Bartłomiej Polaczyk
Improved Overparametrization Bounds for Global Convergence of Stochastic Gradient Descent for Shallow Neural Networks
Jan 28, 2022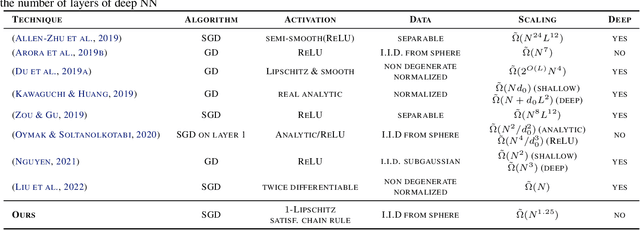
Abstract:We study the overparametrization bounds required for the global convergence of stochastic gradient descent algorithm for a class of one hidden layer feed-forward neural networks, considering most of the activation functions used in practice, including ReLU. We improve the existing state-of-the-art results in terms of the required hidden layer width. We introduce a new proof technique combining nonlinear analysis with properties of random initializations of the network. First, we establish the global convergence of continuous solutions of the differential inclusion being a nonsmooth analogue of the gradient flow for the MSE loss. Second, we provide a technical result (working also for general approximators) relating solutions of the aforementioned differential inclusion to the (discrete) stochastic gradient descent sequences, hence establishing linear convergence towards zero loss for the stochastic gradient descent iterations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge