Bruno Taillé
Contextualization and Generalization in Entity and Relation Extraction
Jun 15, 2022



Abstract:During the past decade, neural networks have become prominent in Natural Language Processing (NLP), notably for their capacity to learn relevant word representations from large unlabeled corpora. These word embeddings can then be transferred and finetuned for diverse end applications during a supervised training phase. More recently, in 2018, the transfer of entire pretrained Language Models and the preservation of their contextualization capacities enabled to reach unprecedented performance on virtually every NLP benchmark, sometimes even outperforming human baselines. However, as models reach such impressive scores, their comprehension abilities still appear as shallow, which reveal limitations of benchmarks to provide useful insights on their factors of performance and to accurately measure understanding capabilities. In this thesis, we study the behaviour of state-of-the-art models regarding generalization to facts unseen during training in two important Information Extraction tasks: Named Entity Recognition (NER) and Relation Extraction (RE). Indeed, traditional benchmarks present important lexical overlap between mentions and relations used for training and evaluating models, whereas the main interest of Information Extraction is to extract previously unknown information. We propose empirical studies to separate performance based on mention and relation overlap with the training set and find that pretrained Language Models are mainly beneficial to detect unseen mentions, in particular out-of-domain. While this makes them suited for real use cases, there is still a gap in performance between seen and unseen mentions that hurts generalization to new facts. In particular, even state-of-the-art ERE models rely on a shallow retention heuristic, basing their prediction more on arguments surface forms than context.
Separating Retention from Extraction in the Evaluation of End-to-end Relation Extraction
Sep 24, 2021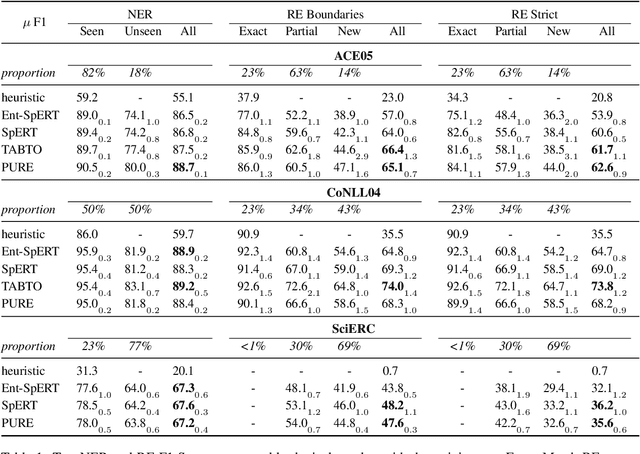
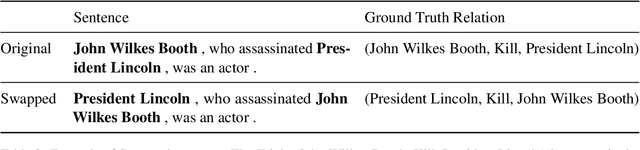
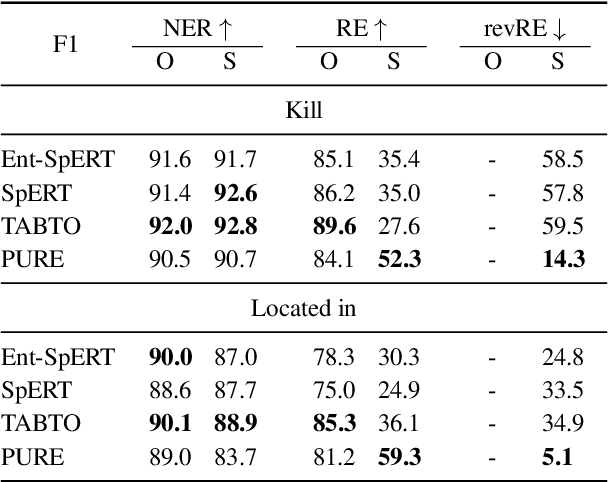
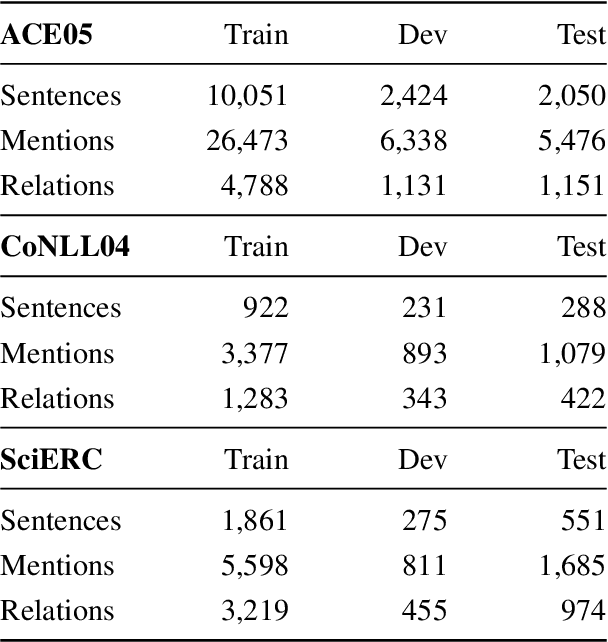
Abstract:State-of-the-art NLP models can adopt shallow heuristics that limit their generalization capability (McCoy et al., 2019). Such heuristics include lexical overlap with the training set in Named-Entity Recognition (Taill\'e et al., 2020) and Event or Type heuristics in Relation Extraction (Rosenman et al., 2020). In the more realistic end-to-end RE setting, we can expect yet another heuristic: the mere retention of training relation triples. In this paper, we propose several experiments confirming that retention of known facts is a key factor of performance on standard benchmarks. Furthermore, one experiment suggests that a pipeline model able to use intermediate type representations is less prone to over-rely on retention.
Let's Stop Incorrect Comparisons in End-to-end Relation Extraction!
Sep 22, 2020



Abstract:Despite efforts to distinguish three different evaluation setups (Bekoulis et al., 2018), numerous end-to-end Relation Extraction (RE) articles present unreliable performance comparison to previous work. In this paper, we first identify several patterns of invalid comparisons in published papers and describe them to avoid their propagation. We then propose a small empirical study to quantify the impact of the most common mistake and evaluate it leads to overestimating the final RE performance by around 5% on ACE05. We also seize this opportunity to study the unexplored ablations of two recent developments: the use of language model pretraining (specifically BERT) and span-level NER. This meta-analysis emphasizes the need for rigor in the report of both the evaluation setting and the datasets statistics and we call for unifying the evaluation setting in end-to-end RE.
Contextualized Embeddings in Named-Entity Recognition: An Empirical Study on Generalization
Jan 22, 2020



Abstract:Contextualized embeddings use unsupervised language model pretraining to compute word representations depending on their context. This is intuitively useful for generalization, especially in Named-Entity Recognition where it is crucial to detect mentions never seen during training. However, standard English benchmarks overestimate the importance of lexical over contextual features because of an unrealistic lexical overlap between train and test mentions. In this paper, we perform an empirical analysis of the generalization capabilities of state-of-the-art contextualized embeddings by separating mentions by novelty and with out-of-domain evaluation. We show that they are particularly beneficial for unseen mentions detection, especially out-of-domain. For models trained on CoNLL03, language model contextualization leads to a +1.2% maximal relative micro-F1 score increase in-domain against +13% out-of-domain on the WNUT dataset
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge