Ashim Dahal
Redemption Score: An Evaluation Framework to Rank Image Captions While Redeeming Image Semantics and Language Pragmatics
May 22, 2025Abstract:Evaluating image captions requires cohesive assessment of both visual semantics and language pragmatics, which is often not entirely captured by most metrics. We introduce Redemption Score, a novel hybrid framework that ranks image captions by triangulating three complementary signals: (1) Mutual Information Divergence (MID) for global image-text distributional alignment, (2) DINO-based perceptual similarity of cycle-generated images for visual grounding, and (3) BERTScore for contextual text similarity against human references. A calibrated fusion of these signals allows Redemption Score to offer a more holistic assessment. On the Flickr8k benchmark, Redemption Score achieves a Kendall-$\tau$ of 56.43, outperforming twelve prior methods and demonstrating superior correlation with human judgments without requiring task-specific training. Our framework provides a more robust and nuanced evaluation by effectively redeeming image semantics and linguistic interpretability indicated by strong transfer of knowledge in the Conceptual Captions and MS COCO datasets.
EEG-to-Text Translation: A Model for Deciphering Human Brain Activity
May 20, 2025Abstract:With the rapid advancement of large language models like Gemini, GPT, and others, bridging the gap between the human brain and language processing has become an important area of focus. To address this challenge, researchers have developed various models to decode EEG signals into text. However, these models still face significant performance limitations. To overcome these shortcomings, we propose a new model, R1 Translator, which aims to improve the performance of EEG-to-text decoding. The R1 Translator model combines a bidirectional LSTM encoder with a pretrained transformer-based decoder, utilizing EEG features to produce high-quality text outputs. The model processes EEG embeddings through the LSTM to capture sequential dependencies, which are then fed into the transformer decoder for effective text generation. The R1 Translator excels in ROUGE metrics, outperforming both T5 (previous research) and Brain Translator. Specifically, R1 achieves a ROUGE-1 score of 38.00% (P), which is up to 9% higher than T5 (34.89%) and 3% better than Brain (35.69%). It also leads in ROUGE-L, with a F1 score of 32.51%, outperforming T5 by 3% (29.67%) and Brain by 2% (30.38%). In terms of CER, R1 achieves a CER of 0.5795, which is 2% lower than T5 (0.5917) and 4% lower than Brain (0.6001). Additionally, R1 performs better in WER with a score of 0.7280, outperforming T5 by 4.3% (0.7610) and Brain by 3.6% (0.7553). Code is available at https://github.com/Mmurrad/EEG-To-text.
Embedding Shift Dissection on CLIP: Effects of Augmentations on VLM's Representation Learning
Mar 30, 2025Abstract:Understanding the representation shift on Vision Language Models like CLIP under different augmentations provides valuable insights on Mechanistic Interpretability. In this study, we show the shift on CLIP's embeddings on 9 common augmentation techniques: noise, blur, color jitter, scale and rotate, flip, elastic and perspective transforms, random brightness and contrast, and coarse dropout of pixel blocks. We scrutinize the embedding shifts under similarity on attention map, patch, edge, detail preservation, cosine similarity, L2 distance, pairwise distance and dendrogram clusters and provide qualitative analysis on sample images. Our findings suggest certain augmentations like noise, perspective transform and shift scaling have higher degree of drastic impact on embedding shift. This study provides a concrete foundation for future work on VLM's robustness for mechanical interpretation and adversarial data defense.
Analysis of Zero Day Attack Detection Using MLP and XAI
Jan 28, 2025Abstract:Any exploit taking advantage of zero-day is called a zero-day attack. Previous research and social media trends show a massive demand for research in zero-day attack detection. This paper analyzes Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL) based approaches to create Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and scrutinizing them using Explainable AI (XAI) by training an explainer based on randomly sampled data from the testing set. The focus is on using the KDD99 dataset, which has the most research done among all the datasets for detecting zero-day attacks. The paper aims to synthesize the dataset to have fewer classes for multi-class classification, test ML and DL approaches on pattern recognition, establish the robustness and dependability of the model, and establish the interpretability and scalability of the model. We evaluated the performance of four multilayer perceptron (MLP) trained on the KDD99 dataset, including baseline ML models, weighted ML models, truncated ML models, and weighted truncated ML models. Our results demonstrate that the truncated ML model achieves the highest accuracy (99.62%), precision, and recall, while weighted truncated ML model shows lower accuracy (97.26%) but better class representation (less bias) among all the classes with improved unweighted recall score. We also used Shapely Additive exPlanations (SHAP) to train explainer for our truncated models to check for feature importance among the two weighted and unweighted models.
Efficiency Bottlenecks of Convolutional Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks: A Comprehensive Scrutiny with ImageNet, AlexNet, LeNet and Tabular Classification
Jan 27, 2025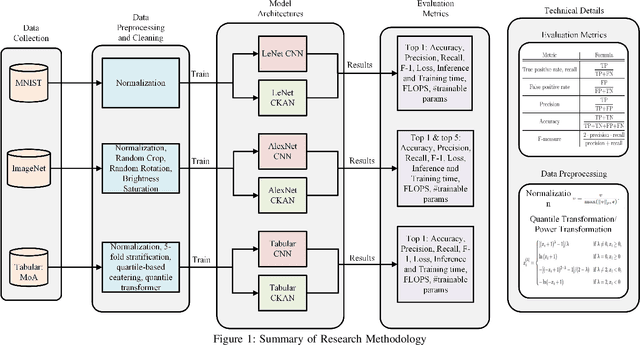
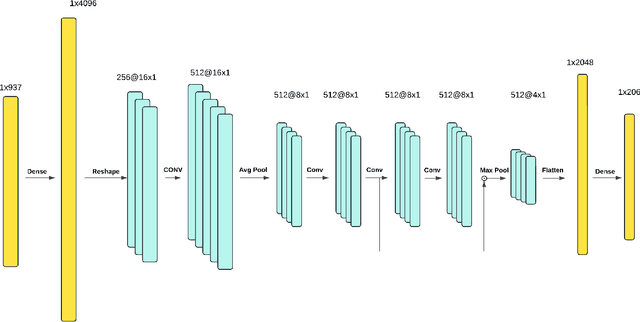

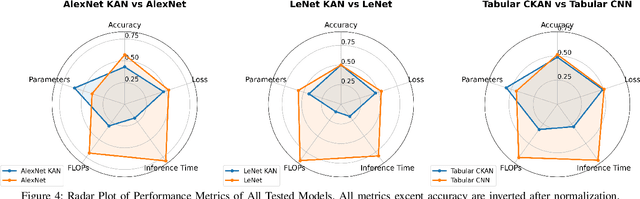
Abstract:Algorithmic level developments like Convolutional Neural Networks, transformers, attention mechanism, Retrieval Augmented Generation and so on have changed Artificial Intelligence. Recent such development was observed by Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks that suggested to challenge the fundamental concept of a Neural Network, thus change Multilayer Perceptron, and Convolutional Neural Networks. They received a good reception in terms of scientific modeling, yet had some drawbacks in terms of efficiency. In this paper, we train Convolutional Kolmogorov Arnold Networks (CKANs) with the ImageNet-1k dataset with 1.3 million images, MNIST dataset with 60k images and a tabular biological science related MoA dataset and test the promise of CKANs in terms of FLOPS, Inference Time, number of trainable parameters and training time against the accuracy, precision, recall and f-1 score they produce against the standard industry practice on CNN models. We show that the CKANs perform fair yet slower than CNNs in small size dataset like MoA and MNIST but are not nearly comparable as the dataset gets larger and more complex like the ImageNet. The code implementation of this paper can be found on the link: \href{https://github.com/ashimdahal/Study-of-Convolutional-Kolmogorov-Arnold-networks}{https://github.com/ashimdahal/Study-of-Convolutional-Kolmogorov-Arnold-networks}
Heuristical Comparison of Vision Transformers Against Convolutional Neural Networks for Semantic Segmentation on Remote Sensing Imagery
Nov 14, 2024


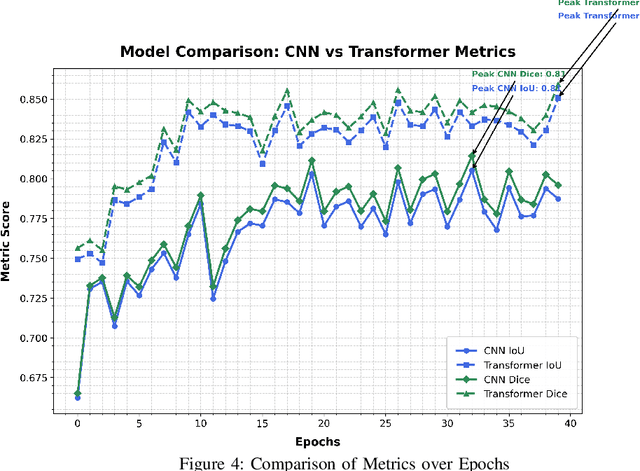
Abstract:Vision Transformers (ViT) have recently brought a new wave of research in the field of computer vision. These models have done particularly well in the field of image classification and segmentation. Research on semantic and instance segmentation has emerged to accelerate with the inception of the new architecture, with over 80\% of the top 20 benchmarks for the iSAID dataset being either based on the ViT architecture or the attention mechanism behind its success. This paper focuses on the heuristic comparison of three key factors of using (or not using) ViT for semantic segmentation of remote sensing aerial images on the iSAID. The experimental results observed during the course of the research were under the scrutinization of the following objectives: 1. Use of weighted fused loss function for the maximum mean Intersection over Union (mIoU) score, Dice score, and minimization or conservation of entropy or class representation, 2. Comparison of transfer learning on Meta's MaskFormer, a ViT-based semantic segmentation model, against generic UNet Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) judged over mIoU, Dice scores, training efficiency, and inference time, and 3. What do we lose for what we gain? i.e., the comparison of the two models against current state-of-art segmentation models. We show the use of the novel combined weighted loss function significantly boosts the CNN model's performance capacities as compared to transfer learning the ViT. The code for this implementation can be found on \url{https://github.com/ashimdahal/ViT-vs-CNN-ImageSegmentation}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge