Bastin Tony Roy Savarimuthu
Social Norm Reasoning in Multimodal Language Models: An Evaluation
Mar 03, 2026Abstract:In Multi-Agent Systems (MAS), agents are designed with social capabilities, allowing them to understand and reason about social concepts such as norms when interacting with others (e.g., inter-robot interactions). In Normative MAS (NorMAS), researchers study how norms develop, and how violations are detected and sanctioned. However, existing research in NorMAS use symbolic approaches (e.g., formal logic) for norm representation and reasoning whose application is limited to simplified environments. In contrast, Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) present promising possibilities to develop software used by robots to identify and reason about norms in a wide variety of complex social situations embodied in text and images. However, prior work on norm reasoning have been limited to text-based scenarios. This paper investigates the norm reasoning competence of five MLLMs by evaluating their ability to answer norm-related questions based on thirty text-based and thirty image-based stories, and comparing their responses against humans. Our results show that MLLMs demonstrate superior performance in norm reasoning in text than in images. GPT-4o performs the best in both modalities offering the most promise for integration with MAS, followed by the free model Qwen-2.5VL. Additionally, all models find reasoning about complex norms challenging.
Harnessing the power of LLMs for normative reasoning in MASs
Mar 25, 2024
Abstract:Software agents, both human and computational, do not exist in isolation and often need to collaborate or coordinate with others to achieve their goals. In human society, social mechanisms such as norms ensure efficient functioning, and these techniques have been adopted by researchers in multi-agent systems (MAS) to create socially aware agents. However, traditional techniques have limitations, such as operating in limited environments often using brittle symbolic reasoning. The advent of Large Language Models (LLMs) offers a promising solution, providing a rich and expressive vocabulary for norms and enabling norm-capable agents that can perform a range of tasks such as norm discovery, normative reasoning and decision-making. This paper examines the potential of LLM-based agents to acquire normative capabilities, drawing on recent Natural Language Processing (NLP) and LLM research. We present our vision for creating normative LLM agents. In particular, we discuss how the recently proposed "LLM agent" approaches can be extended to implement such normative LLM agents. We also highlight challenges in this emerging field. This paper thus aims to foster collaboration between MAS, NLP and LLM researchers in order to advance the field of normative agents.
Impact of meta-roles on the evolution of organisational institutions
Aug 07, 2020
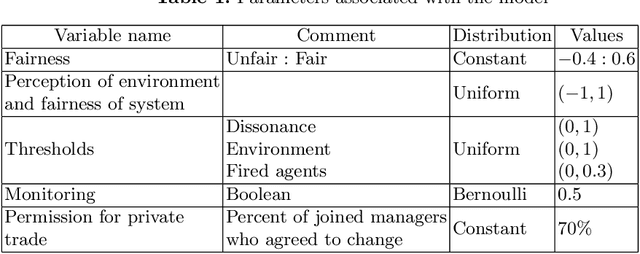
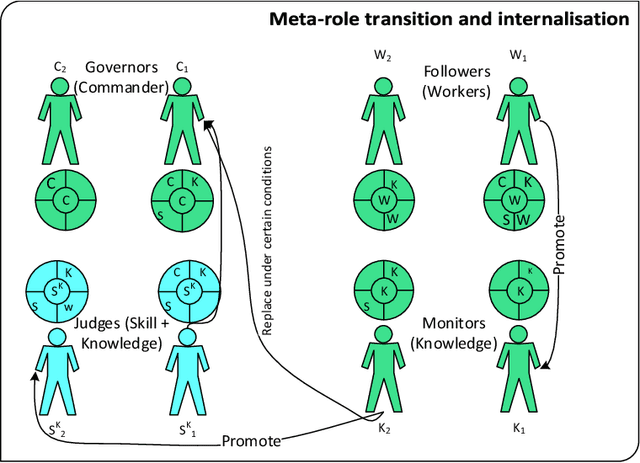
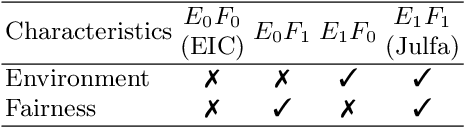
Abstract:This paper investigates the impact of changes in agents' beliefs coupled with dynamics in agents' meta-roles on the evolution of institutions. The study embeds agents' meta-roles in the BDI architecture. In this context, the study scrutinises the impact of cognitive dissonance in agents due to unfairness of institutions. To showcase our model, two historical long-distance trading societies, namely Armenian merchants of New-Julfa and the English East India Company are simulated. Results show how change in roles of agents coupled with specific institutional characteristics leads to changes of the rules in the system.
Impact of different belief facets on agents' decision -- a refined cognitive architecture
Apr 24, 2020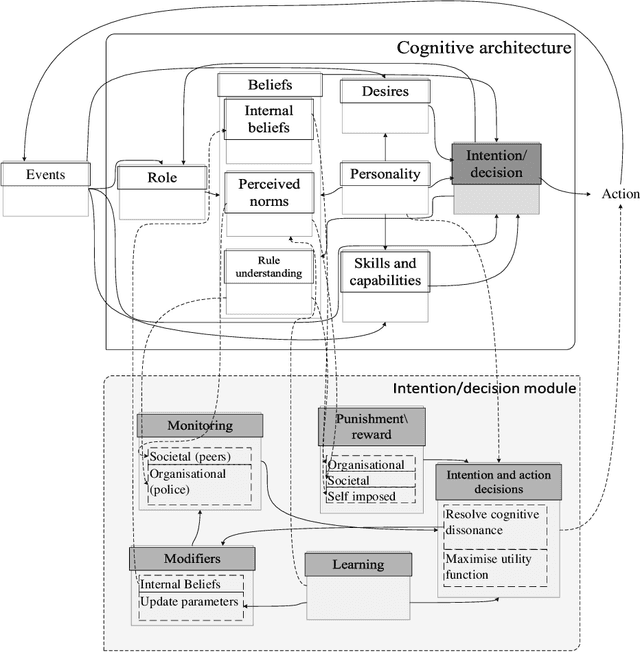
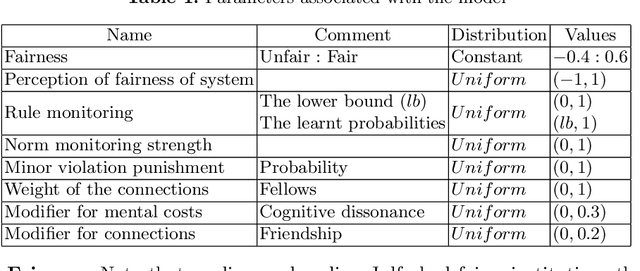
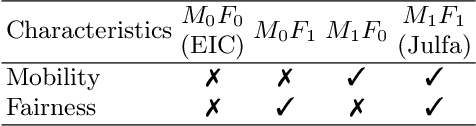
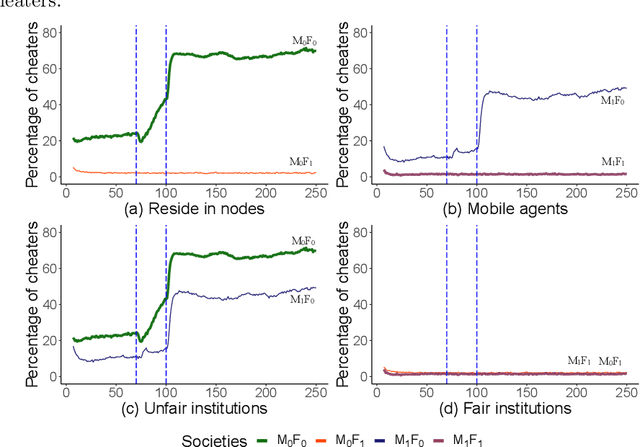
Abstract:This paper presents a conceptual refinement of agent cognitive architecture inspired from the beliefs-desires-intentions (BDI) and the theory of planned behaviour (TPB) models, with an emphasis on different belief facets. This enables us to investigate the impact of personality and the way that an agent weights its internal beliefs and social sanctions on an agent's actions. The study also uses the concept of cognitive dissonance associated with the fairness of institutions to investigate the agents' behaviour. To showcase our model, we simulate two historical long-distance trading societies, namely Armenian merchants of New-Julfa and the English East India Company. The results demonstrate the importance of internal beliefs of agents as a pivotal aspect for following institutional rules.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge