Carsten Spehr
Enhancing Aeroacoustic Wind Tunnel Studies through Massive Channel Upscaling with MEMS Microphones
May 06, 2024Abstract:This paper presents a large 6~m x 3~m aperture 7200 MEMS microphone array. The array is designed so that sub-arrays with optimized point spread functions can be used for beamforming and thus, enable the research of source directivity in wind tunnel facilities. The total array consists of modular 800 microphone panels, each consisting of four unique PCB board designs. This modular architecture allows for the time-synchronized measurement of an arbitrary number of panels and thus, aperture size and total number of sensors. The panels can be installed without a gap so that the array's microphone pattern avoids high sidelobes in the point spread function. The array's capabilities are evaluated on a 1:9.5 airframe half model in an open wind tunnel at DNW-NWB. The total source emission is quantified and the directivity is evaluated with beamforming. Additional far-field microphones are employed to validate the results.
Aeroacoustic testing on a full aircraft model at high Reynolds numbers in the European Transonic Windtunnel
Jul 11, 2023Abstract:This paper presents an end-to-end approach for the assessment of pressurized and cryogenic wind tunnel measurements of an EMBRAER scaled full model close to real-world Reynolds numbers. The choice of microphones, measurement parameters, the design of the array, and the selection of flow parameters are discussed. Different wind tunnel conditions are proposed which allow separating the influence of the Reynolds number from the Mach number, as well as the influence of slotted and closed test sections. The paper provides three-dimensional beamforming results with CLEAN-SC deconvolution, the selection of regions of interest, and the corresponding source spectra. The results suggest that slotted test sections have little influence on the beamforming results compared to closed test sections and that the Reynolds number has a profound, non-linear impact on the aeroacoustic emission that lessens with increasing Reynolds number. Further, sources show a non-linear Mach number dependency at constant Reynolds number but are self-similar in the observed Mach number range. The findings suggest that it is possible to study real-world phenomena on small-scale full models at real-world Reynolds numbers, which enable further investigations in the future such as the directivity of sources.
Automatic source localization and spectra generation from deconvolved beamforming maps
Dec 16, 2020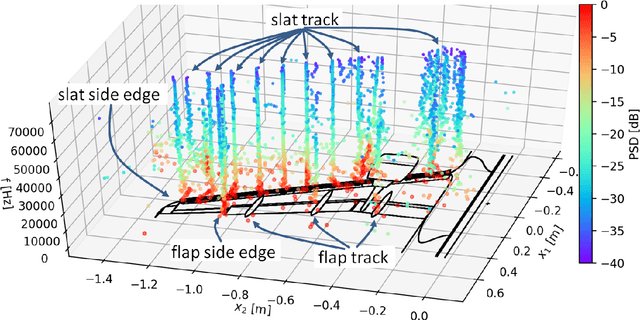
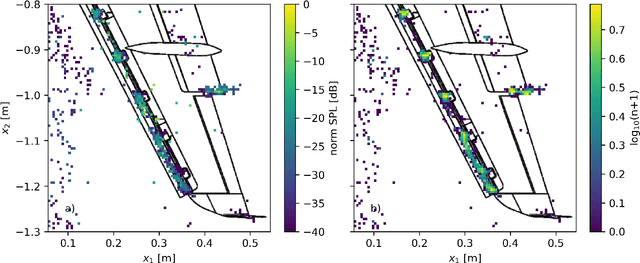
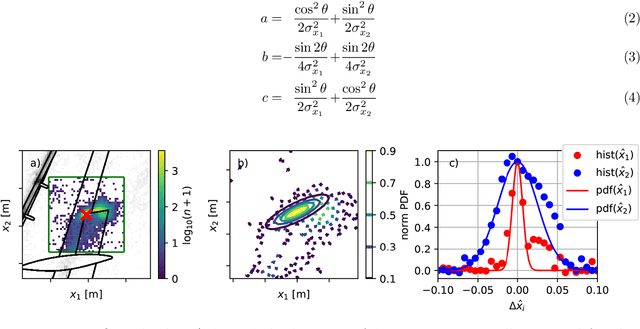
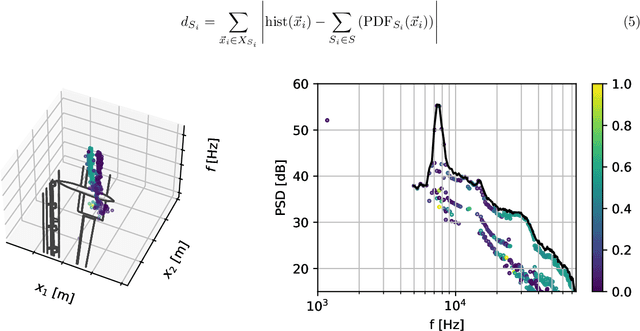
Abstract:We present two methods for the automated detection of aeroacoustic source positions in deconvolved beamforming maps and the extraction of their corresponding spectra. We evaluate these methods on two scaled airframe half-model wind-tunnel measurements. The first relies on the spatial normal distribution of aeroacoustic broadband sources in CLEAN-SC maps. The second uses hierarchical clustering methods. Both methods predict a spatial probability estimation based on which aeroacoustic spectra are generated.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge