Benjamin Siebler
Empirical Fading Model and Bayesian Calibration for Multipath-Enhanced Device-Free Localization
May 11, 2022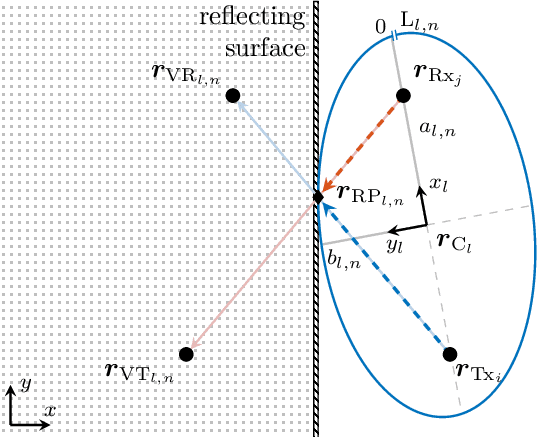
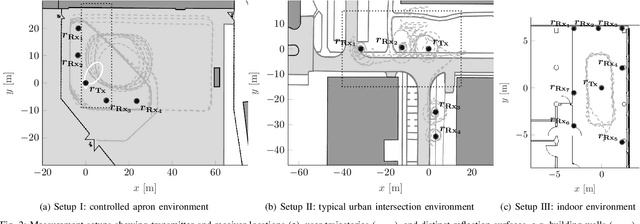
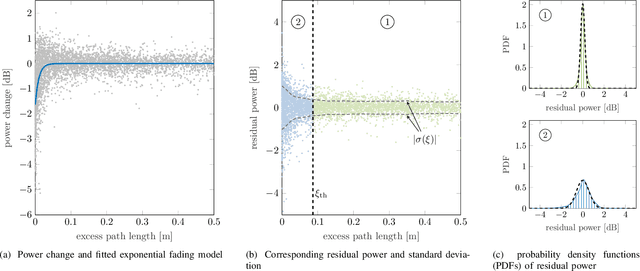
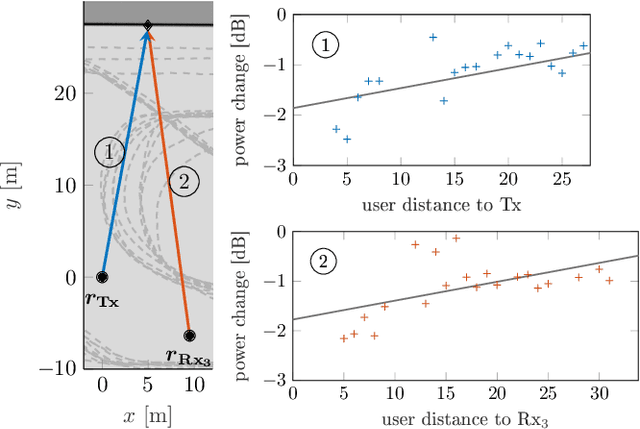
Abstract:The performance of multipath-enhanced device-free localization severely depends on the information about the propagation paths within the network. While known for the line-of-sight, the propagation paths have yet to be determined for multipath components. This work provides a novel Bayesian calibration approach for determining the propagation paths by estimating reflection points. Therefore, first a statistical fading model is presented, that describes user-induced changes in the received signal of multipath components. The model is derived and validated empirically using an extensive set of wideband and ultra-wideband measurement data. Second, the Bayesian approach is presented, which, based on the derived empirical fading model, relates measured changes in the power of a multipath component to the location of the reflection point. Exploiting the geometric properties of multipath components caused by single-bounce reflections, the solution space of possible locations of reflection points is constrained to the delay ellipse. Thus, a one-dimensional elliptic estimation problem can be formulated, which is solved using a point mass filter. The applicability of the proposed approach is demonstrated and evaluated based on measurement data. Independent of the underlying measurement system, the Bayesian calibration approach is shown to robustly estimate the locations of the reflection points in different environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge