Carlos Enrique Gutierrez
MarmoNet: a pipeline for automated projection mapping of the common marmoset brain from whole-brain serial two-photon tomography
Aug 02, 2019


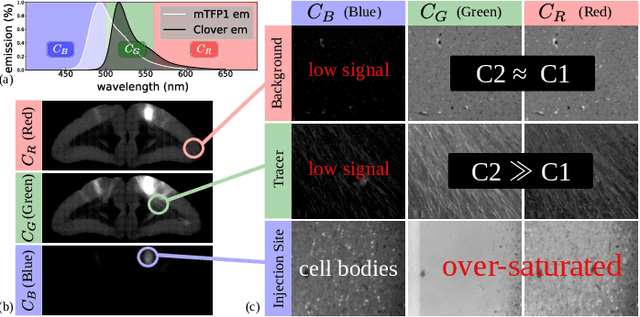
Abstract:Understanding the connectivity in the brain is an important prerequisite for understanding how the brain processes information. In the Brain/MINDS project, a connectivity study on marmoset brains uses two-photon microscopy fluorescence images of axonal projections to collect the neuron connectivity from defined brain regions at the mesoscopic scale. The processing of the images requires the detection and segmentation of the axonal tracer signal. The objective is to detect as much tracer signal as possible while not misclassifying other background structures as the signal. This can be challenging because of imaging noise, a cluttered image background, distortions or varying image contrast cause problems. We are developing MarmoNet, a pipeline that processes and analyzes tracer image data of the common marmoset brain. The pipeline incorporates state-of-the-art machine learning techniques based on artificial convolutional neural networks (CNN) and image registration techniques to extract and map all relevant information in a robust manner. The pipeline processes new images in a fully automated way. This report introduces the current state of the tracer signal analysis part of the pipeline.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge