Catherine M. Foley
Fine-Grained Counting with Crowd-Sourced Supervision
May 30, 2022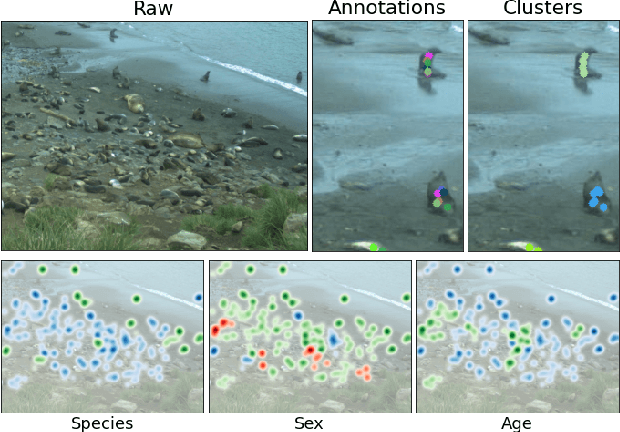
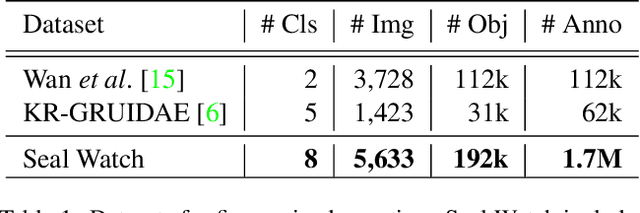

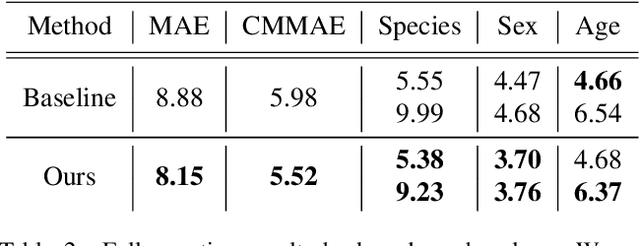
Abstract:Crowd-sourcing is an increasingly popular tool for image analysis in animal ecology. Computer vision methods that can utilize crowd-sourced annotations can help scale up analysis further. In this work we study the potential to do so on the challenging task of fine-grained counting. As opposed to the standard crowd counting task, fine-grained counting also involves classifying attributes of individuals in dense crowds. We introduce a new dataset from animal ecology to enable this study that contains 1.7M crowd-sourced annotations of 8 fine-grained classes. It is the largest available dataset for fine-grained counting and the first to enable the study of the task with crowd-sourced annotations. We introduce methods for generating aggregate "ground truths" from the collected annotations, as well as a counting method that can utilize the aggregate information. Our method improves results by 8% over a comparable baseline, indicating the potential for algorithms to learn fine-grained counting using crowd-sourced supervision.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge