Benjamin D. Shaffer
Structure-Preserving Learning Improves Geometry Generalization in Neural PDEs
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:We aim to develop physics foundation models for science and engineering that provide real-time solutions to Partial Differential Equations (PDEs) which preserve structure and accuracy under adaptation to unseen geometries. To this end, we introduce General-Geometry Neural Whitney Forms (Geo-NeW): a data-driven finite element method. We jointly learn a differential operator and compatible reduced finite element spaces defined on the underlying geometry. The resulting model is solved to generate predictions, while exactly preserving physical conservation laws through Finite Element Exterior Calculus. Geometry enters the model as a discretized mesh both through a transformer-based encoding and as the basis for the learned finite element spaces. This explicitly connects the underlying geometry and imposed boundary conditions to the solution, providing a powerful inductive bias for learning neural PDEs, which we demonstrate improves generalization to unseen domains. We provide a novel parameterization of the constitutive model ensuring the existence and uniqueness of the solution. Our approach demonstrates state-of-the-art performance on several steady-state PDE benchmarks, and provides a significant improvement over conventional baselines on out-of-distribution geometries.
Spectrally Informed Learning of Fluid Flows
Aug 26, 2024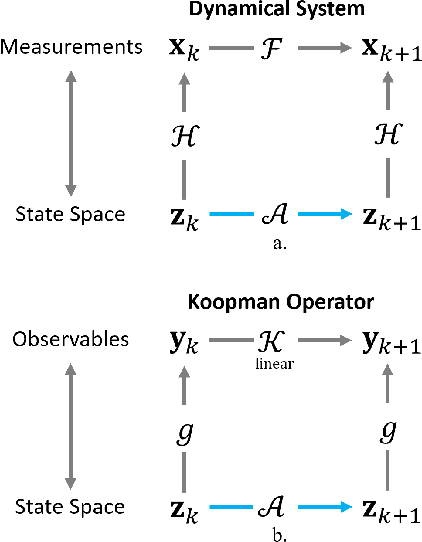
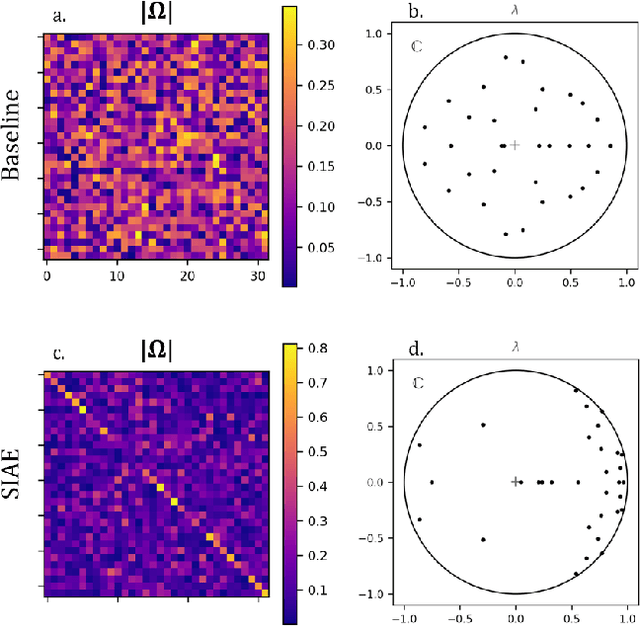
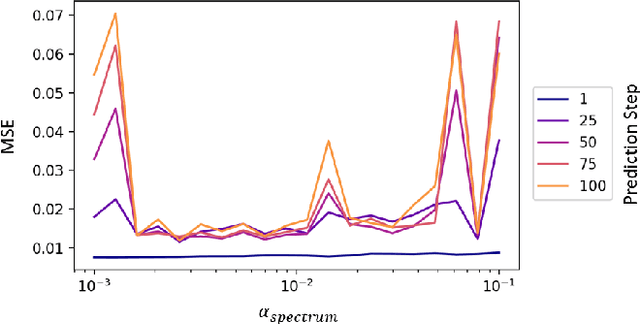
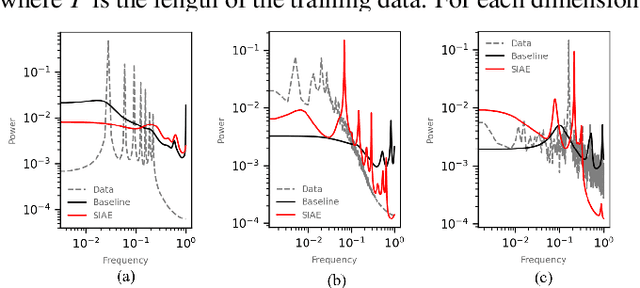
Abstract:Accurate and efficient fluid flow models are essential for applications relating to many physical phenomena including geophysical, aerodynamic, and biological systems. While these flows may exhibit rich and multiscale dynamics, in many cases underlying low-rank structures exist which describe the bulk of the motion. These structures tend to be spatially large and temporally slow, and may contain most of the energy in a given flow. The extraction and parsimonious representation of these low-rank dynamics from high-dimensional data is a key challenge. Inspired by the success of physics-informed machine learning methods, we propose a spectrally-informed approach to extract low-rank models of fluid flows by leveraging known spectral properties in the learning process. We incorporate this knowledge by imposing regularizations on the learned dynamics, which bias the training process towards learning low-frequency structures with corresponding higher power. We demonstrate the effectiveness of this method to improve prediction and produce learned models which better match the underlying spectral properties of prototypical fluid flows.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge