Babitha Dharmaraj
The Use of a Large Language Model for Cyberbullying Detection
Feb 06, 2024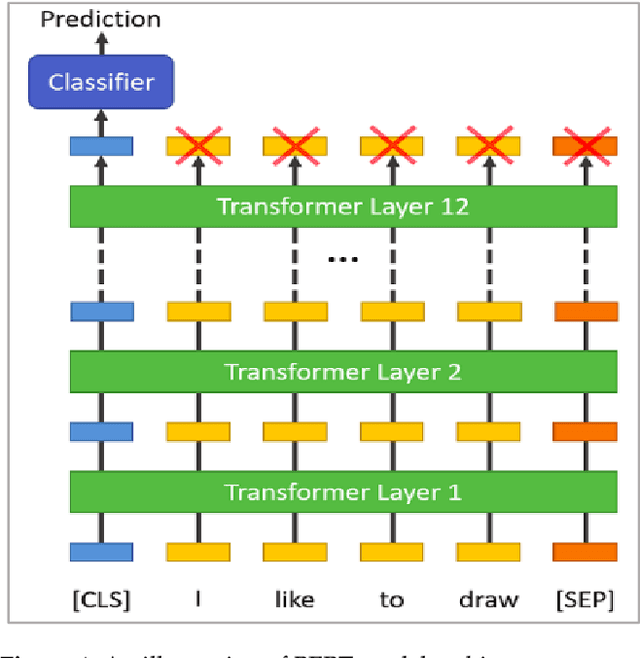


Abstract:The dominance of social media has added to the channels of bullying for perpetrators. Unfortunately, cyberbullying (CB) is the most prevalent phenomenon in todays cyber world, and is a severe threat to the mental and physical health of citizens. This opens the need to develop a robust system to prevent bullying content from online forums, blogs, and social media platforms to manage the impact in our society. Several machine learning (ML) algorithms have been proposed for this purpose. However, their performances are not consistent due to high class imbalance and generalisation issues. In recent years, large language models (LLMs) like BERT and RoBERTa have achieved state-of-the-art (SOTA) results in several natural language processing (NLP) tasks. Unfortunately, the LLMs have not been applied extensively for CB detection. In our paper, we explored the use of these models for cyberbullying (CB) detection. We have prepared a new dataset (D2) from existing studies (Formspring and Twitter). Our experimental results for dataset D1 and D2 showed that RoBERTa outperformed other models.
* 14 pages, Journal of Analytics
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge