Biliana Paskaleva
Non-intrusive data-driven model order reduction for circuits based on Hammerstein architectures
May 30, 2024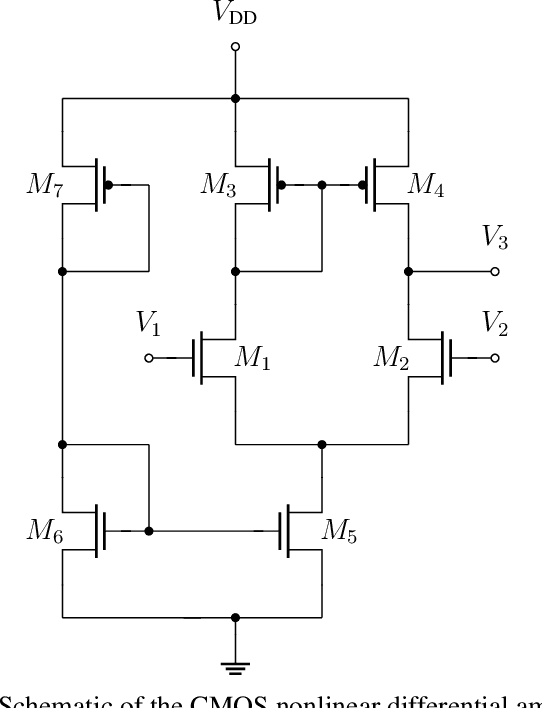
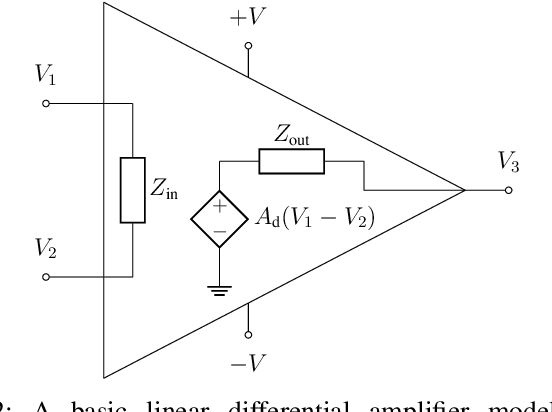
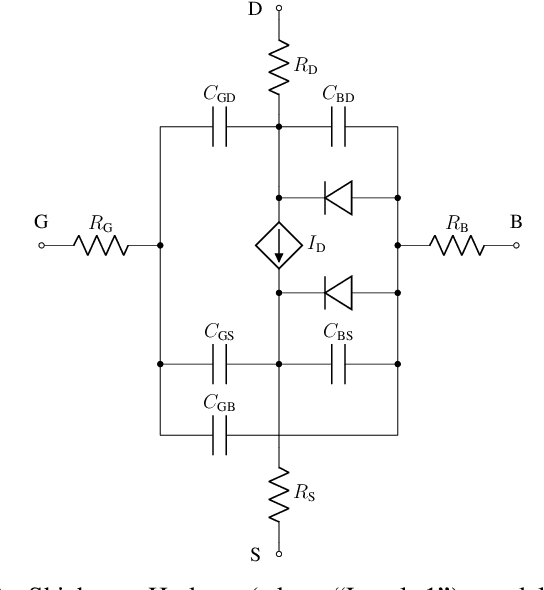
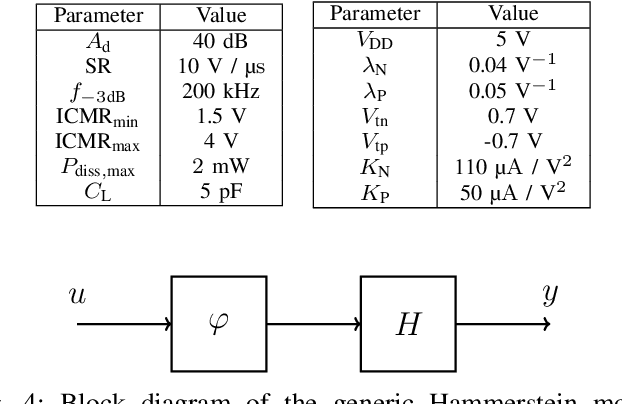
Abstract:We demonstrate that data-driven system identification techniques can provide a basis for effective, non-intrusive model order reduction (MOR) for common circuits that are key building blocks in microelectronics. Our approach is motivated by the practical operation of these circuits and utilizes a canonical Hammerstein architecture. To demonstrate the approach we develop a parsimonious Hammerstein model for a non-linear CMOS differential amplifier. We train this model on a combination of direct current (DC) and transient Spice (Xyce) circuit simulation data using a novel sequential strategy to identify the static nonlinear and linear dynamical parts of the model. Simulation results show that the Hammerstein model is an effective surrogate for the differential amplifier circuit that accurately and efficiently reproduces its behavior over a wide range of operating points and input frequencies.
Learning Compact Physics-Aware Delayed Photocurrent Models Using Dynamic Mode Decomposition
Aug 27, 2020



Abstract:Radiation-induced photocurrent in semiconductor devices can be simulated using complex physics-based models, which are accurate, but computationally expensive. This presents a challenge for implementing device characteristics in high-level circuit simulations where it is computationally infeasible to evaluate detailed models for multiple individual circuit elements. In this work we demonstrate a procedure for learning compact delayed photocurrent models that are efficient enough to implement in large-scale circuit simulations, but remain faithful to the underlying physics. Our approach utilizes Dynamic Mode Decomposition (DMD), a system identification technique for learning reduced order discrete-time dynamical systems from time series data based on singular value decomposition. To obtain physics-aware device models, we simulate the excess carrier density induced by radiation pulses by solving numerically the Ambipolar Diffusion Equation, then use the simulated internal state as training data for the DMD algorithm. Our results show that the significantly reduced order delayed photocurrent models obtained via this method accurately approximate the dynamics of the internal excess carrier density -- which can be used to calculate the induced current at the device boundaries -- while remaining compact enough to incorporate into larger circuit simulations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge