B. Wang
College of Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence, Wenzhou University, Wenzhou, China
UHDRes: Ultra-High-Definition Image Restoration via Dual-Domain Decoupled Spectral Modulation
Nov 07, 2025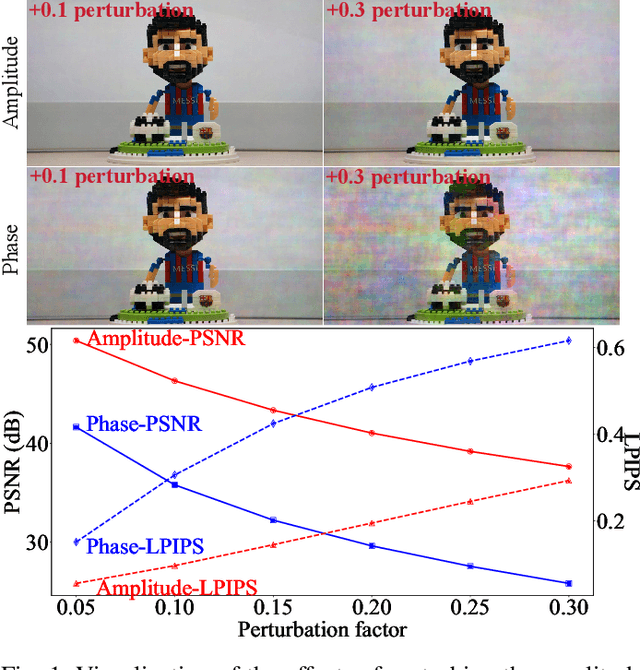



Abstract:Ultra-high-definition (UHD) images often suffer from severe degradations such as blur, haze, rain, or low-light conditions, which pose significant challenges for image restoration due to their high resolution and computational demands. In this paper, we propose UHDRes, a novel lightweight dual-domain decoupled spectral modulation framework for UHD image restoration. It explicitly models the amplitude spectrum via lightweight spectrum-domain modulation, while restoring phase implicitly through spatial-domain refinement. We introduce the spatio-spectral fusion mechanism, which first employs a multi-scale context aggregator to extract local and global spatial features, and then performs spectral modulation in a decoupled manner. It explicitly enhances amplitude features in the frequency domain while implicitly restoring phase information through spatial refinement. Additionally, a shared gated feed-forward network is designed to efficiently promote feature interaction through shared-parameter convolutions and adaptive gating mechanisms. Extensive experimental comparisons on five public UHD benchmarks demonstrate that our UHDRes achieves the state-of-the-art restoration performance with only 400K parameters, while significantly reducing inference latency and memory usage. The codes and models are available at https://github.com/Zhao0100/UHDRes.
Source-Free Domain Adaptation for Question Answering with Masked Self-training
Dec 19, 2022Abstract:Most previous unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) methods for question answering(QA) require access to source domain data while fine-tuning the model for the target domain. Source domain data may, however, contain sensitive information and may be restricted. In this study, we investigate a more challenging setting, source-free UDA, in which we have only the pretrained source model and target domain data, without access to source domain data. We propose a novel self-training approach to QA models that integrates a unique mask module for domain adaptation. The mask is auto-adjusted to extract key domain knowledge while trained on the source domain. To maintain previously learned domain knowledge, certain mask weights are frozen during adaptation, while other weights are adjusted to mitigate domain shifts with pseudo-labeled samples generated in the target domain. %As part of the self-training process, we generate pseudo-labeled samples in the target domain based on models trained in the source domain. Our empirical results on four benchmark datasets suggest that our approach significantly enhances the performance of pretrained QA models on the target domain, and even outperforms models that have access to the source data during adaptation.
Volumetric Image Projection Super-Resolution Ultrasound (VIP-SR) with a 1D Unfocused Linear Array
Jun 08, 2022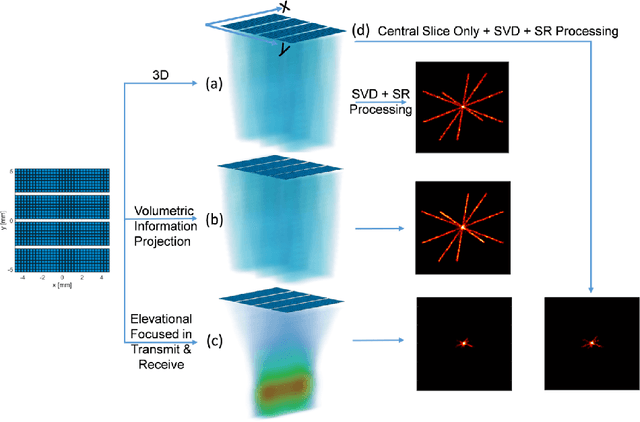
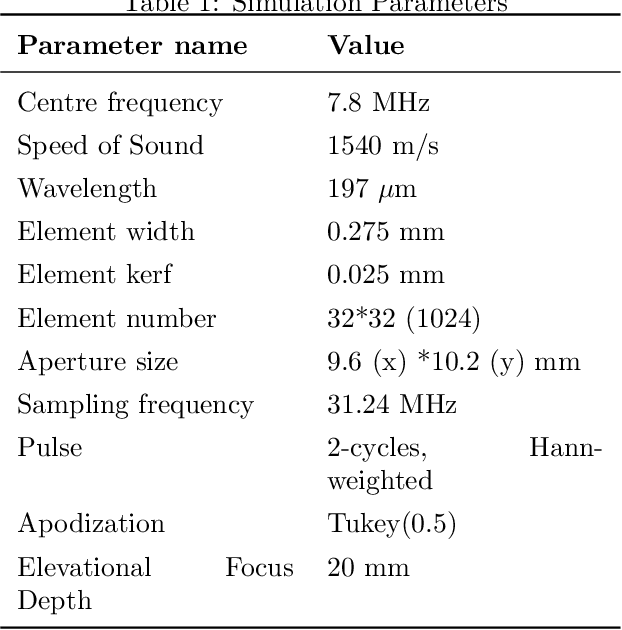
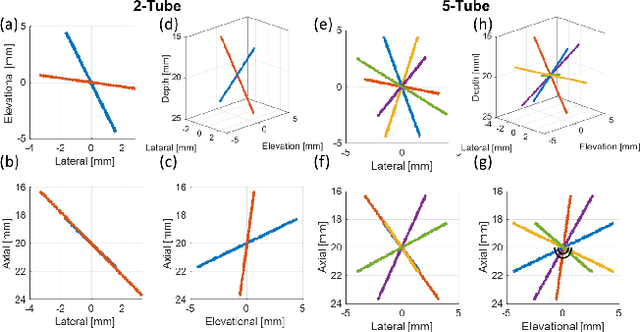
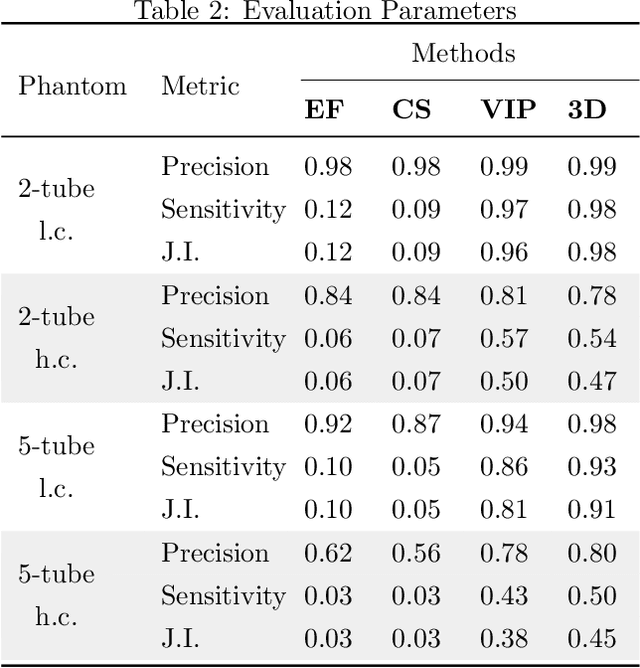
Abstract:Super-Resolution Ultrasound (SRUS) through localizing spatially isolated microbubbles has been demonstrated to overcome the wave diffraction limit and reveal the microvascular structure and flow information at the microscopic scale. However, 3D SRUS imaging remains a challenge due to the fabrication and computational complexity of 2D matrix array probes and connections. Inspired by X-ray radiography which can present volumetric information in a single projection image with much simpler hardware than X-ray CT, this study investigates the feasibility of volumetric image projection super-resolution (VIP-SR) ultrasound using a 1D unfocused linear array. Both simulation and experiments were conducted on 3D microvessel phantoms using a 1D linear array with or without an elevational focus, and a 2D matrix array as the reference. Results show that, VIP-SR, using an unfocused 1D array probe can capture significantly more volumetric information than the conventional 1D elevational focused probe. Compared with the 2D projection image of the full 3D SRUS results using the 2D array probe with the same aperture size, VIP-SR has similar volumetric coverage using 32 folds less independent elements. The impact of bubble concentration and vascular density on the VIP-SR US was also investigated. This study demonstrates the ability of high-resolution volumetric imaging of microvascular structures at significantly reduced costs with VIP-SR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge