Behrooz Mansouri
Survey of Abstract Meaning Representation: Then, Now, Future
May 06, 2025Abstract:This paper presents a survey of Abstract Meaning Representation (AMR), a semantic representation framework that captures the meaning of sentences through a graph-based structure. AMR represents sentences as rooted, directed acyclic graphs, where nodes correspond to concepts and edges denote relationships, effectively encoding the meaning of complex sentences. This survey investigates AMR and its extensions, focusing on AMR capabilities. It then explores the parsing (text-to-AMR) and generation (AMR-to-text) tasks by showing traditional, current, and possible futures approaches. It also reviews various applications of AMR including text generation, text classification, and information extraction and information seeking. By analyzing recent developments and challenges in the field, this survey provides insights into future directions for research and the potential impact of AMR on enhancing machine understanding of human language.
Mathematical Information Retrieval: Search and Question Answering
Aug 21, 2024



Abstract:Mathematical information is essential for technical work, but its creation, interpretation, and search are challenging. To help address these challenges, researchers have developed multimodal search engines and mathematical question answering systems. This book begins with a simple framework characterizing the information tasks that people and systems perform as we work to answer math-related questions. The framework is used to organize and relate the other core topics of the book, including interactions between people and systems, representing math formulas in sources, and evaluation. We close with some key questions and concrete directions for future work. This book is intended for use by students, instructors, and researchers, and those who simply wish that it was easier to find and use mathematical information
FALQU: Finding Answers to Legal Questions
Apr 12, 2023Abstract:This paper presents a new test collection for Legal IR, FALQU: Finding Answers to Legal Questions, where questions and answers were obtained from Law Stack Exchange (LawSE), a Q&A website for legal professionals, and others with experience in law. Much in line with Stack overflow, Law Stack Exchange has a variety of questions on different topics such as copyright, intellectual property, and criminal laws, making it an interesting source for dataset construction. Questions are also not limited to one country. Often, users of different nationalities may ask questions about laws in different countries and expertise. Therefore, questions in FALQU represent real-world users' information needs thus helping to avoid lab-generated questions. Answers on the other side are given by experts in the field. FALQU is the first test collection, to the best of our knowledge, to use LawSE, considering more diverse questions than the questions from the standard legal bar and judicial exams. It contains 9880 questions and 34,145 answers to legal questions. Alongside our new test collection, we provide different baseline systems that include traditional information retrieval models such as TF-IDF and BM25, and deep neural network search models. The results obtained from the BM25 model achieved the highest effectiveness.
Effects of context, complexity, and clustering on evaluation for math formula retrieval
Nov 20, 2021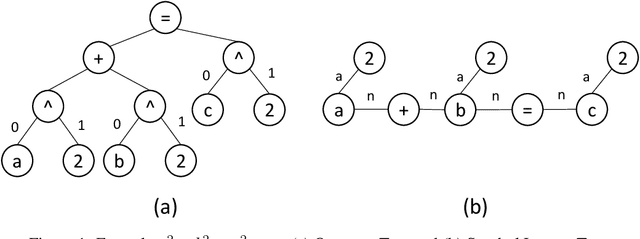
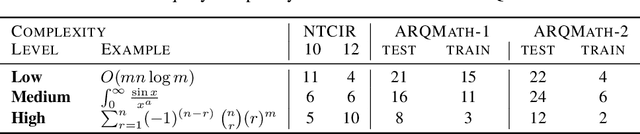

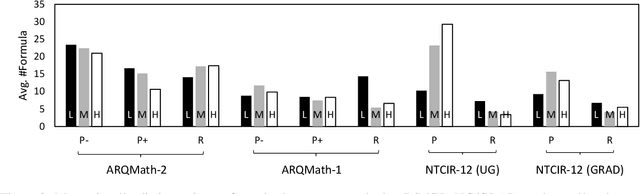
Abstract:There are now several test collections for the formula retrieval task, in which a system's goal is to identify useful mathematical formulae to show in response to a query posed as a formula. These test collections differ in query format, query complexity, number of queries, content source, and relevance definition. Comparisons among six formula retrieval test collections illustrate that defining relevance based on query and/or document context can be consequential, that system results vary markedly with formula complexity, and that judging relevance after clustering formulas with identical symbol layouts (i.e., Symbol Layout Trees) can affect system preference ordering.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge