Carlos M. Lorenzetti
Métodos para la Selección y el Ajuste de Características en el Problema de la Detección de Spam
Oct 14, 2010Abstract:The email is used daily by millions of people to communicate around the globe and it is a mission-critical application for many businesses. Over the last decade, unsolicited bulk email has become a major problem for email users. An overwhelming amount of spam is flowing into users' mailboxes daily. In 2004, an estimated 62% of all email was attributed to spam. Spam is not only frustrating for most email users, it strains the IT infrastructure of organizations and costs businesses billions of dollars in lost productivity. In recent years, spam has evolved from an annoyance into a serious security threat, and is now a prime medium for phishing of sensitive information, as well the spread of malicious software. This work presents a first approach to attack the spam problem. We propose an algorithm that will improve a classifier's results by adjusting its training set data. It improves the document's vocabulary representation by detecting good topic descriptors and discriminators.
* 5 pages, 1 figure, Workshop de Investigadores en Ciencias de la Computaci\'{o}n, WICC 2010, pp 48-52
Learning Better Context Characterizations: An Intelligent Information Retrieval Approach
Apr 27, 2010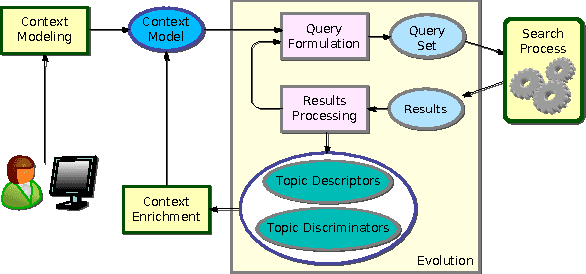
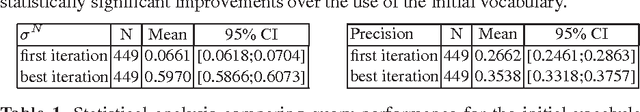
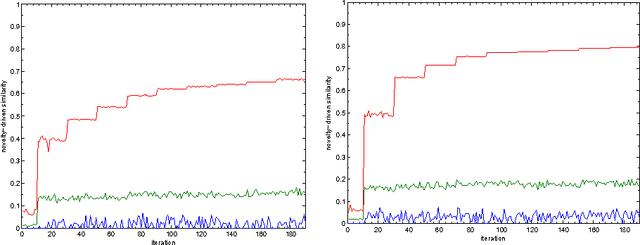
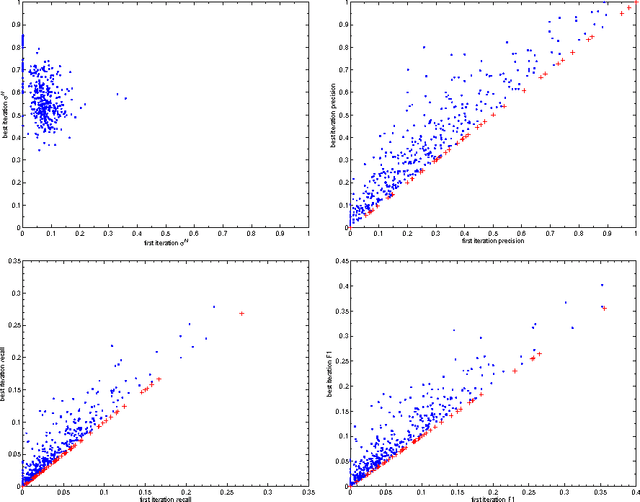
Abstract:This paper proposes an incremental method that can be used by an intelligent system to learn better descriptions of a thematic context. The method starts with a small number of terms selected from a simple description of the topic under analysis and uses this description as the initial search context. Using these terms, a set of queries are built and submitted to a search engine. New documents and terms are used to refine the learned vocabulary. Evaluations performed on a large number of topics indicate that the learned vocabulary is much more effective than the original one at the time of constructing queries to retrieve relevant material.
* 10 pages, 3 figures, CLEI 2008
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge