Bruno Romeira
Optically-triggered deterministic spiking regimes in nanostructure resonant tunnelling diode-photodetectors
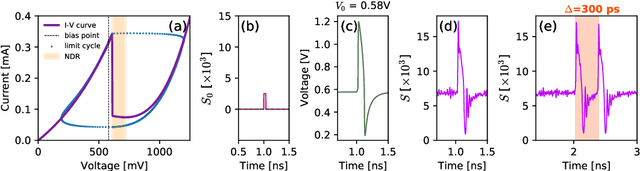
Apr 23, 2023Abstract:This work reports a nanostructure resonant tunnelling diode-photodetector (RTD-PD) device and demonstrates its operation as a controllable, optically-triggered excitable spike generator. The top contact layer of the device is designed with a nanopillar structure 500 nm in diameter) to restrain the injection current, yielding therefore lower energy operation for spike generation. We demonstrate experimentally the deterministic optical triggering of controllable and repeatable neuron-like spike patterns in the nanostructure RTD-PDs. Moreover, we show the device's ability to deliver spiking responses when biased in both regions adjacent to the negative differential conductance (NDC) region, the so-called 'peak' and 'valley' points of the current-voltage ($I$-$V$) characteristic. This work also demonstrates experimentally key neuron-like dynamical features in the nanostructure RTD-PD, such as a well-defined threshold (in input optical intensity) for spike firing, as well as the presence of spike firing refractory time. The optoelectronic and chip-scale character of the proposed system together with the deterministic, repeatable and well controllable nature of the optically-elicited spiking responses render this nanostructure RTD-PD element as a highly promising solution for high-speed, energy-efficient optoelectronic artificial spiking neurons for novel light-enabled neuromorphic computing hardware.
Artificial optoelectronic spiking neuron based on a resonant tunnelling diode coupled to a vertical cavity surface emitting laser
Jun 22, 2022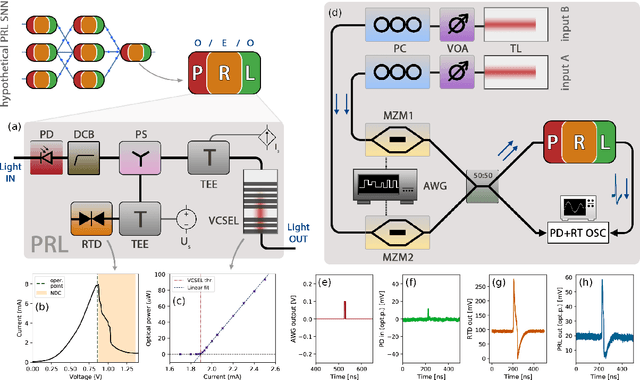
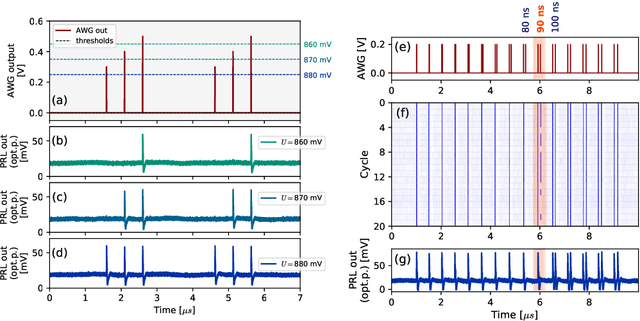
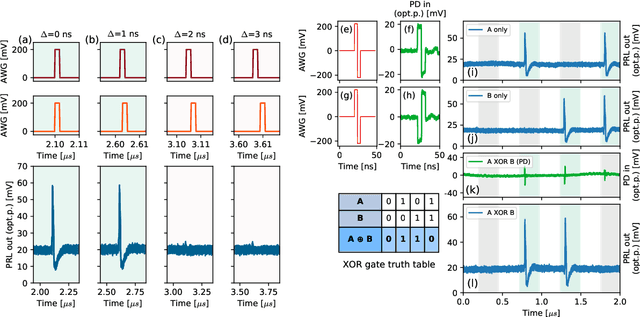
Abstract:Excitable optoelectronic devices represent one of the key building blocks for implementation of artificial spiking neurons in neuromorphic (brain-inspired) photonic systems. This work introduces and experimentally investigates an opto-electro-optical (O/E/O) artificial neuron built with a resonant tunnelling diode (RTD) coupled to a photodetector as a receiver and a vertical cavity surface emitting laser as a the transmitter. We demonstrate a well defined excitability threshold, above which this neuron produces 100 ns optical spiking responses with characteristic neural-like refractory period. We utilise its fan-in capability to perform in-device coincidence detection (logical AND) and exclusive logical OR (XOR) tasks. These results provide first experimental validation of deterministic triggering and tasks in an RTD-based spiking optoelectronic neuron with both input and output optical (I/O) terminals. Furthermore, we also investigate in theory the prospects of the proposed system for its nanophotonic implementation with a monolithic design combining a nanoscale RTD element and a nanolaser; therefore demonstrating the potential of integrated RTD-based excitable nodes for low footprint, high-speed optoelectronic spiking neurons in future neuromorphic photonic hardware.
Resonant tunnelling diode nano-optoelectronic spiking nodes for neuromorphic information processing
Jul 21, 2021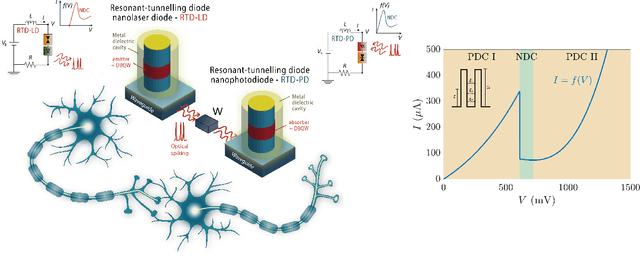
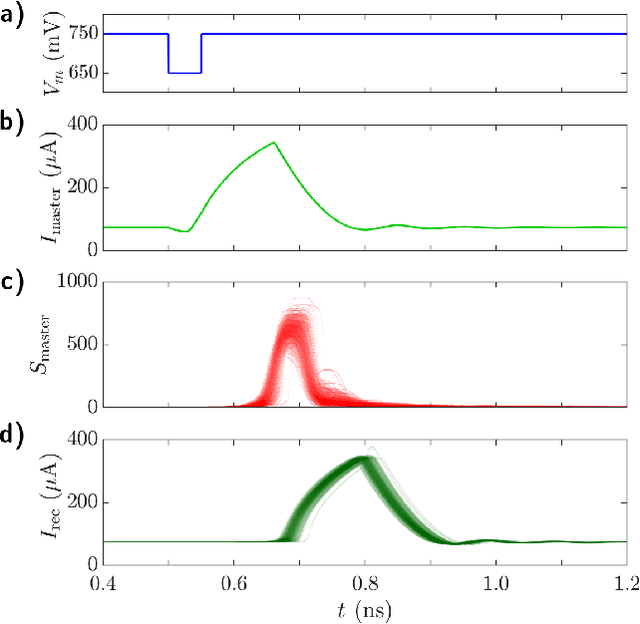
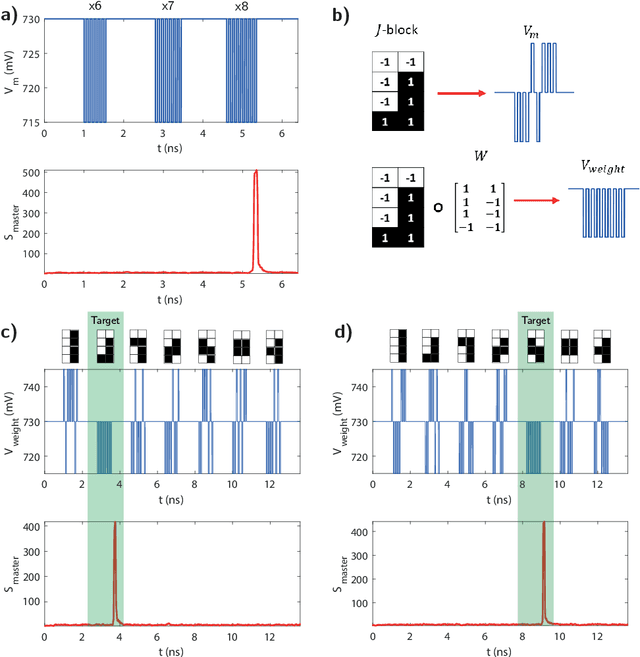
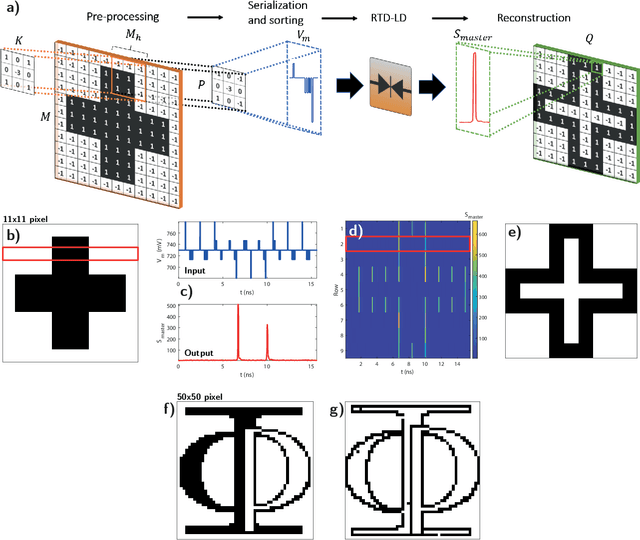
Abstract:In this work, we introduce an optoelectronic spiking artificial neuron capable of operating at ultrafast rates ($\approx$ 100 ps/optical spike) and with low energy consumption ($<$ pJ/spike). The proposed system combines an excitable resonant tunnelling diode (RTD) element exhibiting negative differential conductance, coupled to a nanoscale light source (forming a master node) or a photodetector (forming a receiver node). We study numerically the spiking dynamical responses and information propagation functionality of an interconnected master-receiver RTD node system. Using the key functionality of pulse thresholding and integration, we utilize a single node to classify sequential pulse patterns and perform convolutional functionality for image feature (edge) recognition. We also demonstrate an optically-interconnected spiking neural network model for processing of spatiotemporal data at over 10 Gbps with high inference accuracy. Finally, we demonstrate an off-chip supervised learning approach utilizing spike-timing dependent plasticity for the RTD-enabled photonic spiking neural network. These results demonstrate the potential and viability of RTD spiking nodes for low footprint, low energy, high-speed optoelectronic realization of neuromorphic hardware.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge