Assaf Chen
Lessons Learned Report: Super-Resolution for Detection Tasks in Engineering Problem-Solving
Mar 01, 2023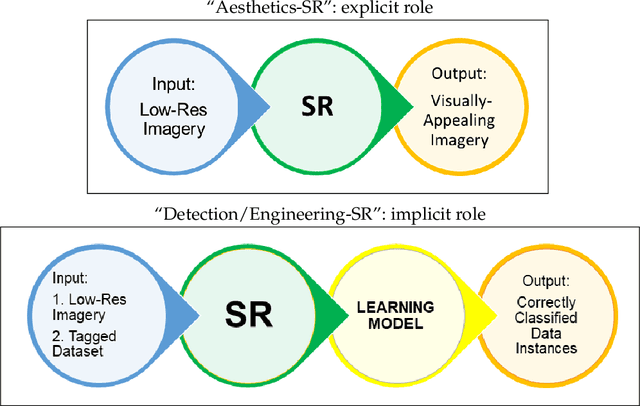
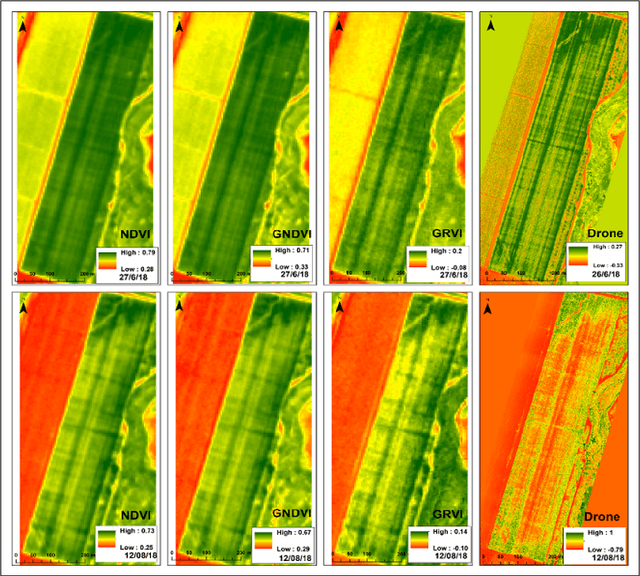
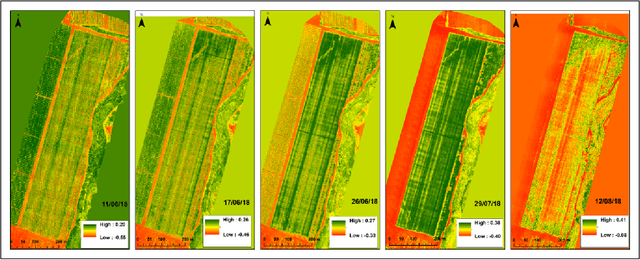
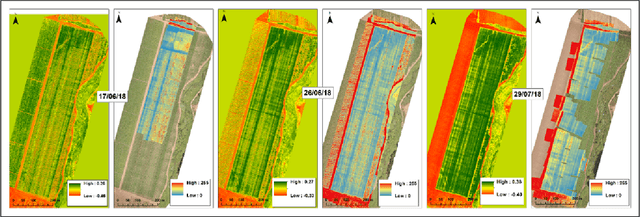

Abstract:We describe the lessons learned from targeting agricultural detection problem-solving, when subject to low resolution input maps, by means of Machine Learning-based super-resolution approaches. The underlying domain is the so-called agro-detection class of problems, and the specific objective is to learn a complementary ensemble of sporadic input maps. While super-resolution algorithms are branded with the capacity to enhance various attractive features in generic photography, we argue that they must meet certain requirements, and more importantly, that their outcome does not necessarily guarantee an improvement in engineering detection problem-solving (unlike so-called aesthetics/artistic super-resolution in ImageNet-like datasets). By presenting specific data-driven case studies, we outline a set of limitations and recommendations for deploying super-resolution algorithms for agro-detection problems. Another conclusion states that super-resolution algorithms can be used for learning missing spectral channels, and that their usage may result in some desired side-effects such as channels' synchronization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge