Avinash Thakur
CoroNetGAN: Controlled Pruning of GANs via Hypernetworks
Mar 13, 2024



Abstract:Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have proven to exhibit remarkable performance and are widely used across many generative computer vision applications. However, the unprecedented demand for the deployment of GANs on resource-constrained edge devices still poses a challenge due to huge number of parameters involved in the generation process. This has led to focused attention on the area of compressing GANs. Most of the existing works use knowledge distillation with the overhead of teacher dependency. Moreover, there is no ability to control the degree of compression in these methods. Hence, we propose CoroNet-GAN for compressing GAN using the combined strength of differentiable pruning method via hypernetworks. The proposed method provides the advantage of performing controllable compression while training along with reducing training time by a substantial factor. Experiments have been done on various conditional GAN architectures (Pix2Pix and CycleGAN) to signify the effectiveness of our approach on multiple benchmark datasets such as Edges-to-Shoes, Horse-to-Zebra and Summer-to-Winter. The results obtained illustrate that our approach succeeds to outperform the baselines on Zebra-to-Horse and Summer-to-Winter achieving the best FID score of 32.3 and 72.3 respectively, yielding high-fidelity images across all the datasets. Additionally, our approach also outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in achieving better inference time on various smart-phone chipsets and data-types making it a feasible solution for deployment on edge devices.
GRITv2: Efficient and Light-weight Social Relation Recognition
Mar 11, 2024Abstract:Our research focuses on the analysis and improvement of the Graph-based Relation Inference Transformer (GRIT), which serves as an important benchmark in the field. We conduct a comprehensive ablation study using the PISC-fine dataset, to find and explore improvement in efficiency and performance of GRITv2. Our research has provided a new state-of-the-art relation recognition model on the PISC relation dataset. We introduce several features in the GRIT model and analyse our new benchmarks in two versions: GRITv2-L (large) and GRITv2-S (small). Our proposed GRITv2-L surpasses existing methods on relation recognition and the GRITv2-S is within 2% performance gap of GRITv2-L, which has only 0.0625x the model size and parameters of GRITv2-L. Furthermore, we also address the need for model compression, an area crucial for deploying efficient models on resource-constrained platforms. By applying quantization techniques, we efficiently reduced the GRITv2-S size to 22MB and deployed it on the flagship OnePlus 12 mobile which still surpasses the PISC-fine benchmarks in performance, highlighting the practical viability and improved efficiency of our model on mobile devices.
MOSAIC: Multi-Object Segmented Arbitrary Stylization Using CLIP
Sep 24, 2023
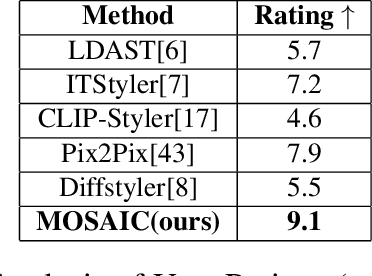
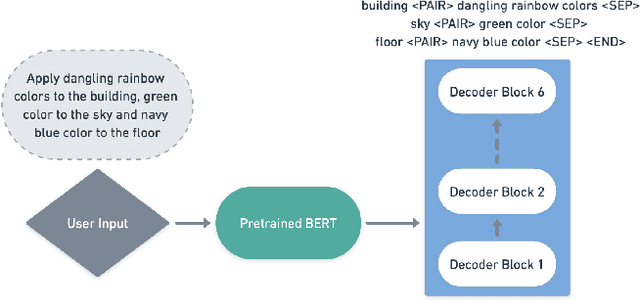
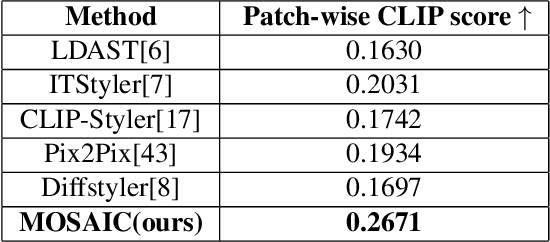
Abstract:Style transfer driven by text prompts paved a new path for creatively stylizing the images without collecting an actual style image. Despite having promising results, with text-driven stylization, the user has no control over the stylization. If a user wants to create an artistic image, the user requires fine control over the stylization of various entities individually in the content image, which is not addressed by the current state-of-the-art approaches. On the other hand, diffusion style transfer methods also suffer from the same issue because the regional stylization control over the stylized output is ineffective. To address this problem, We propose a new method Multi-Object Segmented Arbitrary Stylization Using CLIP (MOSAIC), that can apply styles to different objects in the image based on the context extracted from the input prompt. Text-based segmentation and stylization modules which are based on vision transformer architecture, were used to segment and stylize the objects. Our method can extend to any arbitrary objects, styles and produce high-quality images compared to the current state of art methods. To our knowledge, this is the first attempt to perform text-guided arbitrary object-wise stylization. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach through qualitative and quantitative analysis, showing that it can generate visually appealing stylized images with enhanced control over stylization and the ability to generalize to unseen object classes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge