing methods across various datasets in terms of insight ranking accuracy, descriptive quality, and narrative coherence. The experimental evaluation demonstrates MDSF's ability to automate complex analytical tasks, reduce interpretive biases, and improve user satisfaction. User studies further underscore its practical utility in enhancing content structure, conclusion extraction, and richness of detail.
GraphAD: A Graph Neural Network for Entity-Wise Multivariate Time-Series Anomaly Detection
May 23, 2022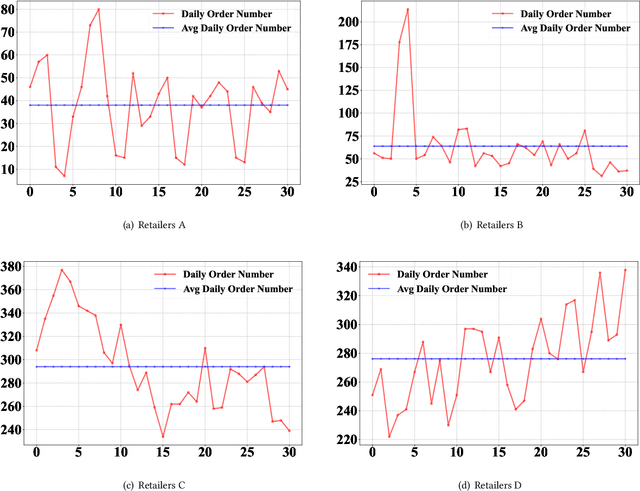
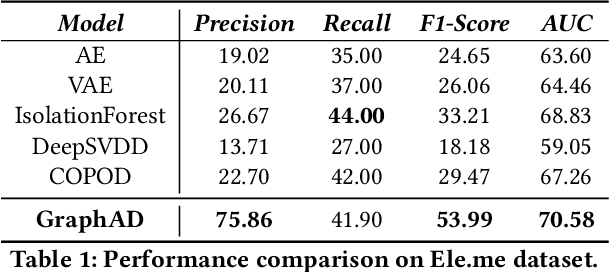
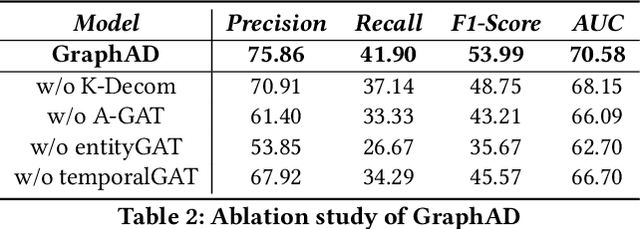
Abstract:In recent years, the emergence and development of third-party platforms have greatly facilitated the growth of the Online to Offline (O2O) business. However, the large amount of transaction data raises new challenges for retailers, especially anomaly detection in operating conditions. Thus, platforms begin to develop intelligent business assistants with embedded anomaly detection methods to reduce the management burden on retailers. Traditional time-series anomaly detection methods capture underlying patterns from the perspectives of time and attributes, ignoring the difference between retailers in this scenario. Besides, similar transaction patterns extracted by the platforms can also provide guidance to individual retailers and enrich their available information without privacy issues. In this paper, we pose an entity-wise multivariate time-series anomaly detection problem that considers the time-series of each unique entity. To address this challenge, we propose GraphAD, a novel multivariate time-series anomaly detection model based on the graph neural network. GraphAD decomposes the Key Performance Indicator (KPI) into stable and volatility components and extracts their patterns in terms of attributes, entities and temporal perspectives via graph neural networks. We also construct a real-world entity-wise multivariate time-series dataset from the business data of Ele.me. The experimental results on this dataset show that GraphAD significantly outperforms existing anomaly detection methods.
HIE-SQL: History Information Enhanced Network for Context-Dependent Text-to-SQL Semantic Parsing
Apr 02, 2022



Abstract:Recently, context-dependent text-to-SQL semantic parsing which translates natural language into SQL in an interaction process has attracted a lot of attention. Previous works leverage context-dependence information either from interaction history utterances or the previous predicted SQL queries but fail in taking advantage of both since of the mismatch between natural language and logic-form SQL. In this work, we propose a History Information Enhanced text-to-SQL model (HIE-SQL) to exploit context-dependence information from both history utterances and the last predicted SQL query. In view of the mismatch, we treat natural language and SQL as two modalities and propose a bimodal pre-trained model to bridge the gap between them. Besides, we design a schema-linking graph to enhance connections from utterances and the SQL query to the database schema. We show our history information enhanced methods improve the performance of HIE-SQL by a significant margin, which achieves new state-of-the-art results on the two context-dependent text-to-SQL benchmarks, the SparC and CoSQL datasets, at the writing time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge