Carlos Mencía
University of Oviedo, Spain
The Sets of Power
Oct 10, 2024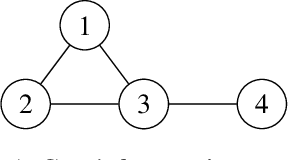
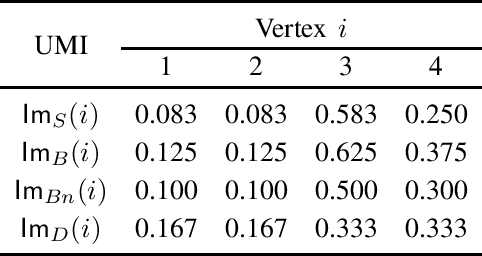
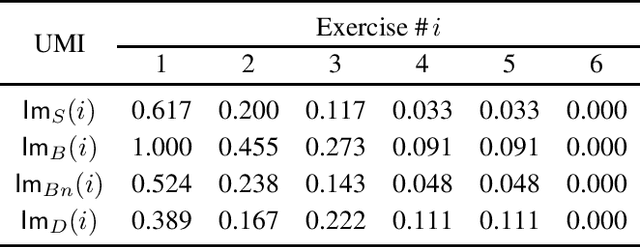
Abstract:Measures of voting power have been the subject of extensive research since the mid 1940s. More recently, similar measures of relative importance have been studied in other domains that include inconsistent knowledge bases, intensity of attacks in argumentation, different problems in the analysis of database management, and explainability. This paper demonstrates that all these examples are instantiations of computing measures of importance for a rather more general problem domain. The paper then shows that the best-known measures of importance can be computed for any reference set whenever one is given a monotonically increasing predicate that partitions the subsets of that reference set. As a consequence, the paper also proves that measures of importance can be devised in several domains, for some of which such measures have not yet been studied nor proposed. Furthermore, the paper highlights several research directions related with computing measures of importance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge