Brandon Bennett
The performance of multiple language models in identifying offensive language on social media
Dec 10, 2023Abstract:Text classification is an important topic in the field of natural language processing. It has been preliminarily applied in information retrieval, digital library, automatic abstracting, text filtering, word semantic discrimination and many other fields. The aim of this research is to use a variety of algorithms to test the ability to identify offensive posts and evaluate their performance against a variety of assessment methods. The motivation for this project is to reduce the harm of these languages to human censors by automating the screening of offending posts. The field is a new one, and despite much interest in the past two years, there has been no focus on the object of the offence. Through the experiment of this project, it should inspire future research on identification methods as well as identification content.
Vagueness in Predicates and Objects
Feb 25, 2023

Abstract:Classical semantics assumes that one can model reference, predication and quantification with respect to a fixed domain of precise referent objects. Non-logical terms and quantification are then interpreted directly in terms of elements and subsets of this domain. We explore ways to generalise this classical picture of precise predicates and objects to account for variability of meaning due to factors such as vagueness, context and diversity of definitions or opinions. Both names and predicative expressions can be given either multiple semantic referents or be associated with semantic referents that incorporate some model of variability. We present a semantic framework, Variable Reference Semantics, that can accommodate several modes of variability in relation to both predicates and objects.
Tackling Domain-Specific Winograd Schemas with Knowledge-Based Reasoning and Machine Learning
Nov 24, 2020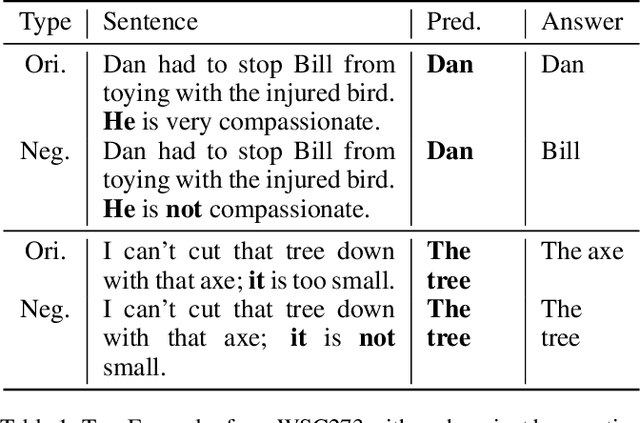
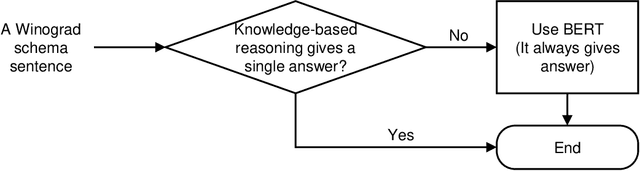

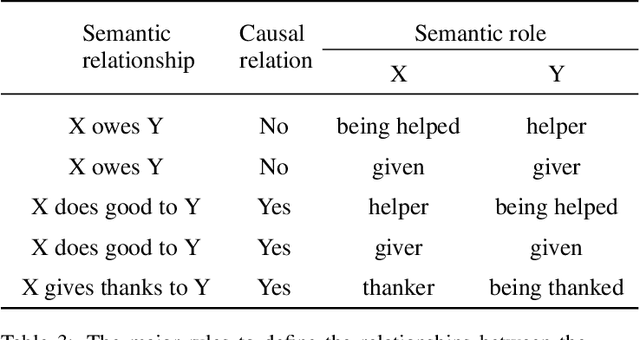
Abstract:The Winograd Schema Challenge (WSC) is a common-sense reasoning task that requires background knowledge. In this paper, we contribute to tackling WSC in four ways. Firstly, we suggest a keyword method to define a restricted domain where distinctive high-level semantic patterns can be found. A thanking domain was defined by key-words, and the data set in this domain is used in our experiments. Secondly, we develop a high-level knowledge-based reasoning method using semantic roles which is based on the method of Sharma [2019]. Thirdly, we propose an ensemble method to combine knowledge-based reasoning and machine learning which shows the best performance in our experiments. As a machine learning method, we used Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) [Kocijan et al., 2019]. Lastly, in terms of evaluation, we suggest a "robust" accuracy measurement by modifying that of Trichelair et al. [2018]. As with their switching method, we evaluate a model by considering its performance on trivial variants of each sentence in the test set.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge