Brittany I. Davidson
Regulatory gray areas of LLM Terms
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly integrated into academic research pipelines; however, the Terms of Service governing their use remain under-examined. We present a comparative analysis of the Terms of Service of five major LLM providers (Anthropic, DeepSeek, Google, OpenAI, and xAI) collected in November 2025. Our analysis reveals substantial variation in the stringency and specificity of usage restrictions for general users and researchers. We identify specific complexities for researchers in security research, computational social sciences, and psychological studies. We identify `regulatory gray areas' where Terms of Service create uncertainty for legitimate use. We contribute a publicly available resource comparing terms across platforms (OSF) and discuss implications for general users and researchers navigating this evolving landscape.
The Accountability Paradox: How Platform API Restrictions Undermine AI Transparency Mandates
May 16, 2025Abstract:Recent application programming interface (API) restrictions on major social media platforms challenge compliance with the EU Digital Services Act [20], which mandates data access for algorithmic transparency. We develop a structured audit framework to assess the growing misalignment between regulatory requirements and platform implementations. Our comparative analysis of X/Twitter, Reddit, TikTok, and Meta identifies critical ``audit blind-spots'' where platform content moderation and algorithmic amplification remain inaccessible to independent verification. Our findings reveal an ``accountability paradox'': as platforms increasingly rely on AI systems, they simultaneously restrict the capacity for independent oversight. We propose targeted policy interventions aligned with the AI Risk Management Framework of the National Institute of Standards and Technology [80], emphasizing federated access models and enhanced regulatory enforcement.
Sentiment Analysis in Digital Spaces: An Overview of Reviews
Oct 30, 2023



Abstract:Sentiment analysis (SA) is commonly applied to digital textual data, revealing insight into opinions and feelings. Many systematic reviews have summarized existing work, but often overlook discussions of validity and scientific practices. Here, we present an overview of reviews, synthesizing 38 systematic reviews, containing 2,275 primary studies. We devise a bespoke quality assessment framework designed to assess the rigor and quality of systematic review methodologies and reporting standards. Our findings show diverse applications and methods, limited reporting rigor, and challenges over time. We discuss how future research and practitioners can address these issues and highlight their importance across numerous applications.
The Politics of Language Choice: How the Russian-Ukrainian War Influences Ukrainians' Language Use on Twitter
May 04, 2023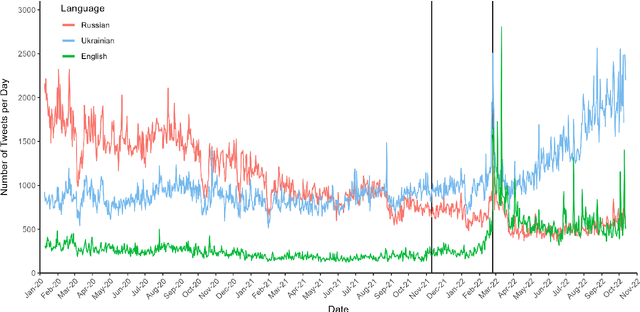
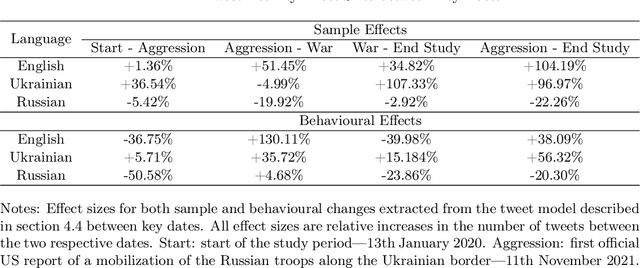
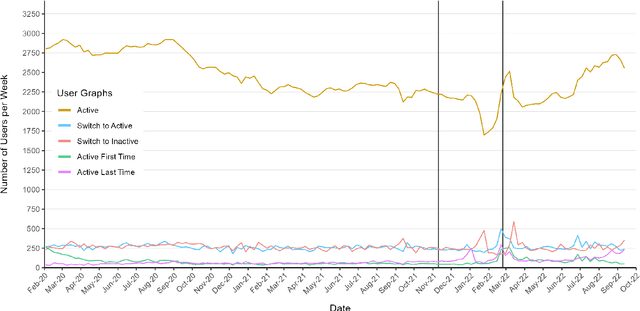
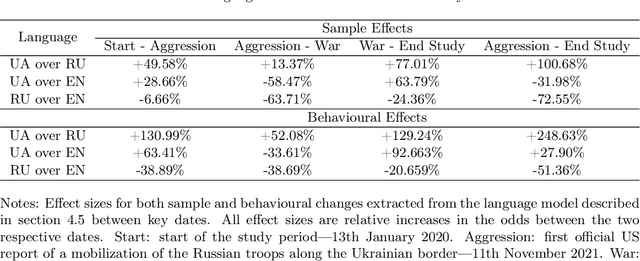
Abstract:The use of language is innately political and often a vehicle of cultural identity as well as the basis for nation building. Here, we examine language choice and tweeting activity of Ukrainian citizens based on more than 4 million geo-tagged tweets from over 62,000 users before and during the Russian-Ukrainian War, from January 2020 to October 2022. Using statistical models, we disentangle sample effects, arising from the in- and outflux of users on Twitter, from behavioural effects, arising from behavioural changes of the users. We observe a steady shift from the Russian language towards the Ukrainian language already before the war, which drastically speeds up with its outbreak. We attribute these shifts in large part to users' behavioural changes. Notably, we find that many Russian-tweeting users perform a hard-switch to Ukrainian as a result of the war.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge